Summary
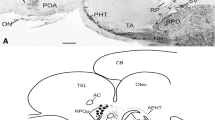
The nucleus praeopticus (NPO) is located on both sides of the preoptic recess and is composed of a pars parvocellularis and a pars magnocellularis. Only in the rainbow trout does the pars magnocellularis consist of separately located medium-sized cells and very large cells. Cytologically, three cell types can be distinguished: 1) unipolar cells ending in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), 2) bipolar cells also ending in the CSF and forming an axon, and 3) multipolar cells which generally do not have a direct connection with the ventricle.
Axons originate from the cell bodies forming the paired preopticohypophysial tract that runs along the border of the diencephalon and the optic tract. A considerable number of NPO fibers leading to the hypophysis makes close contact with the cell bodies of the pars lateralis of the nucleus lateralis tuberis, indicating a functional relationship. Most NPO fibers terminate in the caudal part of the neurohypophysis, around blood capillaries and at the basal lamina of the pars intermedia. Far fewer fibers appear to terminate near the boundary of the neurohypophysis and the rostral and proximal pars distalis.
The nucleus lateralis tuberis (NLT) is located in the caudal hypothalamus, beginning at the rostral end of the horizontal commissure and extending caudally beyond the hypophysial stalk. It consists of the partes rostralis, medialis, lateralis and ventrolateralis. In both species the p. rostralis contains small subependymal neurons and some larger ones. Only in the p. medialis of the Atlantic salmon are large cells present. In both species the most prominent part is the p. lateralis, which consists solely of large cells. Cells situated between the p. medialis and the p. lateralis are grouped in the p. ventrolateralis. It was impossible to trace the axons originating in the NLT, since the cyto- and axoplasm could not be stained specifically.
The structure of the NPO and NLT in the two salmonid species is compared with that of other teleosts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham, M.: Etude de l'ultrastructure des fibres neurosécrétrices dans l'hypophyse des muges (Téléostéens). Rech. Biol. Contemp. 1974, 171–178 (1974)
Båge, G., Ekengren, B., Fernholm, B., Fridberg, G.: The pituitary gland of the roach Leuciscus rutilus. I. The rostral pars distalis and its innervation. Acta Zool. (Stockh.) 55, 25–45 (1974a)
Båge, G., Ekengren, B., Fernholm, B., Fridberg, G.: The pituitary gland of the roach Leuciscus rutilus. II. The proximal pars distalis and its innervation. Acta Zool. (Stockh.) 55, 191–204 (1974b)
Båge, G., Ekengren, E., Fernholm, B., Fridberg, G.: The pituitary gland of the roach Leuciscus rutilus. III. The pars intermedia and its innervation. Acta Zool. (Stockh.) 56, 43–60 (1975)
Ball, J.N., Baker, B.I.: The pituitary gland: anatomy and histophysiology. In: Fish physiology (Hoar, W.S. and D.J. Randall eds.), Vol. II, pp. 1–110. New York-London: Academic Press 1969
Baumgarten, H.G., Braak, H.: Catecholamine im Hypothalamus vom Goldfisch (Carassius auratus). Z. Zellforsch. 80, 246–263 (1967)
Bergquist, H.: Zur Morphologie des Zwischenhirns bei niederen Wirbeltieren. Acta Zool. (Stockh.) 13, 57–304 (1932)
Bern, H.A., Nishioka, R.S., Nagahama, Y.: The relationship between nerve fibers and adenohypophysial cell types in the cichlid teleost Tilapia mossambica. Rech. Biol. Contemp. 1974, 179–194 (1974)
Billenstien, D.C.: The seasonal secretory cycle of the nucleus lateralis tuberis of the hypothalamus and its relation to the reproduction in the eastern brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2, 111–112 (1962)
Billenstien, D.C.: Neurosecretory material from the nucleus lateralis tuberis in the hypophysis of the eastern brook trout, Salvelinus fontinalis. Z. Zellforsch. 59, 507–512 (1963)
Blanc-Livni, N., Abraham, M.: The influence of environmental salinity on the prolactin and gonadotropin-secreting regions in the pituitary of Mugil (Teleostei). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 14, 184–197 (1970)
Bock, R., Ockenfels, H.: Fluoreszenzmikroskopische Darstellung Aldehydfuchsin-positiver Substanzen mit Crotonaldehyd-Diaminobenzophenon. Histochemie 21, 181–188 (1970)
Brehm, H. von: Über jahreszyklische Veränderungen im Nucleus lateralis tuberis der Schleie (Tinca vulgaris). Z. Zellforsch. 49, 105–124 (1958)
Chan, D.K.O.: Comparative physiology of the vasomotor effects of neurohypophysial peptides in the vertebrates. Am. Zool. 17, 751–761 (1977)
Charlton, H.H.: Comparative studies on the nucleus preopticus pars magnocellularis and the nucleus lateralis tuberis in fishes. J. Comp. Neurol. 54, 237–275 (1932)
Da Lage, C.: Innervation neurosécrétoire de l'adénohypophyse chez l'hippocampe. C.R.Ass. Anat. 41, 161–166 (1954)
Demski, L.S., Bauer, D.H., Gerald, J.W.: Sperm release evoked by electrical stimulation of the fish brain: a functional-anatomical study. J. exp. Zool. 191, 215–232 (1975)
Dixit, V.P.: The nucleus lateralis tuberis in the fresh water teleost Clarias batrachus L. Experientia 23, 760–761 (1967)
Dodd, J.M., Follett, B.K., Sharp, P.J.: Hypothalamic control of pituitary function in submammalian vertebrates. Adv. Comp. Physiol. Biochem. 4, 113–223 (1971)
Ekengren, B.: The nucleus preopticus and the nucleus lateralis tuberis in the roach Leuciscus rutilus. Z. Zellforsch. 140, 369–388 (1973)
Ekengren, B., Terlou, M.: Hypothalamic centers and innervation of the hypophysis in the Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and the rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Ann. Biol. Animal. Biochim. Biophys. 18, 837–842 (1978)
Follénius, E.: Etude comparative de la cytologie fine du noyau préoptique (NPO) et du noyau latéral du tuber (NLT) chez la truite (Salmo irideus Gibb) et chez la perche (Perca fluviatilis). Comparaison des deux types de neurosécrétion. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 3, 66–85 (1963)
Follénius, E.: Bases structurales et ultrastructurales des corrélations hypothalamo-hypophysaires chez quelques espèces de poissons téléostéens. Ann. Sci. Natur. Zool. (12) 7, 1–150 (1965)
Follénius, E., Dubois, M.P.: Localisation immunocytologique de peptides analogues à l'α-endorphine dans certains neurones du noyau latéral du tuber de Carassius auratus L. et Cyprinus carpio L. C.R. Acad. Sci. (Paris) 285D, 1065–1068 (1977)
Follénius, E., Dubois, M.P.: Distribution of fibres reacting with an α-endorphin antiserum in the neurohypophysis of Carassius auratus and Cyprinus carpio. Cell Tissue Res. 189, 251–256 (1978)
Fridberg, G., Ekengren, B.: The vascularization and the neuroendocrine pathways of the pituitary gland in the Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar. Can. J. Zool. 55, 1284–1296 (1977)
Fryer, J.N., Peter, R.E.: Hypothalamic control of ACTH secretion in goldfish. II. Hypothalamic lesioning studies. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 33, 202–214 (1977a)
Fryer, J.N., Peter, R.E.: Hypothalamic control of ACTH secretion in goldfish. III. Hypothalamic cortisol implant studies. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 33, 215–225 (1977b)
George, J.C.: Comparative physiology of metabolic responses to neurohypophysial hormones in vertebrates. Am. Zool. 17, 787–808 (1977)
Goldstein, K.: Untersuchungen über das Vorderhirn und Zwischenhirn einiger Knochenfische. Arch. mikr. Anat. 66, 135–219 (1905)
Goos, H.J.Th., Terlou, M.: Hypothalamic control of MSH secretion in lower vertebrates. Front. Hormone Res., Vol. 4, pp. 51–62. Basel: Karger 1977
Goossens, N., Dierickx, K., Vandesande, F.: Immunocytochemical localization of vasotocin and isotocin in the preopticohypophysial neurosecretory system of teleosts. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 32, 371–375 (1977)
Haider, S., Sathyanesan, A.G.: Comparative study of the hypothalamus-neurohypophysial complex in some Indian fresh water teleosts. Acta Anat. (Basel) 81, 202–224 (1972a)
Haider, S., Sathyanesan, A.G.: The nucleus lateralis tuberis of the freshwater teleost Heteropneustes fossilis. Acta Anat. (Basel) 82, 75–84 (1972b)
Haller, B.: Vom Bau des Wirbeltiergehirns. Morph. Jb. 26, 345–641 (1898)
Heller, H.: The effect of neurohypophysial hormones on the female reproductive tract of lower vertebrates. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol., Suppl. 3, 703–714 (1972)
Herlant, M.: Etude critique de deux techniques nouvelles destinées à mettre en évidence les différentes catégories cellulaires présentes dans la glande pituitaire. Bull. Micr. Appl. 10, 37–44 (1960)
Hild, W.: Zur Frage der Neurosekretion im Zwischenhirn der Schleie und ihrer Beziehungen zur Neurohypophyse. Z. Zellforsch. 35, 33–46 (1951)
Holmes, R.L., Ball, J.N.: The pituitary gland. A comparative account. London: Cambridge Univ. Press 1974
Holmgren, N.: Zur Anatomie und Histologie des Vorder- und Zwischenhirns der Knochenfische. Acta Zool. (Stockh.) 1, 137–315 (1920)
Honma, Y., Tamura, E.: Studies on the Japanese chars, the Iwana (genus Salvelinus) II. The hypothalamic neurosecretory system of the Nikko-Iwana, Salvelinus leucomaenis pluvius (Hilgendorf). Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fisheries 31, 878–887 (1965)
Kasuga, S., Takahashi, H.: Some observations on neurosecretory innervation in the pituitary gland of the medaka, Oryzias latipes. Bull. Fac. Fish. Hokkaido Univ. 21, 79–89 (1970)
Kasuga, S., Takahashi, H.: The preoptico-hypophysial neurosecretory system of the medaka Oryzias latipes, and its changes in relation to the annual reproductive cycle under natural conditions. Bull. Fac. Fish. Hokkaido Univ. 21, 259–268 (1971)
Kaul, S., Vollrath, L.: The goldfish pituitary. II. Innervation. Cell Tissue Res. 154, 231–249 (1974)
Knowles, F.: Evidence for a dual control, by neurosecretion, of hormone synthesis and release in the pituitary of the dogfish, Scylliorhinus stellaris, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. [Biol.] 249, 435–455 (1965)
Knowles, F., Vollrath, L.: A dual neurosecretory innervation of the pars distalis of the pituitary of the eel. Nature 208, 1343–1344 (1966a)
Knowles, F., Vollrath, L.: Neurosecretory innervation of the pituitary of the eels Anguilla and Conger. III. The structure and innervation of the pars distalis at different stages of the life-cycle. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. [Biol.] 250, 311–327 (1966b)
La Pointe, J.: Comparative physiology of neurohypophysial hormone action on vertebrate oviductuterus. Am. Zool. 17, 763–773 (1977)
Leatherland, J.F.: Histophysiology and innervation of the pituitary gland of the goldfish, Carassius auratus L.: a light and electron microscope investigation. Can. J. Zool. 50, 835–844 (1972)
Leatherland, J.F., Budtz, P.E., Dodd, J.M.: In situ studies on the hypothalamo-neurohypophysial complex of the European eel Anguilla anguilla (L). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 7, 234–244 (1966)
Leatherland, J.F., Dodd, J.M.: Types of secretory neurons in the preoptic nucleus of the European eel Anguilla anguilla L. Nature 216, 586–587 (1967)
Leatherland, J.F., Dodd, J.M.: Histology and fine structure of the preoptic nucleus and hypothalamic tracts of the European eel Anguilla anguilla L. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. [Biol.] 256, 135–145 (1969)
Lederis, K.: Ultrastructure of the hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system in teleost fishes and isolation of hormone-containing granules from the neurohypophysis of the cod (Gadus morrhua). Z. Zellforsch. 58, 192–213 (1962)
Lederis, K.: Fine structure and hormone content of the hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system of the rainbow trout (Salmo irideus) exposed to sea water. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 4, 638–661 (1964)
Mazzi, V., Franzoni, M.F., Fasolo, A.: A Golgi study of the hypothalamus of Actinopterygii. I. The preoptic area. Cell Tissue Res. 186, 475–490 (1978)
Nieuwenhuys, R.: The comparative anatomy of the actinopterygian forebrain. J. Hirnforsch. 6, 171–192 (1963)
Öztan, N.: The hypothalamic neurosecretory system of a poeciliid fish, Platypoecilus maculatus and its sterile hybrid backcross with Xiphophorus helleri. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 3, 1–14 (1963)
Öztan, N.: The structure of the hypothalamic neurosecretory cells of Zoarces viviparus L. under the conditions of constant dark and light during the reproductive period. Z. Zellforsch. 75, 66–82 (1966)
Palay, S.L.: The fine structure of secretory neurons in the preoptic nucleus of the goldfish (Carassius auratus). Anat. Rec. 138, 417–443 (1960)
Pang, P.K.T.: Osmoregulatory functions of neurohypophysial hormones in fishes and amphibians. Am. Zool. 17, 739–749 (1977)
Pavlović, M., Pantić, V.: Nucleus preopticus and nucleus lateralis tuberis in teleostei Alburnus albidus and Alosa fallax in various stages of sexual cycle. Arh. biol. nauka, Beograd 25, 9–16 (1973)
Perks, A.M.: The neurohypophysis. In: Fish physiology (Hoar, W.S. and D.J. Randall, eds.), Vol. II, pp. 111–205. New York-London: Academic Press 1969
Peter, R.E.: Hypothalamic control of thyroid gland activity and gonadal activity in the goldfish, Carassius auratus. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 14, 334–356 (1970)
Peter, R.E.: The preoptic nucleus in fishes: a comparative discussion of function-activity relationships. Am. Zool. 17, 775–785 (1977)
Peter, R.E., McKeown, B.A.: Effects of hypothalamic and thalamic lesions on prolactin and thyrotropin secretion in teleosts, with special reference to recent studies on the goldfish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 25, 153–165 (1974)
Peter, R.E., Nagahama, Y.: A light and electron microscopic study of the structure of the nucleus preopticus and nucleus lateralis tuberis of the goldfish, Carassius auratus. Can. J. Zool. 54, 1423–1437 (1976)
Peute, J., Bruyn, M.G.A. de, Seldenrijk, R., Oordt, P.G.W.J. van: Cytophysiology and innervation of gonadotropic cells in the pituitary of the black molly (Poecilia latipinna). Cell Tissue Res. 174, 35–54 (1976)
Samuelsson, B., Fernholm, B., Fridberg, B.: Light microscopic studies on the nucleus lateralis tuberis and the pituitary of the roach, Leuciscus rutilus, with reference to the nucleus-pituitary relationship. Acta Zool. (Stockh.) 49, 141–153 (1968)
Sawyer, W.H.: Evolution of active neurohypophysial principles among the vertebrates. Am. Zool. 17, 727–737 (1977)
Scharrer, E.: Die Lichtempfindlichkeit blinder Elritzen (Untersuchungen über das Zwischenhirn der Fische. I.) Z. vergl. Physiol. 7, 1–38 (1928)
Scharrer, E.: Über sekretorisch tätige Zellen im Thalamus von Fundulus heteroclitus L. (Untersuchungen über das Zwischenhirn der Fische. II.) Z. vergl. Physiol. 11, 767–773 (1930)
Scharrer, E.: Über die Beteiligung des Zellkerns an sekretorischen Vorgängen in Nervenzellen. Frankfurt. Z. Path. 47, 143–151 (1935)
Scharrer, E.: Vergleichende Untersuchungen über die zentralen Anteile des vegetativen Systems. Z. Anat. Entw.-Gesch. 106, 169–192 (1936)
Schiebler, T.H.: Darstellung von B-Zellen in Pankreasinseln und von Neurosekret mit Pseudoisocyanin. Naturwissenschaften 45, 214–216 (1958)
Sheldon, R.E.: The olfactory tracts and centers in teleosts. J. Comp. Neurol. 22, 177–339 (1912)
Simon, N., Reinboth, R.: Adenohypophyse und Hypothalamus. Histophysiologische Untersuchungen bei Lepomis (Centrarchidae). Adv. Anat. Embryol. Cell Biol. 48, Fasc. 6 (1974)
Stahl, A.: La neurosécrétion chez les poissons téléostéens. Contribution à l'étude de la neurohypophyse chez les mugilidés. C.R. Soc. Biol. (Paris) 147, 841 (1953)
Stahl, A.: Recherches sur les élaborations cellulaires et la neurosécrétion dans l'encephale des poissons téléostéens. Acta Anat. (Basel) 31, Suppl. 28, 1–158 (1957)
Sterba, G.: Grundlagen des histochemischen und biochemischen Nachweises von Neurosekret (=Trägerprotein der Oxytozine) mit Pseudoisocyaninen. Acta Histochem. (Jena) 17, 268–292 (1964)
Sterba, G., Weiss, J.: Beiträge zur Hydrencephalokrinie: I. Hypothalamische Hydrencephalokrinie der Bachforelle (Salmo trutta fario). J. Hirnforsch. 9, 359–371 (1967)
Terlou, M., Ekengren, B. Hiemstra, K.: Localization of monoamines in the forebrain of two salmonid species, with special reference to the hypothalamo-hypophysial system. Cell Tissue Res. 190, 417–434 (1978a)
Terlou, M., de Jong, J.P., van Oordt, P.G.W.J.: Scanning cytophotometry: a method for studying the amount of neurosecretory material in the preoptic nucleus of the trout (Salmo gairdneri). Ann. Biol. Anim. Biochim. Biophys. 18, 851–856 (1978b)
Vigh-Teichmann, I., Vigh, B., Aros, B.: Cerebrospinal fluid-contacting neurons, ciliated perikarya and “peptidergic” synapses in the magnocellular preoptic nucleus of teleostean fishes. Cell Tissue Res. 165, 397–413 (1976)
Vigh-Teichmann, I., Vigh, B., Koritsánszky, S.: Liquorkontaktneurone im Nucleus lateralis tuberis von Fischen. Z. Zellforsch. 105, 325–338 (1970)
Vollrath, L.: Über die neurosekretorische Innervation der Adenohypophyse von Teleostiern, insbesondere von Hippocampus cuda und Tinca tinca. Z. Zellforsch. 78, 234–260 (1967)
Vollrath, L., Schiebler, T.H.: Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen an den Nuclei laterales tuberis der Schleie. Anat. Anz. Erg.-H. 121, 425–431 (1968)
Weiss, J.: Untersuchungen zur Innervation des Nucleus lateralis tuberis der Bachforelle (Salmo trutta fario). Biol. Zbl. 96, 43–56 (1976)
Zambrano, D.: The nucleus lateralis tuberis system of the gobiid fish Gillichthys mirabilis. I. Ultrastructural and histochemical characterization of the nucleus. Z. Zellforsch. 110, 9–26 (1970a)
Zambrano, D.: The nucleus lateralis tuberis system of the gobiid fish Gillichthys mirabilis. II. Innervation of the pituitary. Z. Zellforsch. 110, 496–516 (1970b)
Zambrano, D.: Innervation of the teleost pituitary. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. Suppl. 3, 22–31 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terlou, M., Ekengren, B. Nucleus praeopticus and nucleus lateralis tuberis of Salmo salar and Salmo gairdneri: Structure and relationship to the hypophysis. Cell Tissue Res. 197, 1–21 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00233550
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00233550