Abstract
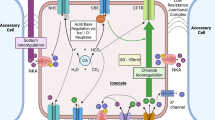
The response of confluent monolayers of HT29-Cl.16E cells to stimulation by extracellular ATP and ATP analogues was investigated in terms of mucin and electrolyte secretion. Mucin secretion was measured as release of glucosamine-labeled macromolecules trapped at the stacking/running gel interface of polyacrylamide gels and electrolyte secretion as shortcircuit current (Isc). Luminal ATP stimulated a transient increase in the release of mucins and of I sc corresponding to a secretory Cl− current. Both secretions peaked at 3 to 5 min after addition of ATP. Maximal ATP-stimulated mucin secretion over 15 min was up to 18-fold above control with an apparent ED50 of approximately 40 μm. Maximal peak I sc after stimulation with ATP was approximately 35 μA/cm2 with an apparent ED50 of about 0.4 mm. ATP-dependent I sc was at least in part due to Cl− secretion since removal of Cl− from the medium reduced the peak I sc by 40% and the I sc integrated over 40 min by 80%. The secretory responses were not associated with cell damage as assessed by failure of ethidium bromide to enter into the cells, absence of release of lactate dehydrogenase, maintenance of monolayer conductance, viability, and responses to repeated applications of ATP. The order of efficacy of nucleotide agonists was similar for both processes with ATP>ADP>AMP≥adenosine. Luminal ATP was much more effective than basolateral addition of this compound. These results suggest involvement of a luminal P2-type receptor which can initiate signaling pathways for granule fusion and mucin release as well as for activation of Cl− channels. P2-receptor-stimulated mucin and I sc release was strongly inhibited by a 30 min preincubation with the classical K+ channel blockers quinine (1 mm), quinidine (1 mm), and Ba2+ (3 mm). Experiments with amphotericin B to measure separately the conductance changes of either luminal or basolateral plasma membrane revealed that quinidine did not directly block the ATP-induced basolateral K+ or the luminal anion channels. The quinidine inhibition after preincubation is therefore most easily explained by interference with granule fusion and location of anion channels in granule membranes. Luminal P2 receptors may play a role in intestinal defense mechanisms with both fluid and mucin secretion aiding in the removal of noxious agents from the mucosal surface.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham, E.D., Prat, A.G., Gerweck, L., Seneveratine, T., Arceci, R.J., Kramer, R., Guidotti, G., Cantiello, H.F. 1993. The multidrug resistance (mdr1) gene functions as an ATP channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:312–316
Augeron, C., Laboisse, C.L. 1984. Emergence of permanently differentiated cell clones in a human colonic cancer cell line in culture after treatment with sodium butyrate. Cancer Res. 44:3961–3969
Augeron, C., Voisin, C., Maoret, J.J., Berthon, B., Laburthe, M., Laboisse, C.L. 1992. Neurotensin and neuromedin N stimulate mucin output from human goblet cells (Cl.16E) via neurotensin receptors. Am. J. Physiol. 262:C470-C476
Arias, I.M., Gatmaitan, Z., Mazzanti, R., Shu, H., Kumamoto, Y. 1990. Structure and function of P-glycoprotein in the normal liver and intestine. Int. Symp. Princess. Takamatsu. Cancer. Res. Fund 21:229–239
Bajnath, R.B., Dekker, K., Vaandrager, A.B., de Jonge, H.R., Groot, J.A. 1992. Biphasic increase of apical Cl− conductance by muscarinic stimulation of HT29.Cl.19A human colon carcinoma cell line: Evidence for activation of different Cl− conductances by carbachol and forskolin. J. Membrane Biol. 127:81–94
Born, G.V., Kratzer, M.A. 1984. Source and concentration of extracellular adenosine triphosphate during haemostasis in rats, rabbits and man. J. Physiol. 354:419–429
Bremer, S., Hoof, T., Wilke, M., Busche, R., Scholte, B., Riordan, J.R., Maass, G., Tummler, B. 1992. Quantative expression patterns of multidrug-resistance P-glycoprotein (MDR1) and differentially spliced cystic-fibrosis transmembrane-conductance regulator mRNA transcripts in human epithelia. Eur. J. Biochem. 206(1): 137–139
Capon, G., Laboisse, C.L., Wieruszeski, J.M., Maoret, J.J., Augeron, C., Fournet, B. 1992. Oligosaccharide structures of mucins secreted by human colonic cancer cell line CL.16E. J. Biol. Chem. 267:1948–1957
Cartwright, C., McRoberts, J.A., Mandel, K.G., Dharmsathaphorn, K. 1985. Synergistic action of cyclic adenosine monophosphate and calcium-mediated chloride secretion. J. Clin. Invest. 76:1837–1842
Chen, T.R. 1977. In situ detection of mycoplasma contamination in cell cultures by fluorescent Hoechst 33258 stain. Exp. Cell. Res. 104:255–262
Clarke, L.L., Boucher, R.C. 1992. Chloride secretory response to extracellular ATP in human normal and cystic fibrosis nasal epithelia. Am. J. Physiol. 263:C348-C356
Cliff, W., Frizzell, R.A. 1990. Separate Cl− conductances activated by cAMP and Ca++ in Cl− secreting epithelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:4956–4960
Cormack, D.H. 1979. In: The digestive system. Ham's Histology, Ninth edition. Chapter 18, p. 509. J.B. Lippincott, Philadelphia
Davis, C.W., Dowell, M.L., Lethem, M, van Scott, M. 1992. Goblet cell degranulation in isolated canine tracheal epithelium: response to exogenous ATP, ADP, and adenosine. Am. J. Physiol. 262:C1313-C1323
DeLisle, R.C., Hopfer, U. 1986. Electrolyte permeabilities of pancreatic zymogen granules: Implications for pancreatic secretion. Am. J. Physiol. 250:G489-G496
Dho, S., Stewart, K., Foskett, J.K. 1992. Purinergic receptor activation of Cl− secretion in T84 cells. Am. J. Physiol. 262:C67-C74
Dubyak, G.R. 1991. Signal transduction by P2-purinergic receptors for extracellular ATP. Am. J. Resp. Cell Mol. Biol. 4:295–300
El-Moatassim C., Dornand, J., Mani, J.C. 1992. Extracellular ATP and cell signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1134:31–45
Findlay, I., Dunne, M.J., Ullrich, S., Wollheim, C.B., Petersen, O.H. 1985. Quinine inhibits Ca2+ independent K+ channels whereas tetraethylammonium inhibits Ca2+-activated K+ channels in insulin-secreting cells. FEBS Lett. 185:4–8
Frizzell R. 1987. Active chloride secretion by rabbit colon: Calciumdependent stimulation by ionophore A23187. J. Membrane Biol. 35:175–187
Gasser, K.W., Goldsmith, A., Hopfer, U. 1990. Regulation of chloride transport in parotid secretory granules by membrane fluidity. Biochemistry 26:7282–7288
Gomperts, B.D. 1983. Involvement of guanine nucleotide-binding protein in the gating of Ca2+ by receptors. Nature 206:64–66
Hayslett, J.P., Gogelein, H., Kunzelmann, K., Greger, R. 1987. Characteristics of apical chloride channels in human colon cells (HT29). Eur. J. Physiol. 410:487–494
Kim, K.C., Lee, B. 1991. P2 purinoceptor regulation of mucin release by airway goblet cells in primary culture. Br. Pharmacol. 103:1053–1056
Kim, H.D., Tsai, Y.S., Franklin, C.C., Turner, J.T. 1988. Characterization of Na+/K+/Cl− cotransport in HT29 human colonic adenocarcinoma cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 946:397–404
Kirk, K.L., Dawson, D.C. 1983. Basolateral potassium channel in turtle colon. Evidence for single file flow. J. Gen. Physiol. 82:297–313
Knowles, M.R., Clarke, L., Boucher, R. 1991. Activation by extracellular nucleotides of chloride secretion in the airway epithelial of patients with cystic fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 325:533–538
Kreusel, K-M, Fromm, M., Shulzke, J-D., Hegel, U. 1991. Cl− secretion in epithelial monolayers of mucus-forming human colon cells (HT-29/B6). Am. J. Physiol. 261:C574-C582
Laburthe, M., Augeron, C., Rouyer-Fessard, C., Roumagnac I., Maoret, J.J., Grasset, E., Laboisse, C.L. 1989. Functional VIP receptors in the human mucus-secreting colonic epithelial cell line CL.16E. Am. J. Physiol. 256:G443-G450
Madara, J.L., Patapoff, T.W., Gillece-Castro, B., Colgan, S.P., Parkos, C.A., Delp, C., Mrsny, R.J. 1993. 5′-adenosine monophosphate is the neutrophil-derived paracrine factor that elicits chloride secretion from T84 intestinal epithelial cell monolayers. J. Clin. Invest. 91:2320–2325
Madara, J.L., Stafford, J. 1989. Interferon-γ directly affects barrier function of cultured intestinal epithelial monolayers. J. Clin. Invest. 83:724–727
Maoret, J.J., Font, J., Augeron, C., Codogno, P., Bauvy, C., Aubery, M., Laboisse, C.L. 1990. A mucus-secreting human colonic cancer cell line-purification and partial characterization of the secreted mucins. Biochem. J. 267:407–423
Marcon, M.A., McCool, D., Forstner, J., Forstner, G. 1990. Inhibition of mucin secretion in a colonic adenocarcinoma cell line by DIDS and potassium channel blockers. Biochim. Biophys Acta 1052:17–23
Merlin, D., Laboisse, C.L., Hopfer, U. 1992. Evidence for participation of phospholipase D (PLD) and against that of protein kinase A (PKA), or Ca/Calmodulin-stimulated kinase (Ca/CM PK) in the signaling of luminal ATP-induced Cl− secretion in HT29-C116E. FASEB. J. 6(5):A5708
Neutra, M.R., Forstner, J.F. 1987. Gastrointestinal mucus: Synthesis, secretion, and function. In: Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract. L.R. Johnson, editor. Second edition, pp. 975–107. Raven, New York
Phillips, T.E., Huet, C., Bilbo, P.R., Podolsky, D.K., Louvard, D., Neutra, M. 1988. Human intestinal goblet cells in monolayer culture: Characterization of a mucus-secreting subclone derived from the HT29 colon adenocarcinoma cell line. Gastroenterology 94:1390–1403
Reisin, I.L., Prat, A.G., Abraham, E.H., Amara, J., Gregory, R., Ausiello, D.A., Cantiello, H.F. 1992. Expression of CFTR results in the appearance of an ATP channel. J. Gen. Physiol. 100:33a
Roumagnac, I., Laboisse, C.L. 1987. A mucus-secreting human colonic epithelial cell responsive to cholinergic stimulation. Biol. Cell. 61:65–68
Rouyer-Fessard, C., Augeron, C., Maoret, J.J., Laboisse, C.L., Laburthe, M. 1989. VIP receptors and control of short circuit current in the human intestinal clonal cell line Cl.19A. Experientia 45:1103–1105
Spoelstra, E.C., Dekker, H., Shuurhuis, G.J., Broxterman, H.J., Lankelma, J. 1992. P-glycoprotein drug efflux pump involved in the mechanisms of intrinsic drug resistance in various colon cancer cell lines. Evidence for a saturation of active daunorubicin transport. Biochem. Pharmacol. 41(1):349–359
Stanley, E.F., Ehrenstein, G. 1985. A model for exocytosis based on the opening of calcium-activated potassium channels in vesicles. Life. Sci. 37:1985–1995
Stutts, M.J., Chinet, T.C., Mason, S.J., Fullton, J.M., Clarke, L.L., Boucher, R.C. 1992. Regulation of Cl− channels in normal and cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells by extracellular ATP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:1621–1625
Thévenod, F., Chathadi, K.V., Jiang, B., Hopfer, U. 1992. ATP-sensitive K+ conductance in pancreatic zymogen granules: Block by glyburide and activation by diazoxide. J. Membrane. Biol. 129: 253–266
Tien, X.Y., Laboisse, C.L., Hopfer, U. 1991. Regulation of Cl− secretion by apical purinergic receptors in HT29-CL.16E cells. FASEB. J. 5:A1764
Tilly, B.C., Kansen, M., van Gageldonk, P.G., van den Berghe, N., Galjaard, H., Bijman, J., de Jonge, H. 1991. G-proteins mediate intestinal chloride channel activation. J. Biol. Chem. 266:2036–2040
Vaandrager, A.B., Bajnath, R., Groot, J.A., Bot, A.G., De Jonge, H.R. 1991. Ca2+ and cAMP activate different chloride efflux pathways in HT-29.Cl19A colonic epithelial cell line. Am. J. Physiol. 261:G958-G965
Wong, S.M., Tesfaye, A., DeBell, M.C., Chase, H.S. 1990. carbachol increases basolateral K+ conductance in T84 cells. J. Gen. Physiol. 96:1271–1285
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (DK 39658) to U.H., the Philippe Foundation to D.M., the French Cystic Fibrosis Foundation (AFLM) and L'Association Pour La Recherche Sur Le Cancer to C.L. The authors thank Mr. J. Polack for his efforts and skill with electron microscopy and Dr. George Dubyak for helpful discussions. We also acknowledge the Cystic Fibrosis Center Core grant (DK-27651) for its support of electron and light microscopy.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Merlin, D., Augeron, C., Tien, X.Y. et al. ATP-stimulated electrolyte and mucin secretion in the human intestinal goblet cell line HT29-C1.16E. J. Membarin Biol. 137, 137–149 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00233483
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00233483