Summary
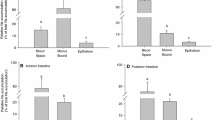
Transepithelial fluid transport was measured gravimetrically in rabbit gallbladder (and net Na+ transport was calculated from it), at 27°C, in HCO −3 -free bathing media containing 10−4 m acetazolamide. Whereas luminal 10−4 m bumetanide or 10−4 m 4-acetamido-4′-iso-thiocyanostilbene-2,2′-disulfonate (SITS) did not affect fluid absorption, 25 mm SCN− abolished it; hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) in the luminal medium reduced fluid absorption from 28.3±1.6 (n = 21) to 8.6±1.6 μl cm−2 hr−1 (n = 10), i.e., to about 30%. This maximum effect was already obtained at 10−3 m concentration; the apparent IC510 was about 2×10−4 m. The residual fluid absorption, again insensitive to SITS, was completely inhibited by SCN− or bumetanide. Cl− influx at the luminal border of the epithelium, measured under the same conditions and corrected for the extracellular space and paracellular influx, proved insensitive to 10−4 m bumetanide, but was slowly inhibited by 10−3 m HCTZ, with maximum inhibition (about 54%) reached after a 10-min treatment; it subsequently rose again, in spite of the presence of HCTZ. However, if the epithelium, treated with HCTZ, was exposed to 10−4 m bumetanide during the measuring time (45 sec), inhibition was completed and the subsequent rise of Cl− influx eliminated. Intracellular Cl− accumulation with respect to the predicted activity value at equilibrium decreased significantly upon exposure to 10−3 m HCTZ, reached a minimum within 15–30 min of treatment, then rose again significantly at 60 min. Simultaneous exposure to HCTZ and bumetanide decreased the accumulation to a significantly larger extent as compared to HCTZ alone, already in 15 min, and impeded the subsequent rise. Intracellular K+ activity rose significantly within 30 min treatment with HCTZ; the increase proved bumetanide dependent.
The results obtained show that Na+-Cl− symport, previously detected under control conditions, is the HCTZ-sensitive type; its inhibition elicits bumetanide-sensitive Na+-K+-2Cl− cotransport. Thus, the three forms of neutral Na+-Cl−-coupled transport so far evidenced in epithelia, Na+/H+, Cl−/HCO −3 double exchange (in the presence of exogenous bicarbonate), HCTZ-sensitive Na+-Cl− symport and bumetanide-sensitive Na+-K+-2Cl− cotransport, are all present in the apical membrane of rabbit gallbladder.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvo, M., Calamia, J., Eveloff, J. 1985. Lack of potassium effect on Na-Cl cotransport in the medullary thick ascending limb. Am. J. Physiol. 249:F34-F39
Aronson, P.S., Seifter, J. 1984. Cl− transport via anion exchange. Fed. Proc. 43:2483–2484
Baerentsen, H., Giraldez, F., Zeuthen, T. 1983. Influx mechanisms for Na+ and Cl− across the brush border membrane of leaky epithelia: A model and microelectrode study. J. Membrane Biol. 75:205–218
Beaumont, K., Vaughn, D.A., Fanestil, D.D. 1988. Thiazide diuretic drug receptors in rat kidney: Identification with [3H]metolazone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:2311–2314
Beaumont, K., Vaughn, D.A., Maciejewski, A.R., Fanestil, D.D. 1989. Reversible downregulation of thiazide diuretic receptors by acute renal ischemia. Am. J. Physiol. 256:F329-F334
Bottà, G., Meyer, G., Rossetti, C., Cremaschi, D. 1987. Isolation of apical plasma membrane in rabbit gallbladder epithelium by Percoll density gradient centrifugation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 897:315–323
Costanzo, L.S., Windhager, E.E. 1978. Calcium and sodium transport by distal convoluted tubule of the rat. Am. J. Physiol. 235:F492-F506
Cremaschi, D., Hénin, S. 1975. Na+ and Cl− transepithelial routes in rabbit gallbladder. Tracer analysis of the transports. Pfluegers Arch. 361:33–41
Cremaschi, D., Hénin, S., Ferroni, A. 1974. Intracellular electric potential in the epithelial cells of rabbit gallbladder. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 1:208–216
Cremaschi, D., Hénin, S., Meyer, G. 1979. Stimulation by HCO −3 of Na+ transport in rabbit gallbladder. J. Membrane Biol. 47:145–170
Cremaschi, D., James, P.S., Meyer, G., Rossetti, C., Smith, M.W. 1984. Developmental changes in intra-enterocyte cation activities in hamster terminal ileum. J. Physiol. 354:363–373
Cremaschi, D., Meyer, G. 1982. Amiloride-sensitive sodium channels in rabbit and guinea-pig gallbladder. J. Physiol. 326:21–34
Cremaschi, D., Meyer, G., Bermano, S., Marcati, M. 1983. Different sodium chloride cotransport systems in the apical membrane of rabbit gallbladder epithelial cells. J. Membrane Biol. 73:227–235
Cremaschi, D., Meyer, G., Bottà, G., Rossetti, C. 1987b. The nature of the neutral Na+-Cl− coupled entry at the apical membrane of rabbit gallbladder epithelium: II. Na+-Cl− symport is independent of K+. J. Membrane Biol. 95:219–228
Cremaschi, D., Meyer, G., Rossetti, C., Bottà, G., Palestini, P. 1987a. The nature of the neutral Na+-Cl− coupled entry at the apical membrane of rabbit gallbladder epithelium: I. Na+/H+, Cl−/HCO −3 double exchange and Na+-Cl− symport. J. Membrane Biol. 95:209–218
Cremaschi, D., Rossetti, C., Porta, C., Bottà, G., Meyer, G. 1990. Sensibilità all'idroclorotiazide del cotrasporto Na+-Cl− presente nell'epitelio di cistifellea di coniglio. Attivazione omeostatica di un cotrasporto Na+-K+-2Cl−. pp. D23–D25. (Abstr.) Autumn Meeting of Italian Physiological Soc., Perugia
Davis, C.W., Finn, A.L., 1985. Effects of mucosal sodium removal on cell volume in Necturus gallbladder epithelium. Am. J. Physiol. 249:C304-C312
Duffey, M.E., Frizzell, R.A. 1984. Flounder urinary bladder. Mechanism of inhibition by hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ). Fed. Proc. 43:932 (Abstr.)
Eknoyan, G., Sawa, H., Hyde, S., Wood, J.M., III, Schwartz, A., Suki, W. 1975. Effect of diuretics on oxidative phosphorylation of dog kidney mitochondria. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 194:614–623
Ellory, J.C., Dunham, P.B., Logue, P.J., Steward, G.O. 1982. Anion-dependent cation transport in erythrocytes. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. London B 299:483–495
Ericson, A.C., Spring, K.E. 1982. Volume regulation by Necturus gallbladder: Apical Na+/H+ and Cl−/HCO −3 exchange. Am. J. Physiol. 243:C146-C150
Eveloff, J., Kinne, R. 1983. Sodium-chloride transport in the medullary thick ascending limb of Henle's loop: Evidence for a sodium-chloride cotransport system in plasma membrane vesicles. J. Membrane Biol. 72:173–181
Eveloff, J.L., Warnock, D.G. 1987. Activation of ion transport systems during cell volume regulation. Am. J. Physiol. 252:F1-F10
Frizzell, R.A., Dugas, M.C., Schultz, S.G. 1975. Sodium chloride transport in rabbit gallbladder. Direct evidence for a coupled NaCl influx process. J. Gen. Physiol. 65:769–795
Frizzell, R.A., Field, M. 1984. NaCl cotransport across the apical membrane of flounder intestinal cells. Fed. Proc. 43:2478–2479
Geck, P., Pietrzyk, C., Burckhardt, B.C., Pfeiffer, B., Heinz, E. 1980. Electrically silent cotransport of Na+, K+ and Cl− in Ehrlich cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 600:432–477
Gilman, A.G., Goodman, L.S., Gilman, A. (editors) 1980. The pharmacological basis of therapeutics, pp. 899–903. MacMillan, New York
Greger, R. 1984. The Na+/K+/Cl− system in the diluting segment of rabbit kidney. Fed. Proc. 43:2473–2476
Heintze, K., Petersen, K.-U. 1980. Na/H and Cl/HCO3 exchange as a mechanism for HCO3-stimulated NaCl absorption by gallbladder. In: Hydrogen Ion Transport in Epithelia. I. Schultz, G. Sachs, J.G. Forte, and K.J. Ulrich, editors, pp. 345–354. Elsevier North-Holland Biomedical, Amsterdam
Hénin, S., Cremaschi, D. 1975. Transcellular ion route in rabbit gallbladder. Electric properties of the epithelial cells. Pfluegers Arch. 355:125–139
Lang, F., Volkl, H., Haussinger, D. 1990. General principles in cell volume regulation. In: Comparative Physiology. R.K.H. Kinne, E. Kinne-Saffran, and K.W. Beyenbach, editors. Vol. 4, pp. 1–25. Karger, Basel
Liedtke, C.M., Hopfer, U. 1977. Anion transport in brush border membranes isolated from rat small intestine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 76:579–585
Liedtke, C.M., Hopfer, U. 1982a. Mechanism of Cl− translocation across small intestinal brush border membrane: I. Absence of Na+-Cl− cotransport. Am. J. Physiol. 242: G263-G271
Liedtke, C.M., Hopfer, U. 1982b. Mechanism of Cl− translocation across small intestinal brush border membrane: II. Demonstration of Cl−-OH− exchange and Cl− conductance. Am. J. Physiol. 242:G272-G280
Manuel, M.A., Weiner, M.W. 1976. Effects of ethacrynic acid and furosemide on isolated rat kidney mitochondria: Inhibition of electron transport in the region of phosphorylation site II. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 198:209–221
Manuel, M.A., Weiner, M.W. 1977. Effects of ethacrynic acid and furosemide on phosphorylation reactions of kidney mitochondria. Inhibition of the adenine nucleotide translocase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 460:445–454
Meyer, G., Bottà, G., Rossetti, C., Cremaschi, D. 1990. The nature of the neutral Na+-Cl− coupled entry at the apical membrane of rabbit gallbladder epithelium: III. Analysis of transports on membrane vesicles. J. Membrane Biol. 118:107–120
Meyer, G., Rossetti, C., Bottà, G., Cremaschi, D. 1985. Construction of K+- and Na+-sensitive theta microelectrodes with fine tips. An easy method with high yield. Pfluegers Arch. 404:378–381
Moore, P.F. 1968. The effects of diazoxide and benzothiadiazine diuretics upon phosphodiesterase. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 150:256–260
Murer, H., Hopfer, U., Kinne, R. 1976. Sodium/proton antiport in brush border membrane vesicles isolated from rat small intestine and kidney. Biochem. J. 154:597–604
Nellans, H.N., Frizzell, R.A., Schultz, S.G. 1973. Coupled sodium chloride influx across the brush border of rabbit ileum. Am. J. Physiol. 225:467–475
Petersen, K.-U., Wehner, F., Winterhager, J.M. 1985. Na/H exchange at the apical membrane of guinea-pig gallbladder epithelium: Properties and inhibition by cyclic AMP. Pfluegers Arch. 405 [Suppl. I]:S115-S120
Petersen, K.-U., Wehner, F., Winterhager, J.M. 1990. Transcellular bicarbonate transport in rabbit gallbladder epithelium: Mechanisms and effects of cyclic AMP. Pfluegers Arch. 416:312–321
Reuss, L. 1984. Independence of apical membrane Na+ and Cl− entry in Necturus gallbladder epithelium. J. Gen. Physiol. 84:423–445
Reuss, L. 1987. Cyclic AMP inhibits Cl−/HCO −3 exchange at the apical membrane of Necturus gallbladder epithelium. J. Gen. Physiol. 90:173–196
Reuss, L., Petersen, K.-U. 1985. Cyclic AMP inhibits Na+/H+ exchange at the apical membrane of Necturus gallbladder epithelium. J. Gen. Physiol. 85:409–430
Spring, K.R. 1984. NaCl cotransport by Necturus gallbladder epithelium. Fed. Proc. 43:2479–2481
Stokes, J.B. 1984. Sodium chloride absorption in the urinary bladder of the winter flounder. A thiazide-sensitive electrically neutral transport system. J. Clin. Invest. 74:7–16
Sullivan, B., Berndt, W.O. 1973. Transport by isolated rabbit gallbladders in phosphate-buffered solutions. Am. J. Physiol. 225:836–844
Van Os, C., Siegers, J.F.G. 1971. Correlation between Na+-K+ activated ATPase activities and the rate of isotonic fluid transport of gallbladder epithelium. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 241:89–96
Velasquez, H. 1987. Thiazide diuretics. Renal Physiol. 10:184–197
Velasquez, H., Good, D.W., Wright, F.S. 1984. Mutual dependence of sodium and chloride absorption by renal distal tubule. Am. J. Physiol. 247:F904-F911
Vulliemoz, Y., Verosky, M., Triner, L. 1980. Effect of benzothiadiazine derivatives on cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase and on the tension of the aortic strip. Blood Vessels 17:91–103
Weller, J.M., Borondy, M. 1976. Effects of chlorothiazide on glucose utilization, glycogen content and lactic acid production of aorta. Proc. Exp. Biol. Med. 153:483–485
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported by Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca Scientifica e Tecnologica, Rome, Italy. We are very grateful to Miss P. Vallin for technical assistance.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cremaschi, D., Porta, C., Bottà, G. et al. Nature of the neutral Na+-Cl− coupled entry at the apical membrane of rabbit gallbladder epithelium: IV. Na+/H+, Cl−/HCO −3 double exchange, hydrochlorothiazide-sensitive Na+-Cl− symport and Na+-K+-2Cl− cotransport are all involved. J. Membarin Biol. 129, 221–235 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00232905
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00232905