Abstract
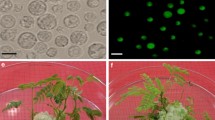
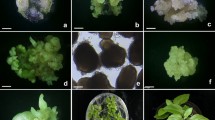
Protoplasts were isolated from hypocotyls of 7-d-old seedlings of three genotypes of Brassica carinata after enzymatic digestion in cellulase R-10 (0.5%) and pectolyase Y-23 (0.025%). The protoplasts were stabilized with 0.4 M mannitol used as osmoticum, and were cultured in darkness in Kao's liquid medium containing 0.4 M glucose and the growth regulators 2,4-D (1.0 mg/l), NAA (0.1 mg/l) and zeatin riboside (0.5 mg/l). Protoplasts were transferred to 16 h photoperiod conditions after 3 d of dark culture, and the medium was diluted to reduce the osmoticum on the seventh and tenth days of culture. Microcolonies were thus obtained which, upon transfer to MS agarose medium with 2,4-D (0.1 mg/l), BAP (1 mg/l) and 0.1 M sucrose, proliferated further to produce callus clumps. The plating efficiency of the three genotypes varied from 1 to 2%. Calli 2–3 mm in diameter were transferred to MS agarose plates with zeatin (2 mg/l) where they produced shoot buds and shoots with frequencies ranging from 22.5 to 74.2% for the three genotypes. The shoots were rooted in medium with IBA (1 mg/l) and were then established in soil. The time required for protoplast to plant development was 8 to 10 weeks.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- IAA:
-
Indole-3-acetic acid
- IBA:
-
Indole-3-butyric acid
- NAA:
-
α-naphthalene acetic acid
- BAP:
-
6-Benzylaminopurine
- KN:
-
Kinetin
- 2IP:
-
6-(Gamma, gamma-dimethylallyl-amino)purine
References
Binding H (1974) Regeneration von haploiden und diploiden pflanzen aus protoplasten von Petunia hybrida L. Z Pflanzenphysiol 74:327–356
Choung PV, Pauls KP, Beversdorf WD (1987) Protoplast culture and plant regeneration from Brassica carinata Braun. Plant Cell Rep. 6:67–69
Glimelius K (1984) High growth rate and regeneration capacity of hypocotyl protoplasts in some Brasslcaceae. Physiol Plant 61:38–44
Gupta V, Agnihotri A, Jagannathan V (1991) Plant regeneration from callus and protoplasts of Brassica nigra (IC 257) through somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Rep 9:427–430
Jaiswal SK, Hammatt N, Bhojwani SS, Cocking EC, Davey MR (1990) Plant regeneration from cotyledon protoplasts of Brassica carinata. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture 22:159–165
Jourdan PS, Earle ED, Mutschler MA (1990) Improved protoplast culture and stability of cytoplasmic traits in plants regenerated from leaf protoplasts of cauliflower (B. oleracea ssp. botrytis). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture 21:227–236
Kao HM, Keller WA, Gleddie S, Brown GG (1990) Efficient plant regeneration from hypocotyl protoplasts of broccoli (B. oleracea L. ssp. italica Planck). Plant Cell Rep 9:311–315
Kao KN (1977) Chromosomal behaviour in somatic hybrids of soybean — Nicotiana glauca. Molec Gen Genet 150:225–230
Kirti PB, Prakash S, Chopra VL (1991) Interspecific hybridization between Brassica juncea and B. spinescens through protoplast fusion. Plant Cell Rep 9:639–642
Kirti PB, Chopra VL (1990) Rapid plant regeneration through organogenesis and somatic embryogenesis from cultured protoplasts. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture 20:65–67
Kirti PB, Chopra VL (1989) Plant regeneration from hypocotyl derived protoplasts of Brassica juncea (L) Czern and Coss. Plant Cell Rep 7:708–710
Murashige T and Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Nagy JJ, Maliga P (1976) Callus induction and plant regeneration from mesophyll protoplasts of Nicotiana sylvestris. Z Pflanzenphysiol 78:453–455
Polsen GB, Nielsen SVS (1989) Regeneration of plants from hypocotyl protoplasts of rapeseed (Brassica napus L. var oleifera) cultivars. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture 17:153–158
Sacristan MD, Gerdemann-Knorck M, Schieder O (1989) Incorporation of hygromycin resistance in Brassica nigra and its transfer to B. napus through asymmetric protoplast fusion. Theor Appl Genet 78:194–200
Shimamoto K, Terada R, Izawa T, Fujimoto F (1989) Fertile transgenic rice plants regenerated from transformed protoplasts. Nature 338:274–276
Thomzik JE, Hain R (1990) Transgenic Brassica napus plants obtained by cocultivation of protoplasts with Agrobacterium tumefaciens Plant Cell Rep 9:233–236
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. C. Phillips
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narasimhulu, S.B., Kirti, P.B., Prakash, S. et al. Rapid and efficient plant regeneration from hypocotyl protoplasts of Brassica carinata . Plant Cell Reports 11, 159–162 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00232171
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00232171