Summary
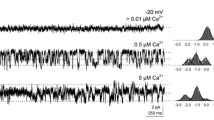
Olfactory neurones of Xenopus laevis were studied by the patch clamp technique under voltage-clamp conditions. Isolated receptor cells were obtained by dissociating the olfactory mucosa in a Ca2+-free solution. Usually some of the resulting isolated olfactory cells lost all of their cilia during the dissociation procedure. Comparing the currents of cells with cilia to those of cells without cilia, a marked difference was found. When all known voltage-gated currents except the Ca2+-current were blocked, cells without cilia showed the voltage-gated Ca2+-current alone whereas cells with cilia clearly had an additional conductance gc. It could be activated in two ways, either by Ca2+ entry through Ca2+-channels or by Ca2+ entry through the Na/Ca-exchanger working in the reversed mode at positive membrane potentials. This ciliar conductance gc had its reversal potential at 0 mV. Replacing extracellular Cl- by isethionate on the one hand, and Na+ by Cs+ or N-methyl-D-glucamine on the other showed that gc was permeable for cations but not for Cl-. In conclusion, there appears to be a Ca2+-dependent unselective cation conductance on the cilia of olfactory neurones. The probable role of gc as the last step in an IP3/Ca mediated transduction path-way is suggested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altner H (1962) Untersuchungen über Leistungen und Bau der Nase des südafrikanischen Krallenfrosches Xenopus laevis (Daudin 1803). Z Vergl Physiol 45:272–306
Blaustein MP (1977) Effects of internal and external cations and of ATP on sodium-calcium and calcium-calcium exchange in squid axons. Biophys J 20:79–111
Blaustein MP (1988) Calcium transport and buffering in neurons. TINS 11:438–443
Breer H, Boekhoff I, Tareilus E (1990) Rapid kinetics of second messenger formation in olfactory transduction. Nature 345:65–68
Boekhoff I, Göggerle S, Breer H (1990) Molecular reaction cascades in olfaction signal transduction. In: Elsner N, Roth G (eds) Brain perception cognition. Proceed 18th Göttingen Neurobiol. Thieme, Stuttgart New York, p 309
Firestein S, Werblin FS (1987) Gated currents in isolated olfactory receptor neurons of the larval tiger salamander. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:6292–6296
Firestein S, Werblin F (1989) Odor-induced membrane currents in vertebrate-olfactory receptor neurons. Science 244:79–82
Föske H (1934) Das Geruchsorgan von Xenopus laevis. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch 103:519–550
Frings S, Lindemann B (1988) Odorant response of isolated olfactory receptor cells is blocked by amiloride. J Membr Biol 105:233–243
Frings S, Lindemann B (1990a) Single unit recording from olfactory cilia. Biophys J 57:1091–1094
Frings S, Lindemann B (1990b) Response of olfactory receptor cells, isolated and in situ, to low concentrations of odorants. In: Schild D (ed) Chemosensory information processing. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp
Getchell TV (1986) Functional properties of vertebrate olfactory receptor neurons. Physiol Rev 66:772–817
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmannn B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391:85–100
Kaczorowski GJ, Barros F, Dethmers JK, Trumble MJ (1985) Inhibition of Na+/Ca2+ exchange in pituitary plasma membrane vesicles by analogues of amiloride. Biochem 24:1394–1403
Kurahashi T (1989) Activation by odorants of cation-selective conductance in the olfactory receptor cell isolated from the newt. J Physiol (Lond) 419:177–192
Kurahashi T, Shibuya T (1989) Membrane response and permeibility changes to odorants in the solitary receptory cells of newt. Zool Sci 6:19–30
Maue RA, Dionne VE (1987) Patch clamp studies of isolated mouse olfactory receptor neurons. J Gen Physiol 90:95–125
Nakamura T, Gold GH (1987) A cyclic nucleotide-gated conductance in olfactory receptor cilia. Nature 325:442–444
Pace U, Hanski E, Salomon Y, Lancet D (1985) Odorant-sensitive adenylate cyclase may mediate olfactory reception. Nature 316:255–258
Persaud KC, Heck GL, DeSimone SK, Getchell TV, DeSimone JA (1988) Ion transport across the frog olfactory mucosa: the action of cyclic nucleotides on the basal and odorant-stimulated states. Biochim Biophys Acta 944:49–62
Schild D (1989) Whole-cell currents in olfactory receptor cells of Xenopus laevis. Exp Brain Res 78:223–232
Schild D, DeSimone JA, Hellwig S (1990) Excitation and adaptation of frog olfactory receptor neurones upon stimulation with second messengers and natural odorants. In: Schild D (ed) Chemosensory information processing. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 9–20
Suzuki N (1989) Voltage- and cyclic nucleotide-gated currents in isolated olfactory receptor cells. In: Brand JS, Cagan RH, Teeter JH, Kare MR (eds) Chemical senses. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 469–493
Swandulla D, Lux HD (1985) Activation of a nonspecific cation conductance by intracellular Ca2+ elevation in bursting pacemaker neurons of Helix pomatia. J Neurophysiol 54:1430–1443
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schild, D., Bischofberger, J. Ca2+ modulates an unspecific cation conductance in olfactory cilia of Xenopus laevis . Exp Brain Res 84, 187–194 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231774
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231774