Abstract
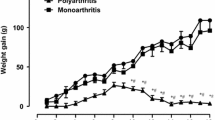
The metabolic changes in the connective tissue glycosaminoglycans were studied in tissues of adjuvant induced arthritic rats. Arthritic process was induced in rats with the inoculation of Freund's adjuvant containing heat killed Mycobacterium tuberculosis in paraffin oil. The connective tissue glycosaminoglycans were fractionated into sulfated and non-sulfated glycosaminoglycans by chemical and enzymatic methods. The biosynthesis of sulfated glycosaminoglycans was examined using radioactive labeled (35S)-sulfate incorporation measurements into the sulfated glycosaminoglycans in tissues such as liver, kidney, spleen and skin of arthritic rats. The catabolism of glycosaminoglycans was studied by measuring the activity of various connective tissue degrading lysosomal glycohydrolases in tissues of experimental animals. In addition, the changes in the contents of total glycosaminoglycans, mono-sulfated, highly-sulfated and non-sulfated glycosaminoglycans were quantitatively assessed in diseased tissues. Alterations in the metabolism of connective tissue glycosaminoglycans were demonstrated in tissues of arthritic rats. The uptake of (35S)-sulfate into the tissue was found to be increased in liver, kidney and spleen, while that of skin decreased during the process of arthritis. The total glycosaminoglycan content was significantly elevated in diseased tissues compared to normal. Similarly, mono-sulfated, highly-sulfated and non-sulfated glycosaminoglycans were found to be increased in arthritic tissues. In addition, the activity of various connective tissue degrading lysosomal glycohydrolases such as β-glucuronidase, β-N-acetylglucosaminidase, cathepsin B, cathepsin L and collagenolytic cathepsin was increased in tissues of arthritic rat. The results presented in this communication indicate that the characteristic alterations were induced in the metabolism of glycosaminoglycans by the dynamic process of adjuvant arthritis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kesava Reddy G, Dhar SC: Studies on carbohydrate moieties of glycoproteins in established adjuvant induced arthritis. Agents Actions 25: 63–70, 1988
Reddy GK, Dhar SC: Metabolism of collagen in bone of adjuvant induced arthritic rat. Bone 10: p, 439–446, 1989
Pearson CM: Experimental joint disease: Observations on adjuvant induced arthritis. J Chronic Dis 16: 863–874, 1963
Kesava Reddy G, Dhar SC, Singh G: Biochemical investigations of a new non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent in adjuvant induced arthritis in relation to serum glycohydrolases and glycoproteins. Leather Science 33: 192–199, 1986
Kesava Reddy G, Dhar SC, Singh GB: Urinary excretion of connective tissue metabolites under the influence of a new non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent in adjuvant induced arthritis. Agents Actions 22: 99–105, 1987
Kesava Reddy G: In Ph. D. Thesis, University of Madras. pp 137–158, 1989
Kesava Reddy G, Dhar SC: Effect of a new non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent on lysosomal stability in adjuvant induced arthritis. Ital J Biochem 36: 205–217, 1987
Mahin DT, Lofberg TT: A simplified method of sample preparation for determination of tritium, carbon-14 or sulfur-35 in blood or tissue by liquid scintillation counting. Anal Biochem 16: 500–509, 1966
Murata K: Acidic glycosaminoglycans in human kidney. Clin Chim Acta 63: 157–169, 1975
Mier PD, Wood M: A simplified technique for the analysis of tissue acid mucopolysaccharides. Clin Chim Acta 24: 105–110,1969
Kawai Y, Anno K: Mucopolysaccharide degrading enzymes from the liver of squid Ommastrephesloni I. Hyaluronidase. Biochim Biophys Acta 242:428–436,1971
Moore JC, Morris JE: A simple automated colorimetric method for determination of N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase. Ann Clin Biochem 19: 157–159, 1982
Barrett AJ: A new assay for cathepsin B1 and other thiol proteinases. Anal Biochem 47: 280–293, 1972
Turk V, Kreger I: Hydrolases. In: HV Bergmeyer (ed) Methods in Enzymatic Analysis Verlag Chemie, Basel, 1984, Vol V, pp 195–210
Anderson AJ: Effect of lysosomal collagenolytic enzymes, anti-inflammatory drugs and other substances on some properties of insoluble collagen. Biochem J 113: 457–463, 1969
Neuman RE, Logan MA: The determination of collagen and elastin in tissues. J Biol Chem 186: 549–556, 1950
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ: Protein measurement with Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193: 265–275,1951
Helin P, Lorenzen I, Garbarsch C, Mathiessen ME: Repair in arterial tissue: morphological and biochemical changes in rabbit aortas after a single dilation injury. Circ Res 29: 542–554,1972
Wolinsky H: Comparative effects of castration and antiandrogen treatment on the aortas of hypertensitive and normotensive rats. Circ Res 33: 183–189, 1973
Shoshan S, Gross J: Biosynthesis and metabolism of collagen and its role in tissue repair processes. Isr J Med Sci 10: 537–561,1974
Herbai G: (dy1970) Double isotope method for determination of the miscible inorganic sulfate pool of the mouse applied in vivo studies of sulfate incorporation into costal cartilage. Acta Physiol Scand 80: 470–491, 1970
Herbai G: Effect of adrenalectamy, corticosteroids and some other anti-inflammatory agents, salazopyrin, thyroxine and vitamin A on the exchangeable sulfate pool and sulfate incorporation in vivo into costal cartilage of mouse. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 29: 164–176, 1971
Schiller S, Dorfman A: The metabolism of mucopolysaccharides in animalas. The effect of cortisone and hydrocortisone on rat skin. Endocrynol 60: 376–381, 1957
Layton LL: Effect of cortisone upon chondroitin sulfate synthesis by animal tissues. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 76: 596–598,1951
Myers SL, Hosseler PA, Castor CW: Connective tissue activation XIX: Plasma levels of the CTAP III platelet antigen in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rhematol 7: 814–819, 1980
Castor CW, Furlong AM, Carter-Su C: Connective tissue activation: Stimulation of glucose transport by connective tissue activating peptide III. Biochemistry 24: 1762–1767, 1985
Sundblad L, Egelius N, Jonsson E: Action of hydrocortisone on the hyaluronic acid of joint fluids in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 6: 295–302, 1954
Bjork J, Kleinau S, Tengblad A, Smedegard G: Elevated levels of serum hyaluronate and corelation with disease activity in experimental models of arthritis. Arthr Rheum 32: 306–311, 1989
Woessner JF: Catabolism of collagen and non-collagen protein in the rat uterus during post-patum involution. Biochem J 83: 304–314, 1962
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kesava Reddy, G., Dhar, S.C. Metabolism of glycosaminoglycans in tissues of adjuvant arthritic rat. Mol Cell Biochem 106, 117–124 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230177
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230177