Abstract
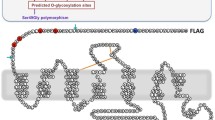
Co-transfection of a truncated natriuretic peptide receptor-B (NPR-B) with the full length receptor results in a decrease of 60–80% in wild-type receptor activity. This reduction correlates with a loss of glycosylation of the full length NPR-B. This effect is dose-dependent, and occurs with no change in the glycosylation of the truncated receptor. Co-transfection of the full length NPR-B with other receptors yields similar results. These data suggest that glycosylation may be crucial for NPR-B function. Cross-linking studies further demonstrate that only fully glycosylated NPR-B receptors are able to bind ligand. Our data therefore argue that carbohydrate modification may be critical for NPR-B receptor ligand binding.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- as:
-
amino acids
- ANF:
-
atrial natriuretic factor
- ANOVA:
-
analysis of variance
- BS3 :
-
bis(sulfosuccinimidyl) suberate
- BSA:
-
bovine serum albumin
- CNP:
-
C-type natriuretic peptide
- DEAE:
-
dextran-diethylaminoethyl-dextran
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium
- DMSO:
-
dimethyl sulfoxide
- dNTP:
-
deoxynucleotide triphosphate
- EDTA:
-
ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid
- IBMX:
-
3-isobutyl-l-methyl-=xanthine
- min:
-
minutes
- N-linked:
-
asparagine-linked
- NPR:
-
natriuretic peptide receptor
- nt:
-
nucleotide
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- RIA:
-
radioimmunoassay
- RP-HPLC:
-
reverse phase-high performance liquid chromatography
- RP-HPLC:
-
reverse phase-high performance liquid chromatography
- SDS:
-
sodium dodecyl sulfate
- UV:
-
ultraviolet
References
Jamison R, Canaan-Kuhl S, Pratt R: The natriuretic peptides and their receptors. Am J Kid Dis XX: 519–530, 1992
Levin ER: Natriuretic peptide C-receptor: More than a clearance receptor. Am J Physiol 264 (27): E483-E489, 1993
Drewett JG, Garbers DL: The family of guanylyl cyclase receptors and their ligands. Endo Rev 15 (2): 135–162, 1994
Anand-Srivastava MB, Trachte GJ: Atrial natriuretic factor receptors and signal transduction mechanisms. Pharmacol Rev 45 (4): 455–497, 1993
Chinkers M, Garbers D: Signal transduction by guanylyl cyclases. Annu Rev Biochem 60: 553–575, 1991
Schultz S, Singh S, Bellet RA, Singh G, Tubb J, Chin H, Gathers D: The primary structure of a plasma membrane guanylate cyclase demonstrates diversity within this new receptor family. Cell 58: 1155–1162, 1989
Chang M-S, Lowe D, Lewis M, Hellmiss R, Chen E, Goeddel DV: differential activation by atrial and brain natriuretic peptides of two different receptor guanylyl cyclases. Nature 341: 68–72, 1989
Duda T, Goraczniak RM, Sitaramayya A, Sharma RK: Cloning and expression of an ATP-regulated human retina C-type natriuretic factor receptor guanylyl cyclase. Biochem 32: 1391–1395, 1993
Lowe D, Chang M-S, Hellmiss R, Chen E, Singh S, Gathers DL, Goeddel DV: Human atrial natriuretic peptide receptor defines a new paradigm for second messenger signal transduction. EMBO J 8: 1377–1384, 1989
Chinkers M, Garbers DL, Chang M-S, Lowe D, Chin H, Goeddel DV, Schulz S: A membrane form of guanylyl cyclase is an atrial natriuretic peptide receptor. Nature 38: 78–83, 1989
Fenrick R, Babinski K, McNicoll N, Therrien M, Drouin J, De Léan A: Cloning and functional expression of the bovine natriuretic peptide receptor-B (natriuretic factor R1C subtype). Mol Cell Biochem 137: 173–182, 1994
Pandey KN, Singh S: Molecular cloning and expression of murine guanylyl cyclase/atrial natriuretic factor receptor cDNA. J Biol Chem 265: 12342–12348, 1990
Garbers DL, Lowe DG: Guanylyl cyclase receptors. J Biol Chem 269 (49): 30741–30744, 1994
Ueno H, Gunn M, Dell K, Tseng A, Williams LA: Truncated form of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 inhibits signal transduction by multiple types of fibroblast growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem 267 (3): 1470–1476, 1992
Ueno H, Colbert H, Escobedo JA, Williams L: Inhibition of PDGF β receptor signal transduction by coexpression of a truncated receptor. Science 252: 844–848, 1991
Kashles O, Yarden Y, Fischer R, Ullrich A, Schlessinger J: A dominant negative mutation suppresses the function of normal epidermal growth factor receptors by heterodimerization. Mol Cell Biol 11: 1454–1463, 1991
Fuller F, Porter JG, Arfsten AE, Miller J, Schilling JW, Scarborough RM, Schenk DB: Atrial natriuretic peptide clearance receptor. J Biol Chem 263: 9395–9401, 1988
Dixon RAF, Kobilka BK, Strader DJ, Benovic JL, Dohlman HG, Frielle T, Bolanowski MA, Bennett CD, Rands E, Diehl RE, Mumford RA, Slater EE, Sigal IS, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ, Strader CD: Cloning of the gene and cDNA for mammalian β-adrenergic receptor and homology with rhodopsin. Nature 321: 75–79, 1986
Kobilka BK, Frielle T, Collins S, Yang-Feng T, Kobilka TS, Francke U, Lefkowitz RJ, Carom MG: An intronless gene encoding a potential member of the family of receptors coupled to guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. Nature 329: 75–79, 1987
Cullen BR: Use of eukaryotic expression technology in the functional analysis of cloned genes. Meth Enzymol. 152: 684–703, 1987
Féthiere J, Meloche S, Nguyen TT, Ong H, De Léan A: Distinct properties of atria] natriuretic factor receptor subpopulations in epithelial and fibroblast cell lines. Mol Pharm 35: 584–592, 1989
Larose L, McNicoll N, Rondeau J-J, Escher E, De Léan A: Photoaffinity labelling of atrial natriuretic factor (ANF)-R1 receptor by underivatized 125I-ANF. Biochem J 267: 379–384, 1990
Rondeau J-J, McNicoll N, Lord C, Larose L, Meloche S, Gagnon J, Ong H, De Léan A: Production of polyclonal antibody to the bovine adrenal atrial natriuretic factor-RI receptor. J Receptor Research 12 (4): 485–505, 1992
De Léan A, Munson PJ, Rodbard D: Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: Application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose response curves. Am J Physiol 235: E97-E102, 1978
Bennett B, Bennett G, Vitangcol R, Jewett J, Burnier J, Henzel W, Lowe D: Extracellular domain-IgG fusion proteins for three human natriuretic peptide receptors. J Biol Chem 266: 23060–23067, 1991
Lowe DG, Fendly BM: Human natriuretic peptide receptor-A guanylyl cyclase. J Biol Chem 267: 21691–21697, 1992
Koller K, Lipari T, Goeddel DV: Proper glycosylation and phosphorylation of the type A natriuretic peptide receptor are required for hormone-stimulated guanylyl cyclase activity. J Biol Chem 268: 5997–6003, 1993
Chinkers M, Wilson EM: Ligand-independent oligomerization of natriuretic peptide receptors. J Biol Chem 267: 18589–18597, 1992
Wilson EM, Chinkers M: Identification of sequences mediating guanylyl cyclase dimerization. Biochem 34: 4696–4701, 1995
Thompson DK, Garbers DL: Dominant negative mutations of the guanylyl cyclase-A receptor. 270: 425–430, 1995
Lowe DG: Human natriuretic peptide receptor-A guanylyl cyclase is self-associated prior to hormone binding. Biochem 31: 10421–10425, 1992
Meloche S, Ong H, De Léan A: Functional heterogeneity of atrial natriuretic factor in bovine adrenal zona glomerulosa is explained by an amiloride-sensitive high affinity molecular complex. J Biol Chem 262: 10252–10258, 1987
Rondeau J-J, McNicoll N, Gagnon J, Bouchard N, Ong H, De Léan A: Stiochiometry of the atrial natriuretic factor-R1 receptor complex in the bovine zona glomerulosa. Biochem 34: 2130–2136, 1995
Kornfeld R, Kornfeld S: Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccarides. Ann Rev Biochem 54: 631–664, 1985
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Address for offprints:Department of Pharmacology, University of Montreal, 2900 Edouard Montpetit, Montreal, Quebec, H3C3J7, Canada
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fenrick, R., McNicoll, N. & De Léan, A. Glycosylation is critical for natriuretic peptide receptor-B function. Mol Cell Biochem 165, 103–109 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00229471
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00229471