Summary
A two-chain polypeptide, which corresponds to amino acid residues 115–143 and 144–184(185) of bovine serum albumin, connected to each other by a disulfide bridge, potentiated the effects of insulin on glucose transport and glucose metabolism in isolated rat adipocytes. Although the peptide alone had little activity, it shifted the concentration-response curves of insulin-stimulated D-[I-14C]glucose oxidation, 2-deoxyglucose transport, and lipid synthesis from D-[U-14C]glucose to lower insulin concentrations. It also increased the maximal responses of these parameters to insulin. However, it did not affect insulin binding to adipocytes. The peptide protected insulin considerably from degradation, but this effect alone cannot account for its effect in increasing the maximal responses to the hormone, and even when degradation of a submaximal concentration of insulin was suppressed by bacitracin, the peptide still had an enhancing effect. These results suggest not only that the peptide influences a step distal to receptor-mediated insulin binding but also that inhibition of insulin degradation alone cannot explain its total effect.
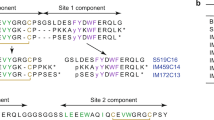
The peptide lost its insulin-stimulating activity completely when it was further digested with V8 or lysinespecific endopeptidase, or when it was reduced and then carboxamidomethylated or oxidized with performic acid. Similar active tryptic fragments were obtained from human and rat albumins.
Insulin-stimulating peptides should be useful in studies on the mechanisms of insulin action including both the sensitivities and responsiveness of target cells to the hormone.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ISP:
-
insulin-stimulating peptide
- HEPES:
-
N-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazine-N′-2-ethanesulfonic acid
- HPLC:
-
high-performance liquid chromatography
- SDS:
-
sodium dodecyl sulfate
References
Arner P, Bolinder J, Ostman J: Marked increase in insulin sensitivity of human fat cells 1 hour after glucose ingestion. J Clin Invest 71: 709–714, 1983.
Livingston JN, Kingston WJ, Finocchiaro L, Moxley III RT: Rapid increase in the insulin sensitivity of rat adipocytes after intravenous glucose administration. Endocrinology 115: 55–59, 1984.
Arakaki N, Oribe T, Ueno A, Inoue H, Takeda Y: Insulinstimulating protein from human plasma. FEBS Lett 177: 217–220, 1984.
Dean B, Peluso I, Harrison LC: A postbinding inhibitor of insulin action: increased concentrations in the plasma of non-insulin-dependent diabetic subjects. Diabetes 33: 450–454, 1984.
Glaser E, Halpern G: Über die Aktivierung des Insulins durch Hefepre\saft. Biochem Z 207: 377–383, 1929.
Duckworth WD, Solomon SS, Kitabchi AE: Effect of chronic sulfonylurea therapy on plasma insulin and proinsulin levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 35: 585–591, 1972.
Chang AY, Wyse BM, Gilchrist BJ, Peterson T, Diani AR: Ciglitazone, a new hypoglycemic agent. I. Studies in ob/ob and db/db mice, diabetic Chinese hamsters, and normal and streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetes 32: 830–838, 1983.
Chipkin RE, Kreutner W, Billard W: Potentiation of the hypoglycemic effect of insulin by thiorphan, an enkephalinase inhibitor. Eur J Pharmacol 102: 151–154, 1984.
Kikuchi K, Larner J, Freer RJ, Day AR: Enhanced specific insulin binding and insulin action with C-terminal B-chain pentapeptide derived from insulin. FEBS Lett 119: 161–164, 1980.
Kikuchi K, Larner J, Freer RJ, Day AR: Effect of insulin fragments on biological activity of insulin and desoctapeptide insulin. I. Potentiation of biological activities. J Biol Chem 256: 9441–9444, 1981.
Kikuchi K, Larne J, Freer RJ, Day AR: Effect of insulin fragments on biological activity of insulin and desoctapeptide insulin. II. Enhanced binding and mechanism studies. J Biol Chem 256: 9445–9449, 1981.
Ng FM, Bornstein J, Pullin CE, Bromley JO, Macaulay SL: The minimal amino acid sequence of the insulinpotentiating fragments of human growth hormone: its mechanism of action. Diabetes 29: 782–787, 1980.
Joost HG, Steinfelder HJ: Modulation of insulin sensitivity by adenosine: effects on glucose transport, lipid synthesis, and insulin receptors of the adipocyte. Mol Pharmacol 22: 614–618, 1982.
Ueno A, Arakaki N, Inoue H, Oribe T, Takeda Y: Insulinstimulating peptide from tryptic digest of bovine serum albumin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 122: 1179–1185, 1984.
Ueno A, Hong Y-M, Arakaki N, Takeda Y: Insulinstimulating peptide from a tryptic digest of bovine serum albumin: purification and characterization. J Biochem (Tokyo) 98: 269–278, 1985.
Brown JR: Structure of bovine serum albumin. Fed Proc Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 34: 591, 1975.
Rodbell M: Metabolism of isolated fat cells. I. Effects of hormones on glucose metabolism and lipolysis. J Biol Chem 239: 375–380, 1964.
Fain JN, Reed N, Saperstein R: The isolation and metabolism of brown fat cells. J Biol Chem 242: 1887–1894, 1967.
Ono M, Inoue H, Suzuki F, Takeda Y: Studies on ornithine decarboxylase from the liver of thioacetamide-treated rats: purification and some properties. Biochim Biophys Acta 284: 285–297, 1972.
Maloff BL, Lockwood DH: In vitro effects of a sulfonylurea on insulin action in adipocytes: potentiation of insulin-stimulated hexose transport. J Clin Invest 68: 85–90, 1981.
Gliemann J, Østerlind K, Vinten J, Gammeltoft S: A procedure for measurement of distribution spaces in isolated fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 286: 1–9, 1972.
Gammeltoft S, Gliemann J: Binding and degradation of 125I-labelled insulin by isolated rat fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 320: 16–32, 1973.
Berson SA, Yalow RS: Quantitative aspects of the reaction between insulin and insulin-binding antibody. J Clin Invest 38: 1996–2016, 1959.
Dole VP, Meinertz H: Microdetermination of long-chain fatty acids in plasma and tissues. J Biol Chem 235: 2595–2599, 1960.
Hirs CHW: Performic acid oxidation. In: CHW Hirs (ed), Methods in Enzymology, Vol 11. Academic Press, New York, 1967, pp 197–199.
Marquardt H, Hunkapiller MW, Hood LE, Twardzik DR, De Larco JE, Stephenson JR, Todaro GJ: Transforming growth factors produced by retrovirus-transformed rodent fibroblasts and human melanoma cells: amino acid sequence homology with epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80: 4684–4688, 1983.
Simpson RJ, Neuberger MR, Liu TY: Complete amino acid analysis of proteins from a single hydrolysate. J Biol Chem 251: 1936–1940, 1976.
Bernstein RS: Insulin insensitivity and altered glucose utilization in cultured rat adipose tissue. J Lipid Res 20: 848–856, 1979.
Desbuquois B, Krug F, Cuatrecasas P: Inhibitors of glucagon inactivation: effect on glucagon-receptor interactions and glucagon-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity in liver cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 343: 101–120, 1974.
LeCam A, Freychet P: Effect of insulin on amino acid transport in isolated rat hepatocytes. Diabetologia 15: 117–123, 1978.
Larner J, Cheng K, Schwartz C, Kikuchi K, Tamura S, Creacy S, Dubler R, Galasko G, Pullin C, Katz M: A proteolytic mechanism for the action of insulin via oligopep tide mediator formation. Fed Proc Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 41: 2724–2729, 1982.
Gliemann J, Sonne O: Binding and receptor-mediated degradation of insulin in adipocytes. J Biol Chem 253: 7857–7863, 1978.
Hammons GT, Smith RM, Jarett L: Inhibition by bacitracin of rat adipocyte plasma membrane degradation of 125I-insulin is associated with an increase in plasma membrane bound insulin and a potentiation of glucose oxidation by adipocytes. J Biol Chem 257: 11563–11570, 1982.
Suzuki K, Kono T: Internalization and degradation of fat cell-bound insulin: separation and partial characterization of subcellular vesicles associated with iodo-insulin. J Biol Chem 254: 9786–9794, 1979.
Cuatrecasas P: Membrane receptors. Annu Rev Biochem 43: 169–214, 1974.
Caro JF, Amatruda JM: Evidence for modulation of insulin action and degradation independently of insulin binding. Am J Physiol 240: E325-E332, 1981.
Donner DB, Nakayama K, Tani S, Lutz U, Sonenberg M: The uptake and degradation of growth hormone fragments by isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem 253: 6717–6723, 1978.
Osborne CK, Monaco ME, Lippman ME, Kahn CR: Correlation among insulin binding, degradation, and biological activity in human breast cancer cells in long-term tissue culture. Cancer Res 38: 94–102, 1978.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ueno, A., Arakaki, N., Oribe, T. et al. Studies on the biological activity of an insulin-stimulating peptide from a tryptic digest of bovine serum albumin. Mol Cell Biochem 70, 121–130 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00229427
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00229427