Summary
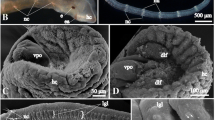
Development of the axon cap neuropil of the Mauthner neuron in post-hatching larval goldfish brains was observed electron-microscopically. The axonal initial segment of newly hatched (day-4) larvae is completely covered with synaptic terminals containing clear spherical synaptic vesicles. Profiles of thin terminal axons, the spiral fibers, containing similar synaptic vesicles, rapidly increase in number around the initial segment and form glomerular neuropil similar to the central core of the adult axon cap by day 7. Three types of synapses are formed in the core neuropil. Bouton-type synapses contacting the initial segment are most abundant in day-4 to-14 larvae; they decrease thereafter and are rare on the distal half of the initial segment of day-40 larvae. Asymmetric axo-axonic synapses are commonly observed between spiral fibers in the core neuropil of day-7 to -19 larvae, but become fewer by day 40. Unique symmetrical axo-axonic synapses showing accumulation of synaptic vesicles on either side of apposed membrane thickenings first appear in day-14 core neuropil, gradually increase in number, and become the predominant type in day-40 core neuropil. Thick myelinated axons, which lose their myelin sheaths in the glial cap cell layer, start to penetrate into the axon cap on day 10. They gradually increase in number and form the peripheral part of the axon cap together with the cap dendrites, which finally grow into the axon cap from the axon hillock region of the Mauthner cell by day 40.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartelmetz GW (1915) Mauthner's cell and the nucleus motorius tegmenti. J Comp Neurol 25:87–128
Bodian D (1937/1938) The structure of the vertebrate synapse. A study of the axon endings of Mauthner's cell and neighboring centers in the goldfish. J Comp Neurol 68:117–159
Cochran SL, Hackett JT, Brown L (1980) The anuran Mauthner cell and its synaptic bed. Neuroscience 5:1629–1646
Eaton RC, Farley RD, Kimmel CB, Schabtach E (1977) Functional development in the Mauthner cell system of embryos and larvae of the zebra fish. J Neurobiol 8:151–172
Faber DS, Korn H (1978) Electrophysiology of the Mauthner cell: Basic properties, synaptic mechanism, and associated networks. In: Faber DS, Korn H (eds) Neurobiology of the Mauthner cell. Raven Press, New York, p. 47–131
Furukawa T (1966) Synaptic interaction at the Mauthner cell of goldfish. Prog Brain Res 21A:44–70
Furukawa T, Furshpan EJ (1963) Two inhibitory mechanisms in the Mauthner neurons of goldfish. J Neurophysiol 26:140–176
Ito R (1980) Fine structure of the axon initial segment and the axon cap of the Mauthner cell in the bullfrog tadpole. Arch Histol Jpn 43:231–240
Kimmel CB, Schabtach E (1974) Patterning in synaptic knobs which connect with Mauthner's cell (Ambystoma mexicanum). J Comp Neurol 156:49–80
Kimmel CB, Sessions SK, Kimmel RJ (1981) Morphogenesis and synaptogenesis of the zebrafish Mauthner neuron. J Comp Neurol 198:101–120
Kohno K (1970) Symmetrical axo-axonic synapses in the axon cap of the goldfish Mauthner cell. Brain Res 23:255–258
Nakajima Y, Kohno K (1978) Fine structure of the Mauthner cell: synaptic topography and comparative study. In: Faber DS, Korn H (eds) Neurobiology of the Mauthner cell. Raven Press, New York, p 133–166
Rock MK (1980) Functional properties of Mauthner cell in the tadpole of Rana catesbeiana. J Neurophysiol 44:135–150
Ronnevi L-O (1977) Spontaneous phagocytosis of boutons on spinal motoneurons during early postnatal development. An electron microscopical study in the cat. J Neurocytol 6:487–504
Stefanelli A, Caravita S (1964) Ultrastruttura dei sistemi sinaptici del neurone di Mauthner di un teleosteo (Brachydanio rerio). Z Zellforsch mikrosk Anat 62:1–15
Triller A, Korn H (1981) Morphologically distinct classes of inhibitory synapses arise from the same neurons: ultrastructural identification from crossed vestibular interneurons intracellularly stained with HRP. J Comp Neurol 203:131–155
Triller A, Korn H (1982) Transmission at a central inhibitory synapse. III. Ultrastructure of physiologically identified and stained terminals. J Neurophysiol 48:708–734
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, R., Kohno, K. Development of the axon cap neuropil of the Mauthner cell in the goldfish. Cell Tissue Res. 237, 49–55 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00229199
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00229199