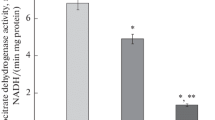
Summary
High protein dietary content stimulates urea formation in ureotelic animals but does not exert almost any effect on ammonia production from L-amino acids in vitro. L-histidine and L-threonine are the only amino acids which are most actively deaminated by ureotelic animals fed on a high protein diet.
All the steps of L-histidine metabolism have been studied: it has been found that both the histidine transaminase pathway and the histidase pathway are stimulated. Glutamic acid is also a product of histidine catabolism through the histidase pathway, but its catabolism is unaffected by the dietary protein content. These data suggest the existence of independent mechanism controlling the catabolism of the two amino acids.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schimke, R. T., 1962. J. Biol. Chem. 237, 459–468.
Schimke, R. T., 1962. J. Biol. Chem. 237, 1921–1924.
Schimke, R. T., 1963. J. Biol. Chem. 238, 1012–1018.
Cedrangolo, F., Zappia, V., Galletti, P., Oliva, A., 1974. Rend. Acc. Naz. Lincei 56, 385–388.
Cedrangolo, F., Illiano, G., Cortese, R., 1971. Rend. Acc. Naz. Lincei 50, 37–39.
Cedrangolo, F., Galletti, P., Federico, A., 1972. Rend. Acc. Naz. Lincei 52, 207–213.
Cedrangolo, F., in The Urea Cycle, 1976. (Grisolia, S., Baguena, R. Mayor, F., eds), 551–567. John Wiley & Sons, New York-London.
Servillo, L., Illiano, G., Arienzo, O., Cedrangolo, F., 1976. Bordeaux, XII Journées Biochimiques Latines, Résumés des communications, 13, A51.
Spolter, P. D., Baldridge, R. C., 1963. J. Biol. Chem. 238, 2071–2074.
Schirmer, M. D., Harper, A. E., 1970. J. Biol. Chem. 245, 1204–1211.
Tabor, H., Mehler, A. H., 1955. Methods in Enzymology, (Colowick, S. P., Kaplan, N. O., eds), Vol. 2, 228–233, Academic Press, New York-London.
Gupta, N. K., Robinson, W. G., 1961. Fed. Proc., 20, 4.
Tabor, H., Wyngarden, L., 1959. J. Biol. Chem. 234, 1830–1846.
Conway, E. J., 1950. Microdiffusion Analysis and Volumetric Error, 3rd ed. Crosby, Lockwood & son Ltd, London.
Cedrangolo, F., Salvatore, F., Cimino, F., Zappia, V., 1965. Enzymologia 29, 143–154.
Strecker, H. J., 1955. Methods in Enzymology, (Colowick, S. P., Kaplan, N. O., eds), Vol. 2, 220–225, Academic Press, New Yoik-London.
Daniels, F., Alberty, R. A., 1975. Physical Chemistry, 4th ed., 311–313, John Wiley & sons, New York-London.
Morris, M. L., Lee, S., 1973. J. Biol. Chem. 248, 1459–1465.
Lamartiniere, C. A., Feigelson, M., 1977. J. Biol. Chem. 252, 3234–3239.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cedrangolo, F., Illiano, G., Servillo, L. et al. Histidine degradation enzymes in rat liver: Induction by high protein intake. Mol Cell Biochem 23, 123–128 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00226232
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00226232