Summary
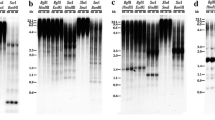
We studied rDNA restriction fragment length polymorphism between two tomato lines used for F1 hybrid seed production: line A, containing the Tm-1 gene responsible for tobacco mosaic virus tolerance introgressed from the wild species Lycopersicon hirsutum, and line B, a tobacco mosaic virus sensitive line. Hybridization patterns led to distinct rDNA maps with two size classes, 10.4 and 10.7 kb, in line A and a single, 8.9-kb class in line B. Size differences were located in the intergenie sequence (IGS). A highly specific 54-bp TaqI fragment was cloned from the line A IGS and used in dot blot experiments to probe total DNA from line A, line B, and their F1 hybrid. It proved capable of discriminating B from A and the hybrid. This probe could thus serve to screen inbreds in commercial seed lots where line A is used as male. This fragment showed 80–90% sequence homology with the 53-bp subrepeats previously characterized in a region of the tomato IGS close to the 25S rRNA gene. Preliminary comparison of rDNA in line A and several wild related species indicated that the L. hirsutum H2 genotype was the closest to line A. rDNA variations between line A and this wild genotype could be explained by recombination during the introgression process involving numerous backcrosses or by an important intraspecific polymorphism. Our results strongly suggest that Tm-1 and the rDNA were introgressed together into tomato from L. hirsutum through linkage drag.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beckmann JS (1988) Oligonucleotide polymorphisms: a new tool for genomic genetics. Biotechnology 6:1061–1065
Beckmann JS, Soller M (1983) Restriction fragment length polymorphisms in genetic improvement: methodologies, mapping, and costs. Theor Appl Genet 67:35–43
Benslimane A, Hartmann C, Buyser J de, Henry Y, Picard E, Rode A (1988) Ribosomal DNA as a convenient probe to follow segregation and possible divergency from expected homozygosity after haploidization of an androgenetic process. Theor Appl Genet 75:389–396
Borisjuk NV, Momot VP, Gleba Y (1988) Novel class of rDNA repeat units in somatic hybrids between Nicotiana and Atropa. Theor Appl Genet 76:108–112
de Courcel A (1989) L'exploitation du polymorphisme moléculaire de l'ADN: un nouvel outil pour la sélection des espèces potagères. PhD thesis, University of Paris-Sud, Orsay
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A plant DNA minipreparation: version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1:19–21
Delseny M, Laroche M, Penon P (1984) Methylation pattern of radish (Raphanus sativus) nuclear ribosomal RNA genes. Plant Physiol 76:627–632
Dobrowolski B, Glund K, Metzlaff M (1989) Cloning of tomato nuclear ribosomal DNA. rDNA organization in leaves and suspension-cultured cells. Plant Sci 60:199–205
Ellis THN, Davies DR, Castleton JA, Bedford ID (1984) The organization and genetics of rDNA length variants in peas. Chromosoma 91:74–81
Flavell RB (1986) The structure and control of expression of ribosomal RNA genes. Oxford Surv Plant Mol Cell Biol 3:251–274
Helentjaris T, Slocum M, Wright S, Schaefer A, Nienhuis J (1986) Construction of genetic linkage maps in maize and tomato using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Theor Appl Genet 72:761–769
Howe G, Aldrich J (1988) Use of oligonucleotide probes to discriminate chloroplast-encoded streptomycin-resistant from streptomycin-sensitive tobacco plants using total DNA minipreps. Plant Mol Biol Rep 6:258–265
Jorgensen RA, Cuellar RE, Thompson WF, Kavanagh TA (1987) Structure and variation in ribosomal RNA genes of pea. Plant Mol Biol 8:3–12
Kiss T, Kis M; Abel S, Solymosy F (1988) Nucleotide sequence of the 17S–25S spacer region from tomato rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res 16:7179
Kiss R, Kis M, Solymosy F (1989 a) Nucleotide sequence of a 25S gene from tomato. Nucleic Acids Res 17:796
Kiss T, Szkukàlek A, Solymosy F (1989b) Nucleotide sequence of a 17S(18S) rRNA gene from tomato. Nucleic Acids Res 17:2127
Long EO, Dawid IB (1980) Repeated genes in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem 49:727–764
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor/NY
May CE, Appels R (1987) Variability and genetics of spacer DNA sequences between the ribosomal RNA genes of hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum) Theor Appl Genet 74:617–624
Polans NO, Weeden NF, Thompson WF (1986) Distribution, inheritance, and linkage relationships of ribosomal DNA spacer length variants in pea. Theor Appl Genet 72:289–295
Primard C, Vedel F, Mathieu C, Pelletier G, Chèvre AM (1988) Interspecific somatic hybridization between Brassica napus and Brassica hirta (Sinapis alba L.) Theor Appl Genet 75:546–552
Rogers SO, Bendich AJ (1987) Ribosomal RNA genes in plants: variability in copy number and in the intergenic spacer. Plant Mol Biol 9:509–520
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KM; Jorgensen RA, Allard RW (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location, and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:8014–8018
San HL, Vedel F, Sihachakr D, Rémy R (1990) Morphological and molecular characterization of fertile tetraploid somatic hybrids produced by protoplast electrofusion and PEG-induced fusion between Lycopersicon esculentum Mill and Lycopersicon peruvianum Mill. Mol Gen Genet 221:17–26
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Sarfatti M, Katan J, Fluhr R, Zamir D (1989) An RFLP marker in tomato linked to the Fusarium oxysporum resistance gene I2. Theor Appl Genet 78:755–759
Schmidt-Puchta W, Günther I, Sänger HL (1989) Nucleotide sequence of the intergenic spacer (IGS) of the tomato ribosomal DNA. Plant Mol Biol 13:251–253
Stevens MA, Rick CM (1987) Genetics and breeding. In: Atherton JG, Rudich J (eds) The tomato crop, a scientific basis for improvement. Chapman and Hall, New York, pp 35–109
Tanksley SD, Mutschler MA, Rick CM (1987) Linkage map of the tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) (2n=24). In: O'Brien SJ (ed) Genetic maps. A compilation of linkage and restriction maps of genetically studied organisms. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor/NY, pp 655–669
Uchimiya H, Ohgawara T, Kato H, Akiyama T, Harada H, Sugiura M (1983) Detection of two different nuclear genomes in parasexual hybrids by ribosomal RNA gene analysis. Theor Appl Genet 64:117–118
Vallejos CE, Tanksley SD, Bernatzky R (1986) Localization in the tomato genome of DNA restriction fragments containing sequences homologous to the rRNA (45S), the major chlorophyll a/b binding polypeptide, and the ribulose biphosphate carboxylase genes. Genetics 112:93–105
Vedel F, Quétier F, Bayen M (1976) Specific cleavage of chloroplast DNA from higher plants by EcoRI restriction nuclease. Nature 263:440–442
Waldron J, Dunsmuir P, Bedbrook J (1983) Characterization of the rDNA repeat units in the Mitchell Petunia genome. Plant Mol Biol 2:57–65
Young ND, Tanksley SD (1989) RFLP analysis of the size of chromosomal segments retained around the Tm-2 locus of tomato during backcross breeding. Theor Appl Genet 77:353–359
Young ND, Zamir D, Ganal MW, Tanksley SD (1988) Use of isogenic lines and simultaneous probing to identify DNA markers tightly linked to the Tm-2a gene in tomato. Genetics 120:579–585
Zamir D, Tanksley SD (1988) Tomato genome is comprised largely of fast-evolving, low-copy-number sequences. Mol Gen Genet 213:254–261
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by H. F. Linskens
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Levesque, H., Vedel, F., Mathieu, C. et al. Identification of a short rDNA spacer sequence highly specific of a tomato line containing Tm-1 gene introgressed from Lycopersicon hirsutum . Theoret. Appl. Genetics 80, 602–608 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224218
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224218