Abstract
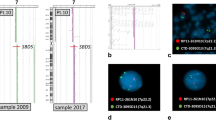
We have used a panel of 13 DNA markers in the distal region of chromosome 14q to characterize deletions in three patients determined cytogenetically to have a ring or terminally deleted chromosome 14. We have characterized one patient with a ring chromosome 14 [r (14) (p13q32.33)] and two with terminal deletions [del (14) (pter→q32.3:)]. The two patients with cytogenetically identical terminal deletions of chromosome 14 were found to differ markedly when characterized with molecular markers. In one patient, none of the markers tested were deleted, indicating that the apparent terminal deletion is actually due to either an undetected interstitial deletion or a cryptic translocation event. In the other patient, the deletion was consistent with the cytogenetic observations. The deleted chromosome was shown to be of paternal origin. The long-arm breakpoint of the ring chromosome was mapped to within a 350-kb region of the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene cluster (IGH). This breakpoint was used to localize markers D14S20 and D14S23, previously thought to lie distal to IGH, to a more proximal location. The ring chromosome represents the smallest region of distal monosomy 14q yet reported.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Byth BC, Cox DW (1993) A (CA)n repeat at the 5′ end of the α1antitrypsin gene. Hum Mol Genet 2:1572
Callen DF, Eyre HJ, Ringenbergs ML, Freemantle CJ, Woodroffe, Haan EA (1991) Chromosomal origin of small ring marker chromosomes in man: characterization by molecular genetics. Am J Hum Genet 48:769–782
Church GM, Gilbert W (1984) Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:1991–1995
Cook GP, Tomlinson IM, Walter G, Riethman H, Carter NP, Buluwela L, Winter G, Rabbitts TH (1994) A map of the human immunoglobulin VH locus completed by analysis of the telomeric region of chromosome 14q. Nature Genet 7:162–168.
Cox DW, Markovic VD, Teshima IE (1982a) Genes for immunoglobulin heavy chains and for α1-antitrypsin are localized to specific regions of chromosome 14q. Nature 297:428–430
Cox DW, Smyth S, Billingsley G (1982b) Three new rare variants of α1antitrypsin. Hum Genet 61:123–126
Cox DW, Woo SLC, Mansfield T (1985) DNA restriction fragments associated with α1-antitrypsin indicate a single origin for deficiency allele PI Z. Nature 316:79–81
Cox DW, Nakamura Y, Gedde-Dahl T Jr (1991) Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of chromosome 14. (11th International Workshop on Human Gene Mapping). Cytogenet Cell Genet 58:605–623
Cox DW, Billingsley G, Nguyen VTT (1994) A linkage map of human chromosome 14, including 13 gene loci. Genomics 23:331–337
Gyapay G, Morissette J, Vignal A, Dib C, Fizames C, Millasseau P, Marc S, Bernardi G, Lathrop M, Weissenbach J (1994) The 1993–1994 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nature Genet 7:246–339
Hoff M, Nakamura Y, Holm T, O'Connell P, Leppert M, Lathrop GM, Lalouel J-M, White R (1988) Isolation and mapping of a polymorphic DNA sequence (pHHH208) on chromosome 14 [D14S19]. Nucleic Acids Res 16:10400
Hofker MH, Smith S, Nakamura Y, Teshima I, White R, Cox DW (1990) Physical mapping of probes within 14q32, a subtelomeric region showing a high recombination frequency. Genomics 6:33–38
Howard PJ, Clark D, Dearlove J (1988) Retinal/macular pigmentation in conjunction with ring 14 chromosome. Hum Genet 80:140–142
Hreidarsson SJ, Stamberg J (1983) Distal monosomy 14 not associated with ring formation. J Med Genet 9:147–149
Kosztolányi G (1987) Does “ring syndrome” exist? An analysis of 207 case reports on patients with a ring autosome. Hum Genet 75:174–179
Kousseff BG, Nichols P, Essig Y-P, Miller K, Weiss A, Tedesco T (1987) Complex chromosome rearrangements and congenital anomalies. Am J Med Genet 26:771–782
Magnani I, Sacchi N, Darfler M, Nisson PE, Tornaghi R, Furman-Conti AM (1993) Identification of the chromosome 14 origin of a C-negative marker associated with a 14q32 deletion by chromosome painting. Clin Genet 43:180–185
Masada CT, Haskins Olney A, Fordyce R, Sanger WG (1989) Partial deletion of 14q and partial duplication of 14q in sibs: testicular mosaicism for t(14q;14q) as a common mechanism. Am J Med Genet 34:528–534
Migone N, Feder J, Cann H, West B van, Hwang J, Takahashi N, Honjo T, Piazza A, Cavalli-Sforza L-L (1983) Multiple DNA fragment polymorphisms associated with immunoglobulin mu chain switch-like regions in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:467–471
Miller BA, Jayakar P, Capó H (1992) Child with multiple congenital anomalies and mosaicism 46,XX/46,XX, del (14) (q32.3). Am J Med Genet 44:635–637
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF (1988) A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res 16:1215
Nakamura Y, Carlson M, Fujimoto E, O'Connell P, Leppert M, Lathrop GM, Lalouel J-M, White R (1988a) Isolation and mapping of a polymorphic DNA sequence (pMCOC12) on chromosome 14 [D14S20]. Nucleic Acids Res 16:6257
Nakamura Y, Krapcho K, Ballard L, O'Connell P, Leppert M, Lathrop GM, Lalouel J-M, White R (1988b) Isolation and mapping of a polymorphic DNA sequence (cKKA39) on chromosome 14 [D14S23]. Nucleic Acids Res 16:3120
Nakamura Y, Culver M, Gill J, O'Connell P, Leppert M, Lathrop GM, Lalouel J-M, White R (1988c) Isolation and mapping of a polymorphic DNA sequence pMLJ14 on chromosome 14 [D14S13]. Nucleic Acids Res 16:381
Nakamura Y, Lathrop M, O'Connell P, Leppert M, Kamboh MI, Lalouel J-M, White R (1989) Frequent recombination is observed in the distal end of the long arm of chromosome 14. Genomics 4:76–81
Nielsen J, Homma A, Rasmussen K, Ried E, Sørenson K, Saldaña-Garcia P (1978) Deletion 14q and pericentric inversion 14. J Med Genet 15:236–238
NIH/CEPH Collaborative Mapping Group (1992) A comprehensive genetic linkage map of the human genome. Science 258:67–76
Pezzolo A, Gimelli G, Cohen A, Lavaggetto A, Romano C, Fogu G, Zuffardi O (1993) Presence of telomeric and subtelomeric sequences at the fusion points of ring chromosomes indicates that the ring syndrome is caused by ring instability. Hum Genet 92:23–27
Shirasaka Y, Ito M, Okuno T, Fujii T, Nozaki K, Mikawa H (1992) Ring 14 chromosome with complex partial seizures: a case report. Brain Dev 14:257–260
Silva AJ, Johnson JP, White RL (1987) Characterization of a highly polymorphic region 5′ to JH in the human immunoglobulin heavy chain. Nucl Acids Res 15:3845–3856
Telford N, Thomson DAG, Griffiths MJ, Ilett S, Watt JL (1990) Terminal deletion (14)(q32.3): a new case. J Med Genet 27:261–263
Uehara S, Akai Y, Takeyama Y, Okamura K, Takabayashi T, Ya-jima A, Natsui M, Nakai H (1993) A case of a female infant with simultaneous occurrence of de novo terminal deletions on chromosome 14q and 20p. Clin Genet 43:28–33
Walter MA, Linsley PS, Cox DW (1987) ApaI polymorphism of a human immunoglobulin VH3 subclass locus. Nucleic Acids Res 15:4697
Walter MA, Surti U, Hofker MH, Cox DW (1990) The physical organization of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain gene complex. EMBO J 9:3303–3313
Wang HS, Allanson JE (1992) A further case of terminal deletion (14) (q32.2) in a child with mild dysmorphic features. Ann Génét 35:171–173
Wang Z, Weber JL (1992) Continuous linkage map of human chromosome 14 short tandem repeat polymorphisms. Genomics 13:532–536
Weissenbach J, Gyapay G, Dib C, Vignal A, Morissette J, Mil-lasseau P, Vaysseix G, Lathrop M (1992) A second-generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature 359:794–801
Williams SR, Goddard JM, Martin DW (1984) Human purine nucleoside phosphorylase cDNA sequence and genomic clone characterization. Nucleic Acids Res 12:5779–5787
Wintle RF, Cox DW (1994) Mapping of human immunoglobulin heavy chain variable gene segments outside the major IGH locus. Genomics 23:151–157
Wyman A, White R (1980) A highly polymorphic locus in human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:6754–6758
Yen F-S, Podruch PE, Weisskopf B (1989) A terminal deletion (14)(q31.1) in a child with microcephaly, narrow palate, gingival hypertrophy, protuberant ears, and mild mental retardation. J Med Genet 26:130–133
Zelante L, Torricelli F, Calvano S, Mingarelli R, Dallapiccola B (1991) Ring chromosome 14 syndrome. Ann Génét 34:93–97
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wintle, R.F., Costa, T., Haslam, R.H.A. et al. Molecular analysis redefines three human chromosome 14 deletions. Hum Genet 95, 495–500 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00223859
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00223859