Summary
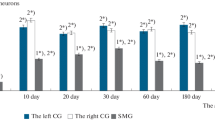
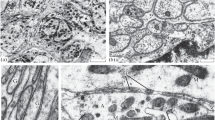
The regeneration of monoaminergic neurons in the cerebral (supraesophageal) ganglion of the earthworm, Allolobophora caliginosa, was studied by the fluorescence method of Falck-Hillarp 3, 4, 5, and 6 weeks after extirpation of the ganglion. The monoamine fluorophores in control and regenerating cerebral ganglia were estimated by microspectrofluorimetric analysis. In the control animals catecholaminergic (noradrenergic, dopaminergic) and indolaminergic (5-HT/5-HTP) neurons were observed. Four weeks after the removal of the cerebral ganglia, two types of monoamine-containing neurons reappeared. Microspectrofluorimetrically dopaminergic and indolaminergic perikarya were identified. Reconstructions from serial sections and counts of the regenerated fluorescent cells showed no further increase in the number of these cells between the 5th and 6th postoperative weeks. In the 5- and 6-week groups the intrinsic and afferent aminergic pathways of the cerebral ganglion were reestablished.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aros, B.: Synapses in the neurosecretory system of the earthworm. VI. Intern. Symp. on Neurosecretion, London 1973 (Abstr.)
Aros, B., Vigh, B.: Regeneration of the neurosecretory system of the cerebral ganglion in the earthworm (Lumbricus terrestris), Acta biol. Acad. Sci. hung. 13, 323–337 (1962)
Bianchi, S.: Sur la présence d'un matériel fluorescent dans les cellules nerveuses des ganglions du système nerveux central de quelques Oligochètes recherches histochimiques et d'histo-spectrographie de fluorescence. Ann. Histochem., Suppl. 2, 143–146 (1962)
Bianchi, S.: The amine secreting neurons in the central nervous system of the earthworm (Octolasium complanatum) and their possible neurosecretory role. Gen. comp. Endocr. 9, 343–348 (1967)
Björklund, A., Ehinger, E., Falck, B.: A method for differentiating dopamine from noradrenaline in tissue sections by microspectrofluorimetry. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 16, 263–270 (1968)
Björklund, A., Ehinger, B., Falck, B.: Analysis of fluorescence excitation peak ratios for the cellular identification of noradrenaline, dopamine or their mixtures. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 20, 56–64 (1972a)
Björklund, A., Falck, B., Owman, C.: Fluorescence microscopic and microspectrofluorimetric techniques for the cellular localization and characterization of biogenic amines. In: S. Barson (ed.), Methods of investigative and diagnostic endocrinology, vol. 1: The thyroid and biogenic amines, ed. by J. E. Rall and I. J. Kopin. Amsterdam: North-Holland Publishing Company 1972b
Björklund, A., Falck, B., Stenevi, U.: Microspectrofluorimetric characterization of monoamines in the central nervous system; evidence for a new neuronal monoamine-like compound. Progr. Brain Res. 34, 63–73 (1971)
Calas, A., Hartwig, H. G., Collin, J. P.: Noradrenergic innervation of the median eminence. Microspectrofluorimetric and pharmacological study in the duck, Anas platyrhynchos. Cell Tiss. Res. 147, 491–504 (1974)
Ehinger, B., Myhrberg, H. E.: Neuronal localization of dopamine, noradrenaline, and 5-hydroxytryptamine in the central and peripheral nervous system of Lumbricus terrestris (L.). Histochemie 28, 265–275 (1971)
Falck, B., Hillarp, N.-A., Thieme, G., Torp, A.: Fluorescence of catecholamines and related compounds condensed with formaldehyde. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 10, 348–354 (1962)
Hartwig, H. G.: Unpublished results.
Herlant-Meewis, H.: Phénomènes neurosécrétoires et ponte chez Eisenia foetida (Sav.). C. R. Acad. Sci. (Paris) 243, 823–825 (1956)
Herlant-Meewis, H.: Régénération du système nerveux chez Eisenia foetida (Sav.). Bull. Biol. France et Belg. 95, 695–730 (1961)
Herlant-Meewis, H.: Neurosecretory phenomena during regeneration of nervous centres in Eisenia foetida. In: Neurosecretion, ed. by H. Heller and R. B. Clark, 267–273. London and New York: Acad. Press (1962)
Hubl, H.: Beiträge zur Kenntnis der Regenerationsvorgänge bei Lumbriciden. Wilhelm Roux' Arch. Entwickl.-Mech. Org. 145, 508–527 (1952)
Hubl, H.: Über die Beziehungen der Neurosekretion zum Regenerationsgeschehen bei Lumbriciden nebst Beschreibung eines neuartigen neurosekretorischen Zelltyps im Unterschlund-ganglion. Wilhelm Roux' Arch. Entwickl.-Mech. Org. 149, 73–87 (1956)
Koritsánszky, S.: Identification of monoaminergic neurons by azan-staining in the cerebral ganglion of the earthworm, Allolobophora caliginosa. Cell Tiss. Res. 149, 137–141 (1974)
Meiniel, A., Collin, J. P., Hartwig, H. G.: Pinéale et troisième oeil de Lacerta vivipara (J.) au cours de la vie embryonnaire et postnatale. Étude cytophysiologique des monoamines en microscopie de fluorescence et en microspectrofluorimétrie. Z. Zellforsch. 144, 89–116 (1973)
Myhrberg, H. E.: Monoaminergic mechanisms in the nervous system of Lumbricus terrestris (L.). Z. Zellforsch. 81, 311–343 (1967)
Ritzén, M.: Cytochemical identification and quantitation of biogenic monoamines. — A microspectrofluorimetric and autoradiographic study. M. D.-thesis, Stockholm 1967
Rude, S.: Monoamine-containing neurons in the nerve cord and body wall of Lumbricus terrestris. J. comp. Neurol. 128, 397–412 (1966)
Scharrer, E., Scharrer, B.: Neuroendocrinology. New York and London: Columbia University Press 1963
Teichmann, I., Aros, B.: Fluorescence microscopic demonstration of catecholamine containing nerve cells and fibers in the central nervous system of invertebrates. Acta. morph. Acad. Sci. hung. 14, 350 (1966)
Zimmermann, P.: Die zentralnervöse Kontrolle der Dehydration bei Lumbricus terrestris L. Z. Zellforsch. 112, 551–571 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by a fellowship from the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation, Federal Republic of Germany, 1973 (S. K.), and by a grant from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (H.G.H.).
The authors are indebted to Professor A. Oksche for his interest in their studies, to Miss I. Lyncker for assistance with the microspectrofluorimetric recordings, to Miss D. Vaihinger for preparing the graphs, to Dr. W. Möller for sharing technical experience, and to Mr. W. Kramer for technical assistance.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koritsánszky, S., Hartwig, H.G. The regeneration of the monoaminergic system in the cerebral ganglion of the earthworm, Allolobophora caliginosa . Cell Tissue Res. 151, 171–186 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222221
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222221