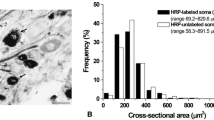
Summary
The carotid body of the rat consists of “glomera” interspersed by blood vessels and nerve bundles. Each “glomus” consists of 2–12 Type I cells, incompletely invested by 1–3 Type II cells. Type I cells are characterised by the presence of numerous dense cored vesicles in their cytoplasm and may exhibit “synaptic”-like contacts with each other.
Small efferent nerve endings make synaptic contact with one or more Type I cells. Large cup-shaped afferent nerve endings make multiple synaptic contacts of two kinds with one or more Type I cells. A second kind of efferent nerve ending is occasionally seen in synaptic contact with one of these afferent nerve endings.
A model for the mode of operation of the glomus as a chemoreceptor is proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott, C. P., Daly, M., de Burgh, Howe, A.: Early ultrastructural changes in the carotid body after degenerative section of the carotid sinus nerve in the cat. Acta anat. (Basel) 83, 161–185 (1972)
Battaglia, G.: Ricerche ultrastrutturali sul glomo carotideo del ratto. Arch. ital. Anat. Embriol. 73, 155–186 (1968)
Biscoe, T. J.: Carotid body: Structure and function. Physiol. Rev. 51, 437–495 (1971)
Biscoe, T. J., Lal, A., Sampson, S. R.: Electron microscopic and electrophysiological studies on the carotid body following intracranial section of the glossopharyngeal nerve. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 208, 133–152 (1970)
Biscoe, T. J., Pallot, D.: Serial reconstruction with the electron microscope of carotid body tissue. The type 1 cell nerve supply. Experientia (Basel) 28, 33–34 (1972)
Biscoe, T. J., Stebhens, W. E.: Ultrastructure of the carotid body. J. Cell Biol. 30, 563–578 (1966)
Blümke, S., Rode, J., Niedorf, H. R.: The carotid body after oxygen deficiency. Z. Zellforsch. 80, 52–77 (1967)
De Castro, F.: Sur la structure et l'innervation du sinus carotidien de l'homme et des mammifères. Nouveaux faits sur l'innervation et la fonction du glomus caroticum. Etudes anatomiques et physiologiques. Trab. Lab. Invest, biol. Univ. Madr. 25, 331–380 (1928)
De Kock, L. L., Dunn, A. E. G.: An electron microscope study of the carotid body. Acta anat. (Basel) 64, 163–178 (1966)
De Robertis, E. D. P.: Synaptic complexes and synaptic vesicles as structural and biochemical units of the central nervous system. In: Nerve as a tissue, eds. K. Rodahl and B. Issekutz, p. 88–115. New York: Hoeber 1966
De Robertis, E. D. P., Bennett, H. S.: Some features of the submicroscopic morphology of synapses in frog and earthworm. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 1, 47–58 (1955)
Eccles, J. C.: The physiology of synapses. Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1964
Gray, E. G.: Axo-somatic and axo-dendritic synapses of the cerebral cortex: An electron microscope study. J. Anat. (Lond.) 93, 420–433 (1959)
Gray, E. G.: A morphological basis for presynaptic inhibition? Nature (Lond.) 198, 82–83 (1962)
Gray, E. G.: Electron microscopy of presynaptic organelles of the spinal cord. J. Anat. (Lond.) 97, 101–106 (1963)
Höglund, R.: An ultrastructural study of the carotid body of horse and dog. Z. Zellforsch. 76, 568–576 (1967)
Hoffman, H., Birrell, J. H. W.: The carotid body in normal and anoxic states: an electron microscope study. Acta anat. (Basel) 32, 297–311 (1958)
Howe, A., Neil, E.: Arterial chemoreceptors. In: Handbook of sensory physiology, vol. 111/1, Enteroceptors, ed. E. Neil. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1971
Kobayashi, S., Uehara, M.: Occurrence of afferent synaptic complexes in the carotid body of the mouse. Arch, histol. jap. 32, 193–201 (1970)
Kondo, H.: An electron microscopic study on innervation of the carotid body of guinea pig. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 37, 544–562 (1971)
Matthews, M. R., Raisman, G.: The ultrastructure and somatic efferent synapses of small granule containing cells in the superior cervical ganglion. J. Anat. (Lond.) 105, 255–282 (1969)
McDonald, D. M., Mitchell, R. A.: A quantitative analysis of synaptic connections in the rat carotid body. In: The peripheral arterial chemoreceptors, ed. M. J. Purves. Cambridge: University Press (in press)
Millonig, G.: Advantages of a phosphate buffer for osmium tetroxide solutions in fixation. J. appl. Physiol. 32, 1637 (1961)
Mullinger, A. M.: The fine structure of ampullary electric receptors in Amiurus. Proc. roy. Soc. B 160, 345–358 (1964)
Palade, G. E., Palay, S. L.: Electron microscope observations of interneuronal and neuromuscular synapses. Anat. Rec. 118, 335–336 (1954)
Peters, A., Palay, S. L., Webster, H. de F.: The fine structure of the nervous system. The cells and their processes. New York: Hoeber 1970
Reynolds, E. S.: The use of lead citrate of high pH as an electron opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208–213 (1963)
Sampson, S. R., Biscoe, T. J.: Efferent control of the carotid body chemoreceptor. Experientia (Basel) 26, 261–262 (1970)
Verna, A.: Infra-structure des divers types de terminaisons nerveuses dans le glomus carotidien du lapin. J. Microscopie 10, 59–66 (1971)
Verna, A.: Terminaisons nerveuses afférentes et efférentes dans le glomus carotidien du lapin. J. Microscopie 16, 299–308 (1973)
Watson, M. L.: Staining of tissue sections for electron microscopy with heavy metals. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 4, 475 (1958)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by a Research Fellowship from the British Heart Foundation (Miriam Morgan) and a Science Research Council Studentship (R. J. Pack).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morgan, M., Pack, R.J. & Howe, A. Nerve endings in rat carotid body. Cell Tissue Res. 157, 255–272 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222070
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222070