Abstract
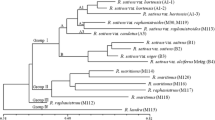
Randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers were used to estimate intra- and interspecific variations in the genus Lens (lentil). Twenty cultivars of L. culinaris ssp. culinaris, including 11 microsperma (small-seeded) and nine macrosperma (large-seeded) types, and 16 wild relatives (four accessions each of L. culinaris ssp. orientalis, L. odemensis, L. nigricans and L. ervoides), were evaluated for genetic variability using a set of 40 random 10-mer primers. Fifty reproducibly scorable DNA bands were observed from ten of the primers, 90% of which were polymorphic. Genetic distances between each of the accessions were calculated from simple matching coefficients. A dendrogram showing genetic relationships between them was constructed by an unweighted pair-group method with arithmetical averages (UPGMA). This study revealed that (1) expect for L. ervoides, the level of intraspecific variation in cultivated lentil is lower than that in wild species, (2) L. culinaris ssp. orientalis is the most likely candidate for a progenitor of the cultivated species, and (3) microsperma and macrosperma cultivars were indistinguishable by the RAPD markers identified here.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barulina H (1930) Lentils of the USSR and of other countries. Bull Appl Bot Plant Breed, Suppl 40:1–319
Castiglione S, Wang G, Damiani G, Bandi C, Bisoffi S, Sala F (1993) RAPD fingerprints for identification and for taxonomic studies of elite poplar (Populus spp.) clones. Theor Appl Genet 87:54–59
Fukuoka S, Hosaka K, Kamijima O (1992) Use of random amplified polymorphic DNAs (RAPDs) for identification of rice accessions. Jpn J Genet 67:243–252
González JM, Ferrer E (1993) Random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis in Hordeum species. Genome 36:1029–1031
Havey MJ, Muehlbauer FJ (1989) Variability for restriction fragment lengths and phylogenesis in lentil. Theor Appl Genet 77:839–843
Hoffman DL, Soltis DE, Muehlbauer FJ, Ladizinsky G (1986) Isozyme polymorphism in Lens (Leguminosae). Systematic Bot 11:392–402
Jain A, Bhatia S, Banga SS, Prakash S, Lakshmikumaran M (1994) Potential use of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) technique to study the genetic diversity in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) and its relationship to heterosis. Theor Appl Genet 88:116–122
Koller B, Lehmann A, McDermott JM, Gessler C (1993) Identification of apple cultivars using RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 85:901–904
Kresovich S, Williams JGK, McFerson JR, Routman EJ, Schaal BA (1992) Characterization of genetic identities and relationships of Brassica oleracea L. via a random amplified polymorphic DNA assay. Theor Appl Genet 85:190–196
Ladizinsky G (1979a) The origin of lentil and its wild genepool. Euphytica 28:179–187
Ladizinsky G (1979b) Species relationships in the genus Lens as indicated by seed-protein electrophoresis. Bot Gaz 140:449–451
Ladizinsky G (1993) Wild lentil. Crit Rev Plant Sci 12:169–184
Ladizinsky G, Braun D, Goshen D, Muehlbauer FJ (1984) The biological species of the genus Lens L. Bot Gaz 145:253–261
Mailer RJ, Scarth R, Fristensky B (1994) Discrimination among cultivars of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) using DNA polymorphisms amplified from arbitrary primers. Theor Appl Genet 87:697–704
Mayer MS, Soltis PS (1994) Chloroplast DNA phytogeny of Lens (Leguminosae): origin and diversity of the cultivated lentil. Theor Appl Genet 87:773–781
Mori M, Hosaka K, Umemura Y, Kaneda C (1993) Rapid identification of Japanese potato cultivars by RAPDs. Jpn J Genet 68:167–174
Muench DG, Slinkard AE, Scoles GJ (1991) Determination of genetic variation and taxonomy in lentil (Lens Miller) species by chloroplast DNA polymorphism. Euphytica 56:213–218
Murai K, Tsunewaki K (1986) Phylogenetic relationships between Avena species revealed by the restriction endonuclease analysis of chloroplast and mitochondrial DNAs. In: Lawes DA, Thomas H (eds) Proc 2nd Int Oats Conf. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, Dordrecht Boston Lancaster, pp 34–38
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Pinkas R, Zamir D, Ladizinsky G (1985) Allozyme divergence and evolution in the genus Lens. P1 Syst Evol 151:131–140
Sneath PHA, Sokal RR (1973) Numerical taxonomy. The principles and practice of numerical classification. W. H. Freeman and Co, San Francisco
Song KM, Osborn TC, Williams PH (1988) Brassica taxonomy based on nuclear restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RELPs). 1. Genome evolution of diploid and amphidiploid species. Theor Appl Genet 75:784–794
Stiles JI, Lemme C, Sondur S, Morshidi MB, Manshardt R (1993) Using randomly amplified polymorphic DNA for evaluating genetic relationships among papaya cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 85:697–701
Tinker NA, Fortin MG, Mather DE (1993) Random amplified polymorphic DNA and pedigree relationships in spring barley. Theor Appl Genet 85:976–984
Welsh J, McClelland M (1990) Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:7213–7218
Wilkie SE, Isaac PG, Slater RJ (1993) Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers for genetic analysis in Allium. Theor Appl Genet 86:497–504
Williams CE, Clair DAS (1993) Phenetic relationships and levels of variability detected by restriction fragment length polymorphism and random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis of cultivated and wild accessions of Lycopersicon esculentum. Genome 36:619–630
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Williams JT, Sanchez AMC, Jackson MT (1974) Studies on lentils and their variation. I. The taxonomy of the species. SABRAO J 6:133–145
Yu LX, Nguyen HT (1994) Genetic variation detected with RAPD markers among upland and lowland rice cultivars (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 87:668–672
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. Mackey
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abo-elwafa, A., Murai, K. & Shimada, T. Intra- and inter-specific variations in Lens revealed by RAPD markers. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 90, 335–340 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221974
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221974