Summary
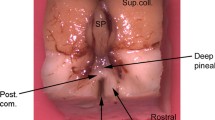
The bovine subcommissural organ was studied by using scanning electron microscopy. The most prominent finding was the existence of protruded and dilated endings of the ependymal cells. The majority of these cells were ciliated with two or more cilia; only a few unciliated cells were seen. Some pore-like structures were also seen on the surface.
From the functional point of view, the most interesting finding was an amorphous heterogeneous material on the subcommissural ependyma. Especially in the caudal part of the organ this material accumulated in abundance. No real filamentous structures such as Reissner's fibre could be seen, however, it was assumed that the heterogeneous material corresponds to this formation. No supraependymal neurones were demonstrated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agduhr, E.: Über ein zentrales Sinnesorgan (?) bei den Vertebraten. Z. Anat. Entwickl.-Gesch. 66, 223–245 (1922)
Allen, D.J., Low, F.N.: The ependymal surface of the lateral ventricle of the dog as revealed by scanning electron microscopy. Amer. J. Anat. 137, 483–489 (1973)
Clementi, F., Marini, D.: The surface of the walls of cerebral ventricles and of choroid plexus in the cat. Z. Zellforsch. 123, 82–95 (1972)
Isomäki, A.M., Kivalo, E., Talanti, S.: Electronmicroscopic structure of the subcommissural organ in the calf (Bos taurus), with special reference to secretory phenomena. Ann. Acad. Sci. Fenn. A 5, No. 111, 1–64 (1965)
Krabbe, K.: L'organe sous-commissural du cerveau chez les mammifères. Kungl. Dansk. Vidensk. Selsk. Biol. Med. 5, 1–83 (1925)
Kozlowski, G.P., Scott, D.E., Murphy, J.A.: Scanning electron microscopy of the lateral ventricles of sheep. Amer. J. Anat. 135, 561–566 (1972)
Leonhardt, H., Lindemann, B.: Über ein supraependymales Nervenzell-, Axon- und Gliazellsystem. Z. Zellforsch. 139, 285–302 (1973)
Noack, W., Dumitrescu, L., Schweichel, J.U.: Scanning and electron microscopical investigations of the surface structures of the lateral ventricles in the cat. Brain Res. 46, 121–129 (1972)
Oksche, A.: Studien am Subkommissuralorgan. Verh. Anat. Ges. Jena. Anat. Anz. 105 (Suppl.), 392–404 (1959)
Oksche, A.: Vergleichende Untersuchungen über die sekretorische Aktivität des Subkommissuralorgans und die Gliacharakter seiner Zellen. Z. Zellforsch. 54, 549–612 (1961)
Olsson, R.: The subcommissural organ. Thesis, Stockholm (1958)
Palkovits, M.: Morphology and function of the subcommissural organ. Studia Biol. Hung. 4, 1–105 (1965)
Reichold, S.: Untersuchungen über die Morphologie des subfornicalen und des subcommissuralen Organs bei Säugetieren und Sauropsiden. Z. mikr.-anat. Forsch. 52, 455–479 (1942)
Schechter, J., Weiner, R.: Ultrastructural changes in the ependymal lining of the median eminence following the intraventricular administration of catecholamine. Anat. Rec. 172, 643–650 (1972)
Scott, D.E., Paull, W.K., Dudley, G.K.: A comparative scanning electron microscopic analysis of the human cerebral ventricular system. I. The third ventricle. Z. Zellforsch. 132, 203–215 (1972)
Sterba, G.: Subcommissuralorgan und Liquorregulation. Biol. Rundschau 10, 309–324 (1972)
Talanti, S.: Studies on the subcommissural organ in some domestic animals with reference to the secretory phenomena. Ann. Med. exp. Fenn. 36, (suppl.), 1–97 (1958)
Vigh-Teichmann, I., Vigh, B., Aros, B.: Liquor-Kontaktneurone im Nucleus infundibularis des Kükens. Z. Zellforsch. 112, 188–200 (1971)
Vigh-Teichmann, I., Vigh, B., Koritsánszky, S.: Liquor-Kontaktneurone im Nucleus paraventricularis. Z. Zellforsch. 103, 483–501 (1970)
Weindl, A., Joynt, R.J.: Ultrastructure of the ventricular walls. Arch. Neurol. (Chic.) 26, 420–427 (1972)
Weindl, A., Schinko, I.: Evidence by scanning electron microscopy for ependymal secretion into the cerebrospinal fluid and formation of Reissner's fiber by the subcommissural organ. Brain Res. 88, 319–324 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindberg, L.A., Talanti, S. The surface fine structure of the bovine subcommissural organ. Cell Tissue Res. 163, 125–132 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221721
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221721