Abstract
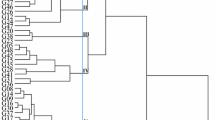
A preliminary genetic map of the dioecious species Asparagus officinalis L. (2n = 20) has been constructed on the basis of restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) and isozyme marker data. With DNA samples digested with either EcoRI or HindIII 61 out of 148 probes (41%) identified RFLPs in six families of doubled haploid lines obtained through anther culture. A higher level of polymorphism (65%) was observed when a single family was screened for RFLPs using six distinct restriction enzymes. Segregation analysis of the BC progenies (40–80 individuals) resulted in a 418-cM extended map comprising 43 markers: 39 RFLPs, three isozymes and one morphological (sex). These markers are clustered in 12 linkage groups and four of them exhibited significant deviations from the expected 1∶1 ratio. One isozyme and three RFLP markers were assigned to the sex chromosome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beckman J, Soller M (1983) Restriction fragment length polymorphisms in genetic improvement: methodologies, mapping and costs. Theor Appl Genet 67:35–43
Bernatsky R, Tanksley S (1986) Toward a saturated linkage map in tomato based on isozymes and random cDNA sequences. Genetics 112:887–898
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1985) In:Molecular biology of plants. In: Malmberg R, Messing J, Sussex I (eds) A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, pp 36–37
Galli MG, Bracale M, Falavigna A, Soave C (1988) Sexual differentiation in Asparagus officinalis. I. DNA characterization and mRNA activities in male and female flowers. Sex Plant Reprod 1:202–207
Gebhardt C, Ritter E, Debner T, Schachtschabel V, Walkemeier B, Uhrig H, Salamini F (1989) RFLP analysis and linkage mapping in Solanum tuberosum. Theor Appl Genet 78:65–75
Havey MJ, Muehlbauer FJ (1989) Linkage between restriction fragment length, isozyme, and morphological markers in lentil. Theor Appl Genet 77:395–401
Helentjaris T, King G, Slocum M, Siedenstrang C, Wegman S (1985) Restriction fragment polymorphisms as probes for plant diversity and their development as tools for applied plant breeding. Plant Mol Biol 5:109–118
Helentjaris T, Slocum M, Wright S, Schaefer A, Nienhuis J (1986) Construction of genetic linkage maps in maize and tomato using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Theor Appl Genet 72:761–766
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: An interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 34:543–552
Landry BS, Kesseli RV, Farrara B, Michelmore R (1987) A genetic map of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) with restriction fragment length polymorphism, isozyme, disease resistance and morphological markers. Genetics 116:331–337
Lark GK, Weisemann JM, Matthews BF, Palmer R, Case K, Macalma T (1993) A genetic map of soybean (Glycine max L.) using an intraspecific cross of two cultivars: “Minosy” and “Noir 1”. Theor Appl Genet 86:901–906
Larkin PJ and Scowcroft WR (1981) Somatoclonal variation — a novel source of variability from cell cultures to plant improvement. Theor Appl Genet 60:197–214
Loptien H (1979) Identification of the sex-chromosome pair in asparagus (Asparagus officinalis L.). Z Pflanzenzucht 82:162–173
Maestri E, Restivo FM, Marziani Longo GP, Falavigna A, Tassi F (1991) Isozyme gene markers in the dioecious species Asparagus officinalis L. Theor Appl Genet 81:613–618
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbour, New York
Marks M (1973) A reconsideration of the genetic mechanism for sex determination in Asparagus officinalis. Proc Eucarpia Meeting on Asparagus, Versailles, pp 122–128
Matzke M, Matzke AJM (1993) Genomic imprinting in plants: parental effects and trans-inactivation phenomena. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 44:53–76
McCouch SR, Kochert G, Yu ZH, Wang ZY, Kush GS, Coffman WR, Tanksley SD (1988) Molecular mapping of rice chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 76:815–829
Slocum MK, Figdore SS, Kennard WC, Suzuki JY, Osborn TC (1990) Linkage arrangement of restriction fragment length polymorphism loci in Brassica oleracea. Theor Appl Genet 80:57–64
Soller M, Beckman J (1983) Genetic polymorphism in varietal identification and genetic improvement. Theor Appl Genet 67:25–33
Tanksley SD (1983) Molecular markers in plant breeding. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1:3–8
Tanksley SD, Rick C (1980) Isozymic gene linkage map of tomato: applications in genetics and breeding. Theor Appl Genet 57:161–170
Vallejos CE, Sakiyama MS, Chase CD (1992) A molecular marker-based linkage map of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Genetics 131:733–740
Van Ooijen JW (1994) DrawMap: a computer program for drawing genetic linkage maps. J Hered 85:66
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by F. Salamini
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Restivo, F.M., Tassi, F., Biffi, R. et al. Linkage Arrangement of RFLP loci in progenies from crosses between doubled haploid Asparagus officinalis L. clones. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 90, 124–128 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221005
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221005