Abstract
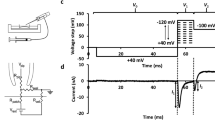
Intracellular pH (pHi) and Na (ana i) were recorded in isolated sheep cardiac Purkinje fibres using ion-selective microelectrodes while simultaneously recording twitch tension. A fall of (pHi) stimulated acid-extrusion via sarcolemmal Na-H exchange but the extrusion was inhibited by reducing extracellular pH (pHo), indicating an inhibitory effect of external H ions upon the exchanger. Intracellular acidosis can reduce contraction by directly reducing myofibrillar Ca2− sensitivity. The activation of Na-H exchange at low (pHi) can offset this direct inhibitory effect of H− ions since exchange-activation elevates ana i which then indirectly elevates Cai 2+ (via Na-Ca exchange) thus tending to restore tension. This protection of contraction during intracellular acidosis can be removed if extracellular (pHi) is also allowed to fall since, under these conditions, Na-H exchange is inhibited.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aronson PS: Kinetic properties of the plasma membrane Na+-H+ exchanger. Annual Review of Physiology 47: 545–560, 1988
Bountra C, Kaila K, Vaughan-Jones RD: Effect of repetitive activity upon intracellular pH, sodium and contraction in sheep cardiac Purkinje fibres. Journal of Physiology 398: 341–360, 1988
Bountra C, Vaughan-Jones RD: Effect of intracellular acidosis on contraction in mammalian cardiac muscle in vitro. Journal of Physiology 407, 1989
Deitmer JW, Ellis D: Interactions between the regulation of the intracellular pH and sodium activity of sheep cardiac Purkinje fibres. Journal of Physiology 304: 471–488, 1980
de Hemptinne A, Marrannes R, Vanheel B: Double-barrelled intracellular (pHi) electrode: construction and illustration of some results. In: Intracellular pH: its measurement, regulation and utilization in cellular functions. R. Nuccitelli, D. Deamer (eds), Alan R. Liss Inc. NY, 1980, p. 7–19
Ellis D, MacLeod KT: Sodium dependent control of intracellular (pHi) in Purkinje fibres of sheep heart. Journal of Physiology 359: 81–105, 1985
Eisner DA, Lederer WJ, Vaughan-Jones RD: The quantitative relationship between twitch tension and intracellular sodium activity in sheep cardiac Purkinje fibres. Journal of Physiology 355: 251–266, 1984
Fabiato A, Fabiato F: Effects of pH on the myofilaments and the sarcoplasmic reticulum of skinned cells from cardiac and skeletal muscles. Journal of Physiology 276: 233–255, 1978
Frelin C, Vigne P, Lazdunski M: The role of Na+/H+ exchange system in the regulation of the internal pH in cultured cardiac cells. European Journal of Biochemistry 149: 1–4, 1985
Gaskell WH: On the tonicity of the heart and blood vessels. Journal of Physiology 3: 48–75, 1980
Green J, Yamaguchi DT, Kleeman CR, Muallen S: Cytosolic (pHi) regulation in osteoblasts. Interaction of Na+ and H+ with the extracellular and intracellular faces of the Na+/H+ exchanger. Journal of General Physiology 92: 239–261, 1988
Jean T, Frelin C, Vigne P, Barbry P, Lazdunski M: Biochemical properties of the Na+/H+ exchange system in rat brain synaptosomes. J Biol Chem 260: 9678–9684, 1985
Kaila K, Vaughan-Jones RD: Influence of sodium-hydrogen exchange on intracellular pH, sodium and tension in sheep cardiac Purkinje fibres. Journal of Physiology 390: 93–118, 1987
Roos A, Boron WJ: Intracellular pH. Physiological Reviews 61: 296–434, 1981
Vaughan-Jones RD, Eisner DA, Lederer WJ: Effects of changes of intracellular pH on contraction in sheep cardiac Purkinje fibres. Journal of General Physiology 89: 1015–1032, 1987
Vanghan-Jones RD: Regulation of intracellular pH in cardiac muscle. In: Proton passage across cell membranes. Wiley, Chichester, 1988. Ciba Foundation Symposium 139, p. 23–46
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vaughan-Jones, R.D., Wu, ML. & Bountral, C. Sodium-hydrogen exchange and its role in controlling contractility during acidosis in cardiac muscle. Mol Cell Biochem 89, 157–162 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00220769
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00220769