Summary
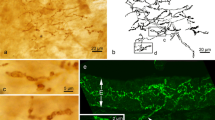
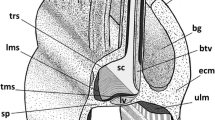
The structure of the neurohypophysis of Poecilia latipinna (green molly, sailfin molly) was studied with the electron microscope. Profile diameters of neurosecretory granules in the non-myelinated neurohypophysial nerve fibres were measured and mathematically corrected for error due to section thickness. Six different types of nerve fibres could be distinguished by statistical classification of their granules and by other ultrastructural features. One fibre-type (type B) contained granules with a mean diameter of 85 nm, and the other five types (types Ala, Alb, A2, A3 and A4) all contained granules with mean diameters greater than 100 nm. Synaptic contacts were observed between type B fibres and all the adenohypophysial cell-types, although in the case of the ACTH cells the synapses were separated from the cell membrane by a continuous double basement membrane. Type A fibres were observed to contact the cells of the proximal pars distalis and pars intermedia, but did not form synapses. However, synapses occurred between type A fibres and pituicytes, and between type A fibres and the pericapillary basement membrane in the interior of the neurohypophysis. The possible roles of the different types of nerve fibres in controlling the adenohypophysial cells are discussed in the context of evidence from other teleosts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham, M.: The ultrastructure of the cell types and of the neurosecretory innervation in the pituitary of Mugil cephalus L. from fresh water, the sea, and a hypersaline lagoon. I. The rostral pars distalis. Gen. comp. Endocr. 17, 334–350 (1971)
Abraham, M.: The ultrastructure of the cell types and of the neurosecretory innervation in the pituitary of Mugil cephalus L. from freshwater, the sea, and a hypersaline lagoon. II. The proximal pars distalis. Gen. comp. Endocr. 24, 121–132 (1974)
Abraham, M.: The ultrastructure of the cell types and of the neurosecretory innervation in the pituitary of Mugil cephalus L. from freshwater, the sea, and a hypersaline lagoon. III. The neuro-intermediate lobe. Gen. comp. Endocr. 29, 511–521 (1976)
Abraham, M., Kieselstein, M., Lisson-Begon, S.: The extravascular channel system in the rostral pituitary of Mugil cephalus (Teleostei) as revealed by use of horseradish peroxidase. Cell Tiss. Res. 167, 289–296 (1976)
Båge, G., Ekengren, B., Fernholm, B., Fridberg, G.: The pituitary gland of the roach Leuciscus rutilus. I. The rostral pars distalis and its innervation. Acta zool. 55, 25–45 (1974)
Båge, G., Ekengren, B., Fernholm, B., Fridberg, G.: The pituitary gland of the roach Leuciscus rutilus. II. The proximal pars distalis and its innervation. Acta zool. 55, 191–204 (1974)
Båge, G., Ekengren, B., Fernholm, B., Fridberg, G.: The pituitary gland of the roach Leuciscus rutilus. III. The pars intermedia and its innervation. Acta zool. 56, 43–60 (1975)
Ball, J.N., Baker, B.I.: The pituitary gland: anatomy and histophysiology. In: Fish physiology (Hoar, W.S. and Randall, D.J., eds.), Vol. II, pp. 1–110. New York: Academic Press 1969
Bargmann, W.: Über das Zwischenhirn-Hypophysensystem von Fischen. Z. Zellforsch. 38, 275–297 (1953)
Batten, T.F.C., Ball, J.N.: Ultrastructural studies on the prolactin cells and their innervation in the teleost Poecilia latipinna. J. Endocr. 69, 35P-36P (1976)
Batten, T., Ball, J.N., Benjamin, M.: Ultrastructure of the adenohypophysis in the teleost Poecilia latipinna. Cell Tiss. Res. 161, 239–261 (1975)
Batten, T.F.C., Ball, J.N., Grier, H.J.: Circadian changes in prolactin cell activity in the pituitary of the teleost Poecilia latipinna in freshwater. Cell Tiss. Res. 165, 267–280 (1976)
Bern, H.A., Nishioka, R.S., Nagahama, Y.: The relationship between nerve fibres and adenohypophysial cell-types in the cichlid teleost Tilapia mossambica. In: Recherches biologiques contemporaines: Manfred Gabe memorial volume (Arvy, L., ed.), pp. 179–194. Nancy: Vagner 1974
Bern, H.A., Zambrano, D., Nishioka, R.S.: Comparison of the innervation of the pituitary of two euryhaline teleost fishes, Gillichthys mirabilis and Tilapia mossambica with special reference to the origin and nature of type ‘B’ fibres. Mem. Soc. Endocr. 19, 817–822 (1971)
Breton, B., Jalabert, B., Billard, R., Weill, C.: Stimulation in vitro de la libération d'hormone gonadotrope hypophysaire par un facteur hypothalamique chez la carpe Cyprinus carpio L. C.R. Acad. Sci. (Paris) D 273, 2591–2594 (1971)
Breton, B., Weill, C., Jalabert, B., Billard, R.: Activité reciproque des facteurs hypothalamique de bélier (Ovis aries) et de poissons téléostéens sur la secretion in vitro des hormones gonadotropes c-HG et LH respectivement par les hypophyses de carpe et de bélier. C.R. Acad. Sci. (Paris) D 274, 2530–2533 (1974)
Follénius, E.: Analyse de la structure fine des différents types des cellules hypophysaires des poissons téléostéens. Path. et Biol. 16, 619–632 (1968)
Follénius, E.: La localisation fine des terminaisons nerveuses fixant la noradrenaline 3H dans les différents lobes de l'adénohypophyse de l'épinoche (Gasterosteus aculeatus L.). In: Aspects of neuroendocrinology (Bargmann, W., Scharrer, gnB.), (eds.), pp. 232–244 (1970a)
Follénius, E.: Mise en évidence, au microscope électronique, de l'innervation de l'hyophyse de Gasterosteus aculeatus L. par la technique de Maillet Champy. C.R. Acad. Sci. (Paris) D 271, 1034–1037 (1970)
Follénius, E.: Cytologie fine de la dégénérescence des fibres aminergiques intrahypophysaires chez le poisson téléostéen Gasterosteus aculeatus après traitement par la 6-hydroxydopamine. Z. Zellforsch, 128, 69–82 (1972)
Gray, E.G., Guillery, R.W.: Synaptic morphology in the normal and degenerating nervous system. Int. Rev. Cytol. 19, 111–182 (1966)
Henderson, N.E.: Structural similarities between the neurohypophyses of brook trout and tetrapods. Gen. comp. Endocr. 12, 148–153 (1969)
Holmes, R.L., Ball, J.N.: The pituitary gland: a comparative account, London: Cambridge University Press 1974
Kaul, S., Vollrath, L.: The goldfish pituitary. II. Innervation. Cell Tiss. Res. 154, 231–249 (1974)
Kerr, T.: The pituitary in polypterines and its relationship to other fish pituitaries. J. Morph. 124, 23–36 (1968)
Knigge, K.M., Scott, D.E., Kobayashi, H., Ishii, S. (eds.): Brain-endocrine interaction II. The ventricular system in neuroendocrine mechanisms. Basel: S. Karger 1975
Knowles, F.: Evidence for a dual control, by neurosecretion, of hormone synthesis and hormone release in the pituitary of the dogfish Scyliorhinus stellaris. Phil. Trans. B 249, 435–456 (1965)
Knowles, F., Vollrath, L.: A dual neurosecretory innervation of the pars distalis of the pituitary of the eel. Nature (Lond.) 208, 1343–1344 (1965)
Knowles, F., Vollrath, L.: Neurosecretory innervation of the pituitary of the eels Anguilla and Conger. I. The structure and ultrastructure of the neurointermediate lobe under normal and experimental conditions. Phil. Trans. B 250, 311–327 (1966)
Knowles, F., Vollrath, L.: Neurosecretory innervation of the pituitary of the eels Anguilla and Conger. II. The structure and innervation of the pars distalis at different stages of the life-cycle. Phil. Trans. B 250, 329–342 (1966)
Kobayashi, H.: Median eminence of the hagfish and ependymal absorption in higher vertebrates. In: Brain-endocrine interaction. Median eminence: structure and function (Knigge, K.M., Scott, D.E., Weindl, A., eds.), pp. 67–78. Basel: S. Karger 1972
Kobayashi, H.: Absorption of cerebrospinal fluid by ependymal cells of the median eminence. In: Brain-endocrine interaction. II. The ventricular system in neuroendocrine mechanisms (Knigge, K.M., Scott, D.E., Kobayashi, H., Ishii, S., eds.), pp. 109–122. Basel: S. Karger 1974
Leatherland, J.F.: Studies on the structure and ultrastructure of the intact and ‘methallibure’-treated mesoadenohypophysis of the viviparous teleost Cymatogaster aggregata Gibbons. Z. Zellforsch. 98, 122–134 (1969)
Leatherland, J.F.: Seasonal variation in the structure and ultrastructure of the pituitary of the marine form (trachurus) of the threespine stickleback, Gasterosteus aculeatus L. I. Rostral pars distalis. Z. Zellforsch. 104, 301–317 (1970)
Leatherland, J.F.: Seasonal variation in the structure and ultrastructure of the pituitary gland in the marine form (trachurus) of the threespine stickleback, Gasterosteus aculeatus L. II. Proximal pars distalis and neurointermediate lobe. Z. Zellforsch. 104, 318–336 (1970)
Leatherland, J.F.: Structure and ultrastructure of the neurohypophysis of the viviparous teleost Cymatogaster aggregata Gibbons. Canad. J. Zool. 48, 1087–1091 (1970)
Leatherland, J.F.: Histophysiology and innervation of the pituitary gland of the goldfish, Carassius auratus L.: a light and electron microscope investigation. Canad. J. Zool. 50, 835–844 (1972)
Lederis, K.: Fine structure and hormone content of the hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system of the rainbow trout Salmo irideus. Gen. comp. Endocr. 4, 638–661 (1964)
McCann, S.M., Porter, J.C.: Hypothalamic pituitary stimulating and inhibiting hormones. Physiol. Rev. 49, 140–284 (1969)
Nagahama, Y., Nishioka, R.S., Bern, H.A., Gunther, R.L.: Control of prolactin secretion in teleosts with special reference to Gillichthys mirabilis and Tilapia mossambica. Gen. comp. Endocr. 25, 166–188 (1975)
Olivereau, M.: Action de la reserpine chez l'Anguille. I. Cellules à prolactine de l'hypophyse du mâle. Z. Zellforsch. 121, 232–243 (1971)
Perks, A.M.: The neurohypophysis. In: Fish physiology (Hoar, W.S., Randall, D.J., eds.), Vol. II, pp. 111–205. New York: Academic Press 1969
Peter, R.E.: Neuroendocrinology of teleosts. Amer. Zool. 13, 743–755 (1973)
Peter, R.E., McKeown, B.A.: Hypothalamic control of prolactin and thyrotropin secretion in teleosts with special reference to recent studies on the goldfish. Gen. comp. Endocr. 25, 153–165 (1975)
Peute, J., de Bruyn, M.G.A., Seldenrijk, R., van Oordt, P.G.W.J.: Cytophysiology and innervation of gonadotropic cells in the pituitary of the black molly (Poecilia latipinna). An electron microscopical study. Cell Tiss. Res. 174, 35–54 (1976)
Polenov, A.L., Belenky, M.A., Konstantinova, M.S.: The hypothalamo-hypohysial system of the lamprey, Lampetra fluviatilis L. I. The neurohypophysis. Cell Tiss. Res. 150, 515–519 (1974)
Rodríguez, E.M.: Ultrastructure of the neurohaemal area of the toad median eminence. Z. Zellforsch. 93, 182–212 (1969)
Rodríguez, E.M.: The comparative morphology of neural lobes of species with different neurohypophysial hormones. Mem. Soc. Endocr. 19, 263–292 (1971)
Sage, M.: Control of prolactin release and its role in colour change in the teleost Gillichthys mirabilis. J. exp. Zool. 173, 121–128 (1970)
Sathyanesan, A.G.: Hypothalamo-hypophysial vascularization in a teleost fish with special reference to its tetrapodean features. Acta anat. (Basel) 81, 349–366 (1972)
Siegel, S.: Non-parametric statistics for the behavioural sciences. New York: McGraw-Hill 1956
Swanson, D.D., Nishioka, R.S., Bern, H.A.: Aminergic innervation of the cranial and caudal neurosecretory systems in the teleost Gillichthys mirabilis. Acta zool. 56, 225–237 (1975)
Thornton, V.F.: Changes in the neurosecretory granules of the eel pituitary pars nervosa associated with change of background colour. Gen. comp. Endocr. 30, 175–181 (1976)
Tsuneki, K., Adachi, T., Ishii, S., Oota, Y.: Morphometric classification of neurosecretory granules in the neurohypophysis of the hagfish Eptatretus burgeri. Cell Tiss. Res. 166, 145–157 (1976)
Vollrath, L.: Über die neurosekretorische Innervation der Adenohypophyse von Teleostiern, insbesondere von Hippocampus cuda and Tinea tinea. Z. Zellforsch. 78, 234–260 (1967)
Vollrath, L.: Morphologic correlates of releasing factors in the pituitary of the eel. Anguilla anguilla. In: Brain-endocrine interaction. Median eminence: structure and function (Knigge, K.M., Scott, D.E., Weindl, A., eds.), pp. 154–163. Basel: S. Karger 1972
Wigham, T., Ball, J.N.: In vivo evidence for catecholaminergic inhibition of prolactin secretion in the teleost Poecilia latipinna. J. comp. Physiol. B 110, 135–143 (1976)
Wigham, T., Ball, J.N., Ingleton, P.M.: Secretion of prolactin and growth hormone by teleost pituitaries in vitro. III. Effect of dopamine on hormone release in Poecilia latipinna. J. comp. Physiol. B 104, 87–96 (1975)
Zambrano, D.: The nucleus lateralis tuberis system of the gobiid fish Gillichthys mirabilis. II. Innervation of the pituitary. Z. Zellforsch. 110, 496–516 (1970)
Zambrano, D.: The nucleus lateralis tuberis system of the gobiid fish Gillichthys mirabilis. III. Functional modification of the neurons and the gonadotropic cells. Gen. comp. Endocr. 17, 164–182 (1971)
Zambrano, D.: Innervation of the teleost pituitary. Gen. comp. Endocr., Suppl. 3, 21–31 (1972)
Zambrano, D., Clarke, W.C., Hawkins, E.F.), (auSage, M.), (auBern. H.A.: Influence of 6-hydroxydopamine on hypothalamic control of prolactin and ACTH secretion in the teleost fish, Tilapia mossambica. Neuroendocr. 13, 284–298 (1973/74)
Zambrano, D., Nishioka, R.S., Bern., H.A.: The innervation of the pituitary gland of teleost fishes; its origin, nature and significance. In: Brain-endocrine interaction. Median eminence: structure and function (Knigge, K.M., Scott, D.E., Weindl, A., eds.), pp. 50–66. Basel: S. Karger 1972
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
We thank Mr. W.A. Thomson and Mr. D.I. Hollingworth for technical assistance, and Dr. D.I.C. Pearson (Department of Physics, University of Nancy, Nancy, France) for advice on mathematical analysis and computer programs. The work was carried out during the tenure of an S.R.C. Research Studentship by T.F.C.B.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Batten, T.F.C., Ball, J.N. Ultrastructure of the neurohypophysis of the teleost Poecilia latipinna in relation to neural control of the adenohypophysial cells. Cell Tissue Res. 185, 409–433 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00220300
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00220300