Summary
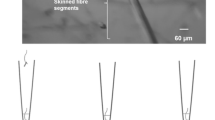
Incubation of mouse skeletal muscle in a physiological Ringer solution containing protamine (60 μg/ml) at +37° C for 1 h induced ultrastructural changes including proliferation of tubular profiles and vesicles at the I-band level close to the A-I junction, formation of numerous acid phosphatase positive lysosomes in the longitudinal sarcoplasmic reticulum and autophagic vacuolation starting at the level of the A-I junction.
Biochemical determination of acid phosphatase in the incubated muscles showed that protamine caused an increase in acid phosphatase activity of about 25 % compared to enzyme activities obtained from muscles incubated without protamine at +37°C or with protamine at +4°C.
The morphological findings suggest that the vesicles arising adjacent to the A-I junction originate from transverse tubules. Such vesicles, designated as endocytic, may acquire acid phosphatase activity in the longitudinal SR and be active in an autophagic process resulting in large vacuoles. A causal relationship between endocytosis and lysosomal activation is suggested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banker, B.Q.: A pathological study of muscular dystrophy in the Bar Harbor 129 house mouse. With particular reference to the ultrastructural features. In: Modern neurology, pp. 241–259 (S. Locke, ed.). Boston: Little, Brown Co. 1969
Bird, J.W.: Skeletal muscle lysosomes. In: Lysosomes in biology and pathology, Vol. 4, pp. 77–109 (J.T. Dingle and R.T. Dean, eds.). Amsterdam: North-Holland Publishing Company 1975
Christie, K.N., Stoward, P.J.: A cytochemical study of acid phosphatase in dystrophic hamster muscle. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 58, 219–234 (1977)
Engel, A.G.: Vacuolar myopathies: Multiple etiologies and sequential structural studies. In: The striated muscle pp. 301–341 (C.M. Pearson, ed.). Baltimore: The Williams and Wilkins Company 1973
Jirmanová, I., Libelius, R., Lundquist, I., Thesleff, S.: Protamine induced intracellular uptake of horseradish peroxidase and vacuolation in mouse skeletal muscle in vitro. Cell Tiss. Res. 176, 463–473 (1977)
Libelius, R.: Evidence for endocytotic uptake of cobra neurotoxin in mouse skeletal muscle. J. Neural Transm. 37, 61–71 (1975)
Libelius, R., Jirmanová, I., Lundquist, I., Thesleff, S.: Increased endocytosis with lysosomal activation in skeletal muscle of dystrophic mouse. To be published
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., Randall, R.J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951)
Malouf, N.N., Sommer, J.R.: Chicken dystrophy. The geometry of the transverse tubules. Amer. J. Path. 84, 299–316 (1976)
Maskrey, P., Pluskal, M.G., Harris, J.B., Pennington, R.J.T.: Studies on increased acid hydrolase activities in denervated muscle. J. Neurochem. 28, 403–409 (1977)
Miller, F., Palade, G.E.: Lytic activities in renal protein absorption droplets. An electron microscopical cytochemical study. J. Cell Biol. 23, 519–552 (1964)
Penningtion, R.J.: Biochemistry of dystrophic muscle. II. Some enzyme changes in dystrophic mouse muscle. Biochem. J. 88, 64–68 (1963)
Ryser, H.J.-P., Hancock, R.: Histones and basic polyamino acids stimulate the uptake of albumin by tumor cells in culture. Science 150, 501–503 (1965)
Schiaffino, S., Hanzlíková, V.: Studies on the effect of denervation in developing muscle. II. The lysosomal system. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 39, 1–14 (1972)
Schotland, D.L.: An electron microscopic investigation of myotonic dystrophy. J. Neuropath, exp. Neurol. 29, 241–253 (1970)
Weinstock, I.M., Iodice, A.A.: Acid hydrolase activity in muscular dystrophy and denervation atrophy. In: Lysosomes in biology and pathology, Vol. 1, pp. 450–468 (J.T. Dingle and H.B. Fell, eds.). Amsterdam: North-Holland Publishing Company 1969
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
We wish to thank Miss Britt-Marie Svensson, Miss Ann-Christin Nilsson and Mrs. Lena Kvist for their able technical assistance. This work was supported by grants from the Medical Faculty, University of Lund, Sweden, and the Swedish Medical Research Council, Stockholm, Sweden (04P-4289, 14X-4286, 14X-3112) and from Muscular Dystrophy Association of America, Inc.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Libelius, R., Lundquist, I. Lysosomal activation in mouse skeletal muscle induced by protamine in vitro. Cell Tissue Res. 186, 1–11 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00219650
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00219650