Summary
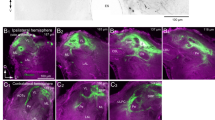
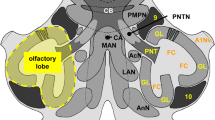
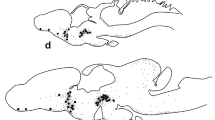
The olfactory tract of the African catfish, Clarias gariepinus, consists of two tracts, the medial and lateral olfactory tract. Ovulated female catfish are attracted by male steroidal pheromones. Attraction tests with catfish in which the medial and lateral olfactory tract have been selectively lesioned show that the effects of these pheromones are mediated by the medial olfactory tract. The central connections of the medial and lateral olfactory tract have been studied by retro- and anterograde transport techniques using horseradish peroxidase as a tracer. Upon entering the forebrain, the medial olfactory tract innervates the posterior pars ventralis and pars supracommissuralis of the area ventralis telencephali and the nucleus preopticus periventricularis, the nucleus preopticus and the nucleus recessus posterioris. Application of horseradish peroxidase to the olfactory epithelium shows that part of the innervation of the area ventralis telencephali and the nucleus preopticus periventricularis can be attributed to the nervus terminalis, which appears to be embedded in the medial olfactory tract. The lateral olfactory tract sends projections to the same brain areas but also innervates the nucleus habenularis and a large terminal field in the area dorsalis telencephali pars lateralis ventralis. Furthermore, the medial olfactory tract carries numerous axons from groups of perikarya localized in the area dorsalis telencephali. Contralateral connections have been observed in the olfactory bulb, telencephalon, diencephalon and mesencephalon. It is suggested that processes of the medial olfactory tract innervating the preoptic region may influence the gonadotropin-releasing hormone system and in doing so may lead to behavioral and physiological changes related to spawning.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bass AH (1981 a) Organization of the telencephalon in the Channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus. J Morphol 169:71–90
Bass AH (1981 b) Olfactory bulb efferents in the Channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus. J Morphol 169:91–111
Bass AH (1981 c) Telencephalic efferents in the Channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus'. Projections to the olfactory bulb and optic tectum. Brain Behav Evol 19:1–16
Burck HC (1981) Histologische Technik-Leitfaden für die Herstellung mikroskopischer Präparate in Unterricht und Praxis. Thieme, Stuttgart, New York
Chandrasekhar K, Khosa D (1973) Effect of electrical Stimulation of the olfactory mucosa on the hypothalamic neurosecretory system and its impact on the ovaries of two fresh water teleostean fishes, Clarias batrachus (Linn.) and Heteropneustis fossilis (Bloch). Ind J Zool 14:81–88
Demski LS, Dulka JG (1984) Functional-anatomical studies on sperm release evoked by electrical stimulation of the olfactory tract in goldfish. Brain Res 291:241–247
Demski LS, Northcutt RG (1983) The terminal nerve: A new chemosensory system in vertebrates? Science 220:435–437
Døving KB, Selset R (1980) Behavior pattern in cod released by electrical stimulation of olfactory tract bundlets. Science 207:559–560
Døving KB, Selset R, Thommesen G (1980) Olfactory sensitivity to bile acids in salmonid fishes. Acta Physiol Scand 108:123–131
Dulka JG, Stacey NE, Sorensen PW, Van der Kraak GJ (1987) A steroid sex pheromone synchronizing male-female spawning readiness in goldfish. Nature 325:251–253
Ebbesson SOE, Meyer DL, Scheich H (1981) Connections of the olfactory bulb in the piranha (Serrasalmus nattereri). Cell Tissue Res 216:167–180
Finger TE (1975) The distribution of the olfactory tracts in the bullhead catfish, Ictalurus nebulosus. J Comp Neurol 161:125–142
Fujita I, Satou M, Ueda K (1984) A field-potential study of centripetal and centrifugal connections of the olfactory bulb in the carp, Cyprinus carpio (L.). Brain Res 321:33–44
Goos HJTh, De Leeuw R, De Zoeten-Kamp C, Peute J, Bläsher S (1985) Gonadotropin-releasing hormone-immunoreactive neuronal structures in the brain and pituitary of the African catfish, Clarias gariepinus (Burchell). Cell Tissue Res 241:593–596
Hara TJ (1967) Electrophysiological studies of the olfactory system of the goldfish, Carassius auratus L. III. Effects of sex hormone on the electrical activity of the olfactory bulb. Comp Biochem Physiol 22:209–226
Hara TJ, Gorbman A (1967) Electrophysiological studies of the olfactory system of the goldfish, Carassius auratus L. I. Modification of the electrical activity of the olfactory bulb by other central nervous structures. Comp Biochem Physiol 21:185–200
Jasinski A, Gorbman A, Hara RJ (1966) Rate of movement and redistribution of stainable neurosecretory granules in hypothalamic neurons. Science 154:776–778
Kah O, Breton B, Dulka JG, Nunez-Rodriguez J, Peter RE, Corrigan A, Rivier JE, Vale WW (1986) A reinvestigation of the Gn-RH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone) systems in the goldfish brain using antibodies to salmon Gn-RH. Cell Tissue Res 244:327–337
Koyama Y, Satou M, Oka Y, Ueda K (1984) Involvement of the telencephalic hemispheres and the preoptic area in sexual behavior of the male goldfish, Carassius auratus: A brain lesion study. Behav Neural Biol 40:70–86
Koyama Y, Satou M, Ueda K (1985) Sexual behavior elicited by electrical stimulation of the telencephalic and preoptic areas in the goldfish, Carassius auratus. Zool Sci 2:565–570
Kyle AL (1987) Effects of nervus terminalis ablation on gonad weight, response to a sex pheromone, and courtship behaviour in the male goldfish (Carassius auratus). In: Idler DR, Crim LW, Walsh JM (eds) Third International Symposium on Reproductive Physiology of Fish, St. John's, Canada, 2–7 August, 1987
Kyle AL, Peter RE (1982) Effects of forebrain lesions on spawning behavior in the male goldfish. Physiol Behav 28:1103–1109
Levine RI, Dethier S (1985) The connections between the olfactory bulb and the brain in the goldfish. J Comp Neurol 237:427–444
Liley NR (1982) Chemical communication in fish. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 39:22–35
Mesulam MM (1982) Tracing neural connections with horseradish peroxidase. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Münz H, Stumpf WE, Jennes L (1981) LHRH-systems in the brain of platyfish. Brain Res 221:1–13
Münz H, Claas B, Stumpf WE, Jennes L (1982) Centrifugal innervation of the retina by luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) immunoreactive telencephalic neurons in teleostean fishes. Cell Tissues Res 222:313–323
Nieuwenhuys R (1963) The comparative anatomy of the actinopterygian brain. J Hirnforsch 6:171–192
Nieuwenhuys R (1967) Comparative anatomy of olfactory centres and tracts. Prog Brain Res 23:1–64
Nozaki M, Fujita I, Saito N, Sukahara TT, Kobayashi H, Ueda K, Oshima K (1985) Distribution of LHRH-like immunoreactivity in the brain of the Japanese eel (Anguilla japonica) with special reference to the nervus terminalis. Zool Sci 2:537–549
Oshima K, Gorbman A (1968) Modification by sex hormones of the spontaneous and evoked bulbar electrical activity in goldfish. J Endocrinol 40:409–420
Partridge BL, Liley NR, Stacey NE (1976) The role of pheromones in the sexual behavior of the goldfish. Anim Behav 24:291–299
Peter RE, Gorbman A (1968) Some afferent pathways to the preoptic nucleus of the goldfish. Neuroendocrinology 3:229–237
Peute J, Schild RG, Schild VA, Buijs RM, Van Asselt LAC, Van Oordt PGWJ (1987) Immunocytochemical evidence for peptidergic (GnRH) and dopaminergic innervation of the gonadotropic cells in the pituitary of African catfish, Clarias gariepinus. Gen Comp Endocrinol 67:303–310
Prasada Rao PD (1970) The effect of electrical stimulation of the olfactory tract on the nucleus preopticus in the catfish Heteropneustes fossilis (Bloch). Experientia 26:1377–1378
Prasada Rao PD, Finger TE (1984) Asymmetry of the olfactory system in the brain of the winter flounder, Pseudopleuronectes americanus. J Comp Neurol 225:492–510
Resink JW (1988) Steroid glucuronides as pheromones in the reproduction of the African catfish, Clarias gariepinus. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Utrecht, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Resink JW, Van den Hurk R, Groeninx van Zoelen RFO, Huisman EA (1987) The seminal vesicle as source of sex attracting substances in the African catfish, Clarias gariepinus. Aquaculture 63:115–128
Satou M (1987) A neuroethological study of reproductive behavior in the salmon. In: Idler DR, Crim LW, Walsh JM (eds), Third International Symposium on Reproductive Physiology of Fish, St. John's, Canada, 2–7 August 1987, pp 154–159
Satou M, Oka Y, Fujita I, Koyama Y, Shiga T, Kusumoki M, Matsushima T, Ueda K (1982) Effects of brain lesion and electrical stimulation on sexual behavior in hime salmon (landlocked red salmon, Oncorhynchus nerka). Zool Mag 91:495
Satou M, Fujita L, Ichikawa M, Yamaguchi K, Ueda K (1983) Field potential and intracellular potentional studies of the olfactory bulb in the carp: evidence for a functional separation of the olfactory bulb into lateral and medial subdivisions. J Comp Physiol 152:319–333
Satou M, Oka Y, Kusunoki M, Matsushima T, Kato M, Fujita L, Ueda K (1984) Telencephalic and preoptic areas integrate sexual behavior in hime salmon (landlocked red salmon, Oncorhynchus nerka): results of electrical brain stimulation experiment. Physiol Behav 33:441–447
Schreibman MP, Halpern LR, Goos HJTh, Margolis-Kazan H (1979) Identification of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LH-RH) in the brain and pituitary gland of fish by immunocytochemistry. J Exp Zool 210:153–160
Schreibman MP, Margolis-Nunno H, Halpern-Sebold L (1986) The structural and functional relationship between olfactory and reproductive systems from birth to old age in fish. In: Duval D, Muller-Schwarze D, Silverstein RM (eds) Chemical Signals in Vertebrates. Volume IV, Fourth International Conference on Chemical Signals in Vertebrates, Laramie Wy, 27–30 July 1985. Plenum Press, New York, pp 155–172
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1969) Biometry. The principles and practice of statistics in biological research. WH Freeman and Company, San Francisco
Stacey NE, Kyle AL (1983) Effects of olfactory tract lesions on sexual and feeding behavior in the goldfish. Physiol Behav 30:621–628
Stacey NE, Sorensen PW (1986) 17α,20β-dihydroxy-4-pregnen-3-one: a steroidal primer pheromone increasing milt volume in the goldfish, Carassius auratus. Can J Zool 64:2412–2417
Stacey NE, Kyle AL, Liley NR (1986) Fish Reproductive Pheromones. In: Duvall D, Muller-Schwarze D, Silverstein RM (eds) Chemical Signals in Vertebrates, Volume IV, Fourth International Conference on Chemical Signals in Vertebrates, Laramie Wy, 27–30 July 1985. Plenum Press, New York, pp 117–133
Stacey NE, Sorensen PW, Dulka JG, Van der Kraak GJ (1987) Teleost sex pheromones: recent studies on identity and function. In: Idler DR, Crim LW, Walsh JM (eds) Third International Symposium on Reproductive Physiology of Fish, St. John's, Canada, 2–7 August, 1987, pp 150–153
Stell WK, Walker SE, Chohan KS, Ball AK (1984) The goldfish nervus terminalis: a luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone and molluscan cardioexcitatory peptide immunoreactive olfactoretinal pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:940–944
Timmers RJM, Lambert JGD, Peute J, Vullings HGB, Van Oordt PGWJ (1987) Localization of aromatase in the brain of the male African catfish, Clarias gariepinus (Burchell), by microdissection and biochemical identification. J Comp Neurol 258:368–377
Timmers RJM, Granneman JCM, Lambert JGD, Van Oordt PGWJ (1988) Estrogen-2-hydroxylase in the brain of the male African catfish, Clarias gariepinus. Gen Comp Endocrinol (in press)
Thomessen G (1982) Specificity and distribution of receptor cells in the olfactory mucosa of char (Salmo alpinus L.). Acta Physiol Scand 115:47–56
Thomessen G (1983) Morphology, distribution, and specificity of olfactory receptor cells in salmonid fishes. Acta Physiol Scand 117:241–249
Von Bartheld CS, Meyer DL, Fiebig E, Ebbesson SOE (1984) Central connections of the olfactory bulb in the goldfish, Carassius auratus. Cell Tissue Res 238:475–487
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Resink, J.W., Voorthuis, P.K., Van den Hurk, R. et al. Pheromone detection and olfactory pathways in the brain of the female African catfish, Clarias gariepinus . Cell Tissue Res. 256, 337–345 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00218890
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00218890