Summary
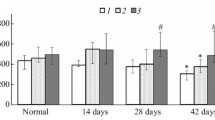
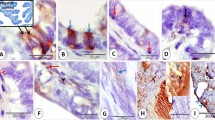
A single administration of progesterone (P) to primed immature rabbits induces the appearance of glycogen in uterine glandular cells. This phenomenon, which is rapid and transitory, precedes a mitotic surge in the glandular epithelium. Ultrastructural studies allowed us to observe the beginning of glycogenesis as early as 1 h after the injection of P. Quantitative image analysis in the course of a kinetic study showed that glycogen levels reached a maximum at the sixth h and after 24 h had fallen dramatically. Promegestone, a potent progestomimetic compound, gave similar results, but estradiol, testosterone and dexamethasone failed to induce the appearance of glycogen in the uterine glands. Mifepristone (RU 486) had an antagonistic effect on the action of P. These results suggest that early P-dependent glycogenesis in the endometrial glandular cells of the rabbit may play an important role in the increased rate of mitosis and cellular proliferation that are necessary events in preparing the endometrium for implantation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baxter JP, Forsham PH (1972) Tissue effects of glucocorticosteroids. Am J Med 53:573–584
Boomsma RA, Verhage HG (1982) The uterine progestational response in cats: ultrastructural changes during chronic administration of progesterone to estradiol-primed and nonprimed animals. Am J Anat 164:243–254
Bouin P, Ancel P (1910) Recherches sur les fonctions du corps jaune gestatif. I. Sur le déterminisme de la préparation de l'utérus à la fixation de l'oeuf. J Physiol Pathol Gén 12:1–16
Clauberg C (1930) Zur Physiologie und Pathologie der Sexualhormone, im besonderen des Hormons des Corpus luteum. I. Mitteilung: Der biologische Test für das Luteohormon (das spezifische Hormon des Corpus luteum) am infantilen Kaninchen. Zentralbl Gynacol 54:3757
Demers LM, Jacobs RD (1973) Comparative effects of ovarian steroids on glycogen metabolism of rat, rabbit and guinea pig uterine tissue. PSEBM 143:1158–1163
Demers LM, Feil PD, Bardin CW (1977) Factors that influence steroid induction of endometrial glycogenesis in organ culture. Ann NY Ac Sc 286:249–259
Gordon M (1975) Cyclic changes in the fine structure of the epithelial cells of human endometrium. Int Rev Cytol 42:127–172
Kohorn EI, Tchao R (1969) Conversion of proliferative endometrium to secretory endometrium by progesterone in organ culture. J Endocrinol 45:401–404
Mac Phail MK (1934) The assay of progestin. J Physiol (London) 83:145–156
Raynaud JP, Bouton MM, Moguilewsky M, Ojasoo T, Philibert D, Beck G, Labrie F, Mornon JP (1980) Steroid hormone receptors and pharmacology. J Steroid Biochem 12:143–157
Secchi J, Lecaque D, Tournemine C, Philibert D (1985) Histopharmacology of RU 486. In: Baulieu EE, Segal SJ (eds) The antiprogestin steroid RU 486 and human fertility control. Plenum Press, New York, pp 79–86
Shapiro SS, Dyer RD, Colas AE (1980) Progesterone-induced glycogen accumulation in human endometrium during organ culture. Am J Obstet Gynecol 136:419–425
Telfer MA, Hisaw FL Jr (1957) Biochemical responses of the rabbit endometrium and myometrium to oestradiol and progesterone. Acta Endocrinol 25:390–404
Thiéry JP (1967) Mise en évidence des polysaccharides sur coupes fines en microscopic électronique. J Microsc 6:987–1018
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Secchi, J., Lecaque, D., Tournemine, C. et al. Early glycogenesis in the uterine glandular cells of the rabbit induced by progestins: a quantitative investigation. Cell Tissue Res. 248, 359–364 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00218203
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00218203