Abstract
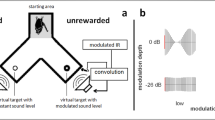
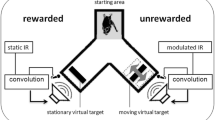
Big brown bats, Eptesicus fuscus, were presented with artificial frequency modulated (FM) echoes that simulated an object becoming progressively closer to the bat. A stereotyped approach phase behavioral response of the bat to the virtual approaching target was used to determine the ability of the bat to analyze FM signals for target distance information. The degree to which the bats responded with approach phase behavior to a virtual approaching target was similar when they were presented with either a naturally structured artificial FM echo or an artificial FM echo constructed from a series of brief pure tone steps. The ability of the bats to respond to an FM signal structured from a sequence of pure tone elements depended on the number of pure tone steps in the series; the bats required the presentation of tone-step FM signals containing about 83 or greater pure tone elements. Moreover, the duration of the individual tone steps of the tone-step FM signals could not exceed a specific upper limit of about 0.05 ms. Finally, it appears that the bats were able to independently resolve individual tone steps within the tone-step FM signals that were separated by about 450 Hz or more.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CF:
-
constant frequency
- FM:
-
frequency modulation
References
Griffin DR (1958) Listening in the dark. Yale Univ Press, New Haven
Grinnell AD (1973) Neural processing mechanisms in echolocating bats, correlated with differences in emitted sounds. J Acoust Soc Am 54:147–156
Heffner R, Heffner H, Masterton B (1971) Behavioral measurement of absolute and frequency-difference thresholds in guinea pig. J Acoust Soc Am 49:1888–1895
Nordmark JO (1968) Mechanisms of frequency discrimination. J Acoust Soc Am 44:1533–1540
Roverud RC (1993) Neural computations for sound pattern recognition: evidence for summation of an array of frequency filters in an echolocating bat. J Neurosci 13:2306–2312
Roverud RC (1994) Complex sound analysis in the lesser bulldog bat: evidence for a mechanism for processing frequency elements of frequency-modulated signals over restricted time intervals. J Comp Physiol A 174:559–565
Roverud RC, Grinnell AD (1985) Discrimination performance and echolocation integration requirements for target detection and distance determination in the CF/FM bat, Noctilio albiventris. J Comp Physiol A 156:447–456
Simmons JA (1973) The resolution of target range by echolocating bats. J Acoust Soc Am 54:157–173
Simmons JA, Grinnell AD (1988) The performance of echolocation: acoustic images perceived by echolocating bats. In: Nachtigall PE, Moore PWB (eds) Animal sonar: processes and performance. Plenum, New York, pp 353–386
Simmons JA, Howell BJ, Suga N (1975) Information content of bat sonar echoes. Am Sci 63:204–215
Simmons JA, Moss CF, Ferragamo M (1990) Convergence of temporal and spectral information into acoustic images of complex sonar targets perceived by the echolocating bat, Eptesicus fuscus. J Comp Physiol A 166:449–470
Thompson RKR, Herman LM (1975) Underwater frequency discrimination in the bottlenosed dolphin (1–140 kHz) and the human (1–8 kHz). J Acoust Soc Am 57:943–948
Vaughan TA (1970) Flight patterns and aerodynamics. In: Wimsatt WA (ed) Biology of bats, vol I. Academic Press, New York, pp 195–216
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roverud, R.C., Rabitoy, E.R. Complex sound analysis in the FM bat Eptesicus fuscus, correlated with structural parameters of frequency modulated signals. J Comp Physiol A 174, 567–573 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00217377
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00217377