Summary
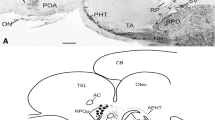
“Falck-positive” monoaminergic neurosecretory cells (MNSC) are found in stage I–II sturgeon larvae in the dorsal zone of the preoptic nucleus (PN) by means of fluorescence and electron microscopy. Single poorly differentiated M-NSC are located mostly among the ependymal cells. At this stage the M-NSC have very short dendrites protruding into the third ventricle. In the process of differentiation the M-NSC move subependymally and their dendrites become longer. Axons of the M-NSC can be clearly traced only in stage IV larvae. Perikarya and dendrites of M-NSC contain little rough endoplasmic reticulum and numerous neurosecretory granules (NSG) 60–150 nm in diameter. Ventricular dendrites of the “Gomori-positive” peptidergic neurosecretory cells (P-NSC) containing NSG 110–200 nm in diameter are observed within the PN in stage III larvae. Thus the M-NSC differentiate earlier than the P-NSC. The intraventricular terminals have kinocilia and show typical macroapocrine secretion. This fact supports the view of a receptory as well as a secretory function of the M-NSC and P-NSC. It is proposed that in early ontogeny monoamine as well as peptide neurohormones are secreted into the cerebrospinal fluid. This transventricular pathway is considered phylogenetically ancient.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barannikova IA (1974) Some peculiarities of the formation of neurosecretory systems and development of endocrine functions in the ontogenesis of fishes. In: Astaurov BL (ed) Hormonal factors of individual development. “Nauka”, Moscow, pp 61–71
Belenky MA, Konstantinova MS, Polenov AL (1970) On neurosecretory and adrenergic fibres in the intermediate lobe of the hypophysis in albino mice. Gen Comp Endocrinol 15:185–197
Efimova NA (1976) Liquor-contacting neurosecretory cells in the preoptic nucleus of juvenile Acipenseridae. In: Polenov AL, Belenky MA (eds) Evolutionary aspects of neuroendocrinology. Proc. VII Internat Symposium on Neurosecretion. Leningrad, p 48
Efimova NA (1978) An electron microscopic study of formation of the preoptic nucleus in early ontogeny of Acipenseridae. Thesis, Leningrad
Efimova NA, Senchik YuI, Yakovleva IV (1975) Electron microscope studies of neurosecretory cells of the sturgeon fry nucleus preopticus. Tsitologiya (Leningrad) 17:620–627
Heller H (1969) Neurohypophysial hormones in the cerebrospinal fluid. In: Sterba G (ed) Zirkumventrikuläre Organe and Liquor. Fischer, Jena, pp 235–242
Konstantinova MS (1979) Catecholaminergic neurons in the hypothalamus of cyclostomes, fish, amphibians and reptiles. In: Turpaev TM, Budantsev AYu (eds) Catecholaminergic neurons. “Nauka”, Moscow, pp 35–47
Konstantinova MS, Polenov AL (1977) Monoaminergic CSF contacting neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus of some Acipenseridae. In: Sterba G, Bargmann W (eds) Circumventriculäre Organe. Nova Acta Leopoldina, Suppl. Nr. 9. Deutsche Akademie der Naturforscher Leopoldina, pp 65–67
Konstantinova MS, Polenov AL (1980) Distribution of biogenic monoamines in the brain of the amphioxus, Branchiostoma lanceolatum. J Evol Biochem Physiol (Leningrad) 16:612–614
Konstantinova MS, Efimova NA, Prosorovskaya MP, Polenov AL, Govyirin VA (1981) Formation of monoaminergic neurosecretory hypothalamic cells in early ontogeny of Acipenseridae. In: Gazaryan KG (ed) Abstracts of VIth All-Union Conference of Embryologists. “Nauka”, Moscow, p 90
Krasnodembskaya KD (1978) Melanin pigmentation, pigment reaction and mechanisms of their regulation in early ontogeny of fish, Teleostei and Acipenseridae in particular. Thesis, Leningrad
Leonhardt H (1980) C. Ependym und Circumventriculäre Organe. In: Oksche A (Hrsg.) Handbuch der mikroskopischen Anatomie des Menschen, Bd. 4, Teil 10: Neuroglia I. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Makarov AYu (1978) Role of the liquor in neurohumoral regulation of physiological functions. Progress in Physiol Sci (Moscow) 9:82–102
McKenna OC, Rosenbluth J (1974) Sensory and secretory catecholamine-containing cells bordering the third ventricle of the toad brain. In: Knowles F, Vollrath L (eds) Neurosecretion — The final neuroendocrine pathway. VI Internat Symposium on Neurosecretion. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 260–265
Meurling P, Larsson L (1974) Pars intermedia control with and without innervation — studies in elasmobranchs and a lizard. In: Knowles F, Vollrath L (eds) Neurosecretion — The final neuroendocrine pathway. VI Internat Symposium on Neurosecretion. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 198–206
Müller H, Sterba G, Weiss J (1971) Beiträge zur Hydrencephalokrinie. III. Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen über die Ausleitung von Neurosekret in den Liquor. Z wiss Zool (Leipzig) 183:156–180
Nakai Y, Shioda S, Tashiro N, Honma Y (1979) Fine structure of the cerebrospinal fluidcontacting neurons in the hypothalamus of the lamprey, Lampetra japonica. Arch Histol Jpn 42:337–353
Olsson R, Wingstrand KG (1954) Reissner's fibre and the infundibular organ in Amphioxus. Universitetet i Bergan Arbok. Naturvit. Rekke 14:1–14
Oordt PGWJ van, Goos HJTh, Peute J, Terlou M (1974) Structure and functional aspects of two types of Gomori-negative neurosecretory centers in the caudal hypothalamus of amphibia. In: Knowles F, Vollrath L (eds) Neurosecretion — The final neuroendocrine pathway. VI Internat Symposium on Neurosecretion. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 182–192
Polenov AL (1968) Hypothalamic neurosecretion. “Nauka”, Leningrad
Polenov AL (1978) Evolutionary basis of the general principle of neuroendocrine regulation. Interaction of peptide and monoamine neurohormones in a dual control mechanism. In: Bargmann W, Oksche A, Polenov A, Scharrer B (eds) Neurosecretion and neuroendocrine activity. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 15–30
Polenov AL, Garlov PE, Konstantinova MS, Belenky MA (1972) The hypothalamo-hypophysial system in Acipenseridae. II. Adrenergic structures of the hypophysial neurointermediate complex. Z Zellforsch 128:470–481
Polenov AL, Belenky MA, Garlov PE, Konstantinova MS (1976) The hypothalamo-hypophysial system in Acipenseridae. VI. The proximal neurosecretory contact region. Cell Tissue Res 170:129–144
Polenov AL, Belenky MA, Konstantinova MS (1981a) Morphological bases of the functional interaction of peptidergic and monoaminergic structures of the hypothalamo-hypophyseal complex. In: Farner DS, Lederis K (eds) Neurosecretion — molecules, cells, systems. Plenum Press, New York London, pp 105–116
Polenov AL, Konstantinova MS, Belenky MA (1981b) Monoaminergic neurosecretory cells and their role in neuroendocrine regulation. In: Mitskevich MS (ed) Actual problems of modern endocrinology. “Nauka”, Moscow, pp 42–58
Vigh B, Vigh-Teichmann I (1973) Comparative ultrastructure of the cerebrospinal fluid-contacting neurons. Int Rev Cytology 35:189–251
Vigh-Teichmann I, Vigh B, Aros B, Jennes L, Sikora K, Kovács J (1979) Scanning and transmission electron microscopy of intraventricular dendrite terminals of hypothalamic cerebrospinal fluid contacting neurons in Triturus vulgaris. Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch 93:609–642
Yakovleva IV (1952) Histogenesis of the thyroid gland and sturgeon hypophysis with special reference to larval stages of the development. Thesis, Leningrad
Yakovleva IV (1966) Histophysiological characteristics of the preoptic-hypophyseal neurosecretory system of the sturgeon young. In: Mitskevich MS (ed) Development of endocrine functions during fetal life. “Nauka”, Moscow, pp 198–210
Yakovleva IV, Efimova NA (1978) Regularities in the development of Nucleus praeopticus in Acipenseridae. In: Bargmann W, Oksche A, Polenov A, Scharrer B (eds) Neurosecretion and neuroendocrine activity. VIIth Internat Symposium on Neurosecretion. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 101–103
Young SN, Anderson GM, Purdy WC (1980) Indoleamine metabolism in rat brain studied through measurements of tryptophan, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid, and indoleacetic acid in cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurochem 34:309–315
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors are greatly indebted to Prof. Irene A. Barannikova and Prof. G.M. Persov who provided the fish for this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Polenov, A.L., Efimova, N.A., Konstantinova, M.S. et al. The hypothalamo-hypophysial system in Acipenseridae. Cell Tissue Res. 232, 651–667 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00216436
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00216436