Summary
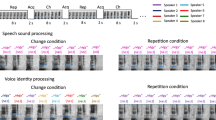
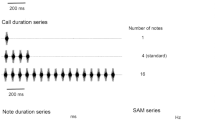
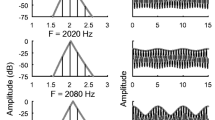
The responses of neurons in field L in the auditory neostriatum of the mynah bird, Gracula religiosa, were recorded during presentation of intact or manipulated mimic voices. A typical mimic voice ‘konnichiwa’ elicited responses in most of the neurons. Neurons in the input layer (L2) of field L showed many peaks on peristimulus time histograms while those in other layers (L1 and L3) exhibited only one or two peaks. Several neurons in L1 and L3 responded only to the affricative consonant /t∫/ in the intact mimic voices. They did not respond to the affricative consonant in the isolated segment or to the one in the playbacked voice in reverse. Forty-five percent of the neurons (33/ 73) decreased in firing rates at the affricative consonant in the isolated segment compared with in the intact voice. Some of these neurons, in which neither the affricative consonant in the isolated segment nor bursts of noise alone elicited responses, exhibited clear phasic responses to /t∫/ in the case when bursts of noise with particular central frequencies preceded the affricative consonant. The responsiveness of these neurons appears to receive temporal facilitation. These results suggest that these neurons code the temporal relationship of speech sound.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HVc :
-
hyperstriatum ventrale, pars caudale
- TFN :
-
temporally facilitated neuron
- TSN :
-
temporally suppressed neuron
References
Bonke D, Scheich H, Langner G (1979) Responsiveness of units in the auditory neostriatum of the guinea fowl (Numida meleagris) to species-specific calls and synthetic stimuli. J Comp Physiol 132:243–255
Butler RA, Diamond IT, Neff WD (1957) Role of auditory cortex in discrimination of changes in frequency. J Neurophysiol 20:108–120
Cornwell P (1967) Loss of auditory pattern discrimination following insular-temporal lesions in cats. J Comp Physiol Psychol 63:165–168
Cowey A, Weiskrantz L (1976) Auditory sequence discrimination in Macaca mulatta: the role of the superior temporal cortex. Neuropsychologia 14:1–10
Dewson JH III (1964) Speech sound discrimination by cats. Science 144:555–556
Dewson JH III, Cowey A, Weiskrantz L (1970) Disruptions of auditory sequence discrimination by unilateral and bilateral cortical ablations of superior temporal gyrus in the monkey. Exp Neurol 28:529–548
Dewson JH III, Pribram KH, Lynch JC (1969) Effects of ablations of temperal cortex upon speech sound discrimination in the monkey. Exp Neurol 24:579–591
Diamond IT, Neff WD (1957) Ablation of temporal cortex and discrimination of auditory patterns. J Neurophysiol 20:300–315
Espinosa IE, Gerstein GL (1988) Cortical auditory neuron interactions during presentation of 3-tone sequences: effective connectivity. Brain Res 450:39–50
Evarts EV (1952) Effect of auditory cortex ablation on frequency discrimination in monkey. J Neurophysiol 15:443–448
Harris DM, Dallos P (1979) Forward masking of auditory nerve fiber responses. J Neurophysiol 42:1083–1107
Heffner HE, Heffner RS (1986) Effect of unilateral and bilateral auditory cortex lesions on the discrimination of vocalizations by Japanese macaques. J Neurophysiol 56:683–701
Hocherman S, Gilat E (1981) Dependence of auditory cortex evoked unit activity on interstimulus interval in the cat. J Neurophysiol 45:987–997
Hose B, Langner G, Scheich H (1987) Topographic representation of periodicities in the forebrain of the mynah bird: one map for pitch and rhythm? Brain Res 422:367–373
Kelley DB, Nottebohm F (1979) Projections of a telencephalic auditory nucleus — field L — in the canary. J Comp Neurol 183:455–470
Klatt DH, Stefanski RA (1974) How does a mynah bird imitate human speech? J Acoust Soc Am 55:822–832
Langner G, Bonke D, Scheich H (1981) Neuronal discrimination of natural and synthetic vowels in field L of trained mynah birds. Exp Brain Res 43:11–24
Leppelsack HJ, Vogt M (1976) Responses of auditory neurons in the forebrain of a songbird to stimulation with species-specific sounds. J Comp Physiol 107:263–274
Margoliash D (1983) Acoustic parameters underlying the responses of song-specific neurons in the white-crowned sparrow. J Neurosci 3:1039–1057
Margoliash D (1987) Neural plasticity in birdsong learning. In: Rauschecker JP, Marler P (eds) Imprinting and cortical plasticity. Wiley, New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto Singapore, pp 23–54
Massopust LC Jr, Wolin LR, Frost V (1971) Frequency discrimination thresholds following auditory cortex ablations in the monkey. J Aud Res 11:227–233
Mckenna TM, Weinberger NM, Diamond DM (1989) Responses of single auditory cortical neurons to tone sequences. Brain Res 481:142–153
Savitzky A, Golay MJE (1964) Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal Chem 36:1627–1639
Scheich H, Langner G, Bonke D (1979) Responsiveness of units in the auditory neostriatum of the guinea fowl (Numida meleagris) to species-specific calls and synthetic stimuli. J Comp Physiol 132:257–276
Schreiner C (1979) Temporal suppression and speech processing. Exp Brain Res Suppl 2:133–139
Smith RL (1977) Short-term adaptation in single auditory nerve fibers: some poststimulatory effects. J Neurophysiol 40:1098–1112
Watanabe T, Katsuki Y (1974) Response patterns of single auditory neurons of the cat to species-specific vocalization. Jpn J Physiol 24:135–155
Wollberg Z, Newman JD (1972) Auditory cortex of squirrel monkey: response patterns of single cells to species-specific vocalizations. Science 175:212–214
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uno, H., Ohno, Y., Yamada, T. et al. Neural coding of speech sound in the telencephalic auditory area of the mynah bird. J Comp Physiol A 169, 231–239 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00215870
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00215870