Summary
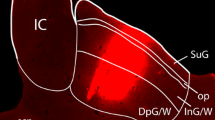
The distribution of presumed GABAergic neurons and axon terminals in nuclei of the higher auditory pathway of the chicken was investigated by immunocytochemical methods employing antisera to the rate-limiting enzyme of GABA synthesis, glutamic acid decarboxylase, and to GABA. In the mesencephalic auditory center (MLD) about 20% of the cells reveal immunoreactivity. In contrast, the thalamic relay station nucleus ovoidalis is devoid of immunostained somata. This nucleus contains a high density of punctate immunoreactive structures presumed to be GABAergic axon terminals. In the auditory forebrain center field L and the auditory portions of the hyperstriatum ventrale, up to 8% of the cells were immunopositive. These neurons were significantly smaller than estimated from measurements of the overall cell population in these nuclei. From the two-dimensional arrangement of immunopositive neurons it is suggested that the GABAergic system in the avian auditory telencephalon consists of two separate groups of neurons: one subgroup mediating local inhibitory interactions, the other responsible for lateral inhibition between different frequency representations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolam JP, Clarke DJ, Smith AD, Somogyi P (1983) A type of aspiny neuron in the rat neostriatum accumulates (3H)gamma-aminobutyric acid: combination of Golgi-staining, autoradiography, and electron microscopy. J Comp Neurol 213:121–134
Bonke BA, Bonke D, Scheich H (1979a) Connectivity of the auditory forebrain nuclei in the guinea fowl (Numida meleagris). Cell Tissue Res 200:101–121
Bonke D, Scheich H, Langner G (1979b) Responsiveness of units in the auditory neostriatum of the guinea fowl to species-specific calls and synthetic stimuli. I. Tonotopy and functional zones of field L. J Comp Physiol 132:243–255
Coles RB, Aitkin LM (1979) The response properties of auditory neurones in the midbrain of the domestic fowl (Gallus gallus) to monaural and binaural stimuli. J Comp Physiol 134:241–251
Faingold CL, Gehlbach G, Caspary DM (1985) Effects of GABA on inferior colliculus neuronal responses to acoustic stimuli. Soc Neurosci [Abstr] 11:247
Francesconi W, Müller CM, Singer W (1984) Acetylcholine mediates the effects of reticular arousal in the cat lateral geniculate nucleus. Pflügers Arch 400:34
Freund TF, Martin KAC, Smith AD, Somogyi P (1983) Glutamate decarboxylase-immunoreactive terminals of Golgi-impregnated axoaxonic cells and of presumed basket cells in synaptic contact with pyramidal neurons of the cat's visual cortex. J Comp Neurol 221:263–278
Giolli RA, Peterson GM, Ribak CE, McDonald HM, Blanks RHI, Fallon JH (1985) GABAergic neurons comprise a major cell type in rodent visual relay nuclei: an immunocytochemical study of pretectal and accessory optic nuclei. Exp Brain Res 61:194–203
Graham RC Jr, Kornovsky M (1966) The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney, ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem 14:291–302
Häusler U (1983) Histologische und elektrophysiologische Untersuchungen an einzelnen Neuronen des Nucleus ovoidalis im Zwischenhirn des Staren (Sturnus vulgaris L.). Master-Thesis, Ruhr-Universität, Bochum
Hamos JE, Davis TL, Sterling P (1983) Four types of neuron in layer IVab of cat cortical area 17 accumulate 3H-GABA. J Comp Neurol 217:449–457
Karten HJ (1967) The organization of the ascending auditory pathway in the pigeon (Columba livia). I. Diencephalic projections of the inferior colliculus (nucleus mesencephalicus lateralis, pars dorsalis). Brain Res 6:409–427
Knudsen EI (1983) Subdivisions of the inferior colliculus in the barn owl (Tyto alba). J Comp Neurol 218:174–186
Knudsen EI, Konishi M (1978) A neural map of auditory space in the owl. Science 200:795–797
Langner G (1983) Evidence for neuronal periodicity detection in the auditory system of the guinea fowl: implications for pitch analysis in the time domain. Exp Brain Res 52:333–355
Leppelsack HJ, Vogt M (1976) Responses of auditory neurons in the forebrain of a songbird to stimulation with species-specific sounds. J Comp Physiol 107:263–274
Montero VM (1983) Ultrastructural identification of axon terminals from the thalamic reticular nucleus in the medial geniculate body in the rat: An EM autoradiographic study. Exp Brain Res 51:338–342
Müller CM (1986a) Strukturelle und funktionelle Aspekte inhibitorischer Interaktionen vermittels gamma-Aminobuttersäure (GABA) auf den oberen Hörbahnstationen des Huhnes (Gallus gallus). PhD-Thesis; Technische Hochschule Darmstadt
Müller CM (1986b) GABA in der Hörbahn des Haushuhnes — biochemische und immunhistochemische Untersuchungen. Verh Dtsch Zool Ges 79:285–286
Müller CM (1987) γ-Aminobutyric acid immunoreactivity in brainstem auditory nuclei of the chicken. Neurosci Lett 77:272–276
Müller CM, Leppelsack H-J (1985) Feature extraction and tonotopic organization in the avian auditory forebrain. Exp Brain Res 59:587–599
Müller CM, Scheich H (1987) GABAergic inhibition increases the neuronal selectivity to natural sounds in the avian auditory forebrain. Brain Res 414:376–380
Müller CM, Scheich H (1988) Contribution of GABAergic inhibition to the response characteristics of auditory units in the avian forebrain. J Neurophysiol (in press)
Mugnaini E, Dahl A-L (1983) Zinc-aldehyde fixation for light-microscopic immunocytochemistry of nervous tissues. J Hislochem Cytochem 31:1435–1438
Oertel WH, Schmechel DE, Mugnaini E, Tappaz ML, Kopin IJ (1981) Immunocytochemical localization of glutamate decarboxylase in rat cerebellum with a new antiserum. Neuroscience 6:2715–2735
Oertel WH, Mugnaini E, Schmechel DE, Tappaz ML, Kopin IJ (1982) The immunocytochemical demonstration of gamma-aminobutyric acid-ergic neurons — methods and application. In: Chan-Palay V, Palay SL (eds) Cytochemical methods in neuroanatomy. Alan R. Liss Inc., New York, pp 297–329
Oksche A, Kirschstein H, Hartwig HG, Oehmke HJ (1974) Secretory parvocellular neurons in the rostral hypothalamus and in the tuberal complex of Passer domesticus. Cell Tissue Res 149:363–370
Pritz MB, Stritzel ME (1986) Percentage of relay and intrinsic neurons in two sensory thalamic nuclei projecting to the noncortical telencephalon in reptiles Caiman crocodilus. Brain Res 376:169–174
Ribak CE (1978) Aspinous and sparsely-spinous stellate neurons in the visual cortex of rats contain glutamic acid decarboxylase. J Neurocytol 7:461–478
Ribak CE, Vaughn JE, Saito K (1978) Immunocytochemical localization of glutamic acid decarboxylase in neuronal somata following colchicine inhibition of axonal transport. Brain Res 140:315–332
Saini KD, Leppelsack H-J (1981) Cell types of the auditory caudomedial neostriatum of the starling (Sturnus vulgaris). J Comp Neurol 198:209–229
Scheich H, Langner G, Bonke D (1979) Responsiveness of units in the auditory neostriatum of the guinea fowl to species-specific calls and synthetic stimuli II. Discrimination of jambus-like calls. J Comp Physiol 132:257–276
Scheich H, Bock W, Bonke D, Langner G, Maier V (1983) Acoustic communication in the guinea fowl (Numida meleagris). In: Ewert J-P, Capranica RR, Ingle DJ (eds) Advances in vertebrate neuroethology. Plenum Press, New York London, pp 731–782
Scopsi L, Larsson L-I (1985) Increased sensitivity in immunocytochemistry. Effects of double application of antibodies and of silver intensification in immunogold and peroxidase-antiperoxidase staining techniques. J Histochem 82:321–329
Singer W (1977) Control of thalamic transmission by corticofugal and ascending reticular pathways in the visual system. Physiol Rev 57:386–420
Skirboll L, Hökfelt T, Norell G, Phillipson O, Kuypers H, Bentivoglio M, Catsman-Berrevoets CE, Visser TJ, Steinbusch H, Verhofstadt A, Cuello AL, Goldstein M, Brownstein M (1984) A method for specific transmitter identification of retrogradely labeled neurons: immunofluorescence combined with fluorescence tracing. Brain Res Rev 8:99–127
Somogyi P, Freund TF, Hodgson AJ, Somogyi J, Beroukas D, Chubb IW (1985) Identified axo-axonic cells are immunoreactive for GABA in the hippocampus and visual cortex of the cat. Brain Res 332:143–149
Stingelin W (1958) Vergleichend morphologische Untersuchungen am Vorderhirn der Vögel auf cytologischer und cytoarchitektonischer Grundlage. Heibig und Lichterhahn, Basel
Thompson GC, Cortez AM, Man-Kit Lam D (1985) Localization of GABA immunoreactivity in the auditory brainstem of guinea pigs. Brain Res 339:119–122
Watanabe T, Simada Z (1971) Picrotoxin: Effect on colliculus auditory neurons. Brain Res 28:582–585
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB 45)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller, C.M. Distribution of GABAergic perikarya and terminals in the centers of the higher auditory pathway of the chicken. Cell Tissue Res. 252, 99–106 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00213830
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00213830