Abstract
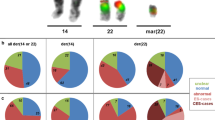
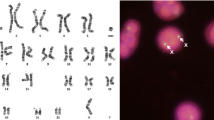
Seventeen patients presenting with either de novo or familial supernumerary marker (mar) 15 chromosomes were shown by fluorescent in situ hybridization techniques (FISH) to have markers derived from and composed entirely of chromosome 15 material. Using a combination of conventional cytogenetics, FISH, Southern blotting and multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods, it was possible to sub-classify the 17 mar(15)s into six distinct morphological and molecular groups. Analysis of DNA and metaphase spreads from the probands and their parents using probes and primers from the pericentromeric and Prader-Willi/Angelman syndromes critical regions (PWS/AS), clearly differentiated between marker 15 s which included the PWS/AS critical regions and those which did not. A direct correlation between the presence of the PWS/AS region in the mar(15) and severe mental retardation was observed. Based on these results, a system of classification of supernumerary marker 15 chromosomes is proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beckmann JS, Tomfohrde J, Barnes RI, Williams M, Broux O, Richard I, Weiggenbach J (1993) A linkage map of human chromosome 15 with an average resolution of 2 cM and containing 55 polymorphic microsatellites. Hum Mol Genet 2: 2019–2030
Berry R, McGavran L, Robinson J, Staley L (1987) Familial duplication of proximal 15q in a Prader-Willi individual and her normal father. Am J Hum Genet 41[Suppl]: A114-A114
Blennow E, Anneren G, Bui TH, Berggren E, Asadi E, Nordenskjold M (1993) Characterization of supernumerary ring marker chromosomes by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Am J Hum Genet 53: 433–442
Buckton KE, Spowart G, Newton MS, Evans HJ (1985) Fortyfour probands with an additional “marker” chromosome. Hum Genet 69: 353–370
Calabro A, Lungarotti MS, Dallapiccola B (1980) A comment on the paper: recurrence of down syndrome associated with microchromosome, by Ramos C, Rivera L, Benitez J, Tejedor E, Sanchez-Cascos A. Hum Genet 53: 287–288
Callen DF, Ringenbergs ML, Fowler JCS, Freemantle J, Haan EA (1990) Small marker chromosomes in man: origin from pericentric heterochromatin of chromosomes 1, 9 and 16. J Med Genet 27: 155–159
Callen DF, Eyre HJ, Ringenbergs ML, Feemantel CJ, Woodroffe P, Haan EA (1991) Chromosomal origin of small ring marker chromosomes in man. Characterization by molecular genetics. Am J Hum Genet 48: 769–782
Callen DF, Eyre H, Yip MY, Freemantle J, Haan EA (1992) Molecular cytogenetic and clinical studies of 42 patients with marker chromosomes. Am J Med Genet 43: 709–715
Choo KH, Earle E, Vissel B, Filby RG (1990) Identification of two distinct subfamilies of alpha satellite DNA that are highly specific for human chromosome 15. Genomics 7: 143–151
Clayton-Smith J, Webb T, Cheng XJ, Pembrey ME, Malcolm S (1993) Duplication of chromosome-15 in the region 15q11–13 in a patient with developmental delay and ataxia with similarities to Angelman syndrome. J Med Genet 30: 529–531
Crolla JA, Dennis NR, Jacobs PA (1992) A non-isotopic in situ hybridisation study of the chromosomal origin of 15 supernumerary marker chromosomes in man. J Med Genet 29: 699–703
De France HF, Beemer FA, Ippel PF (1984) Duplication in chromosome 15q in a boy with the Prader-Willi syndrome; further cytogenetic confusion. Clin Genet 26: 379–382
Dittrich B, Robinson WP, Knoblauch H, Buiting K, Schmidt K, Gillessenkaesbach G, Horsthemke B (1992) Molecular diagnosis of the Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes by detection of parent-of-origin specific DNA methylation in 15q11–13. Hum Genet 90: 313–315
Friedrich U, Nielsen J (1974) Bisatellited extra small metacentric chromosome in newborns. Clin Genet 6: 23–23
Fujita H, Sakamoto Y, Hamamoto Y (1980) An extra idic(15p) (q11) chromosome in Prader-Willi syndrome. Hum Genet 55: 409–411
Hall JG (1990) Genomic imprinting: review and relevance to human diseases. Am J Hum Genet 46: 857–873
Hassold TJ, Jacobs PA (1984) Trisomy in man. Annu Rev Genet 18: 69–97
Higgins MJ, Hungshu W, Shtromas I, Haliotis T, Roder JC, Holden JJA, White BN (1985) Organization of a repetitive human 1. 8 kb Kpnl sequence localized in the heterochromatin of chromosome 15. Chromosoma 93: 77–86
Kuwano A, Mutirangura A, Dittrich B, Buiting K, Horsthemke B, Saitoh S, Niikawa N (1992) Molecular dissection of the PraderWilli/Angelman syndrome region (15q-11) by YAC cloning and FISH analysis. Hum Mol Genet 6: 417–425
Ledbetter DH, Mascarello JT, Riccardi VM, Harper VD, Airhart SD, Strobel RJ (1982) Chromosome 15 abnormalities and the Prader-Willi syndrome: A follow-up report of 40 cases. Am J Hum Genet 34: 278–285
Maraschio P, Cuoco C, Gimelli G, Zuffardi O, Tiepolo L (1988) Origin and clinical significance of inv dup(15). In: The cytogenetics of mammalian autosomal rearrangements. Alan R Liss, New York, pp 615–634
Mattci JF, Mattei MG, Giraud F (1983) Prader-Willi syndrome and chromosome 15. Hum Genet 64: 356–362
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF (1988) A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res 16: 1215–1215
Moses MJ, Karatsis PA, Hamilton AE (1979) Synaptonemal complex analysis of heteromorphic trivalents in lemur hybrids. Chromosoma 70: 141–160
Mutirangura A, Greenberg F, Butler MG, Malcolm S, Nicholls RD, Chakravarti A, Ledbetter DH (1993) Multiplex PCR of 3 dinucleotide repeats in the Prader-Willi-Angelman critical region (15q11-q13) — molecular diagnosis and mechanism of uniparental disomy. Hum Mol Genet 2: 143–151
Ozcelik T, Leff S, Robinson W, Donlon T, Lalande M, Sanjines E, Schinzel A (1992) Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptide N(SNRPN), an expressed gene in the Prader-Willi syndrome critical region. Nat Genet 2: 265–269
Pettigrew AL, Gollin SM, Greenberg F, Riccardi VM, Ledbetter DH (1987) Duplication of proximal 15q as a cause of Prader Willi syndrome. Am J Med Genet 28: 791–802
Pinkel D, Landegent J, Collins C, Fuscoe J, Segraves R, Lucas J, Gray J (1988) Fluroescence in situ hybridization with human chromosome-specific libraries: detection of trisomy 21 and translocations of chromosome 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 9138–9142
Plattner R, Heerema NA, Howardpeebles PN, Miles JH, Soukup S, Palmer CG (1993) Clinical findings in patients with marker chromosomes identified by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Hum Genet 91: 589–598
Polani PE, Crolla JA, Roberts HJ (1989) Meiosis in trisomic female mice with Robertsonian translocations. I. Prophase pairing. Cytogenet Cell Genet 52: 111–117
Prieto F, Badia L, Ribes C, Medina VH (1981) Trisomie 21 par translocation 21/21 chez deux fils d'une mère avec un microchromosome surnumeraire. Ann Genet Paris 24: 117–119
Ramos C, Rivers L, Benitez J, Tejedor E, Sanchez-Cascos A (1979) Recurrence of Down syndrome associated with microchromosome. Hum Genet 49: 7–10
Rauch LA, Nevin NC (1991) Duplication of 15q112 → 15q13 in five cases with different phenotypes. J Med Genet 28: 573–574
Robinson WP, Wagstaff J, Bernasconi F, Baccichetti C, Artifoni L, Franzoni E, Suslak L (1993a) Uniparental disomy explains the occurrence of the Angelman or Prader-Willi syndrome in patients with an additional small inv dup(15) chromosome. J Med Genet 30: 756–760
Robinson WP, Binkert F, Gine R, Vazquez C, Muller W, Rosenkranz W, Schinzel A (1993b) Clinical and molecular analysis of five inv dup(15) patients. Eur J Hum Genet 1: 37–50
Schweizer D, Ambros P, Andrle M (1978) Modification of DAPI banding on human chromosomes by prestaining with a DNA-binding oligopeptide antibiotic, distamycin A. Exp Cell Res 111: 327–332
Speed RM (1984) Meiotic configurations in female trisomy 21 fetuses. Hum Genet 66: 176–180
Telenius H, Pelmear AH, Tunnacliffe A, Carter NP, Behmel A, Fergusonsmith MA, Nordenskjold M (1992) Cytogenetic analysis by chromosome painting using DOP-PCR amplified flow-sorted chromosomes. Gene Chromosome Cancer 4: 257–263
Wallace BMN, Hulten MA (1983) Triple chromosome synapsis in oocytes from a human foetus with trisomy 21. Ann Hum Genet 47: 271–276
Wisniewski LP, Witt ME, Ginsberg-Fellner F, Wilner J, Desnick RJ (1980) Prader-Willi syndrome and a bisatellited derivative of chromosome 15. Clin Genet 18: 42–47
Wulfsberg EA, Sparkes RS, Klisak IJ, Gurfield WB (1982) A 15→1 translocation in a patient mosaic for presence or absence of an isodic (15p)(q11). Am J Mod Genet 13: 417–421
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crolla, J.A., Harvey, J.F., Sitch, F.L. et al. Supernumerary marker 15 chromosomes: a clinical, molecular and FISH approach to diagnosis and prognosis. Hum Genet 95, 161–170 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00209395
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00209395