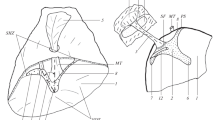
Summary
Electron microscopic studies of the carotid body of the domestic fowl (Gallus gallus domesticus) have shown Type I and Type II cells combined with axons into compact groups. The many Type I cells in the depths of the organ had a body, containing the nucleus, and an elongated, flared process. Some of the Type I cells in the superficial regions tended to be spindle-shaped. Type I cells were characterised by membrane-bound, dense-cored vesicles about 120 nm in diameter. Type II cells invested the Type I cells and had axons embedded in them as in Schwann cells.
The fine structure of the carotid body in the domestic fowl resembles that of the Lovebird (Uroloncha domestica) and of various amphibia and mammals. The possibility is discussed that the Type I cells may have a chemoreceptor or a general secretory function, or even both pathway for functions together. The main role of the Type II cells seems to be to provide a of these axons leading to or from Type I cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, W. E.: The comparative morphology of the carotid body and carotid sinus. Springfield, Ill.: Thomas 1958
Al-Lami, F., Murray, R. G.: Fine structure of the carotid body of Macaca mulatta monkey. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 24, 465–478 (1968a)
Al-Lami, F., Murray, R. G.: Fine structure of the carotid body of normal and anoxic cats. Anat. Rec. 160, 697–718 (1968b)
Battaglia, G.: Ricerche ultrastrutturali sul glomo carotideo del ratto. Arch. ital. Anat. Embriol. 73, 155–186 (1968)
Biscoe, T. J.: Carotid body: structure and function. Physiol. Rev. 51, 437–495 (1971)
Biscoe, T. J., Stehbens, W. E.: Ultrastructure of the carotid body. J. Cell Biol. 30, 563–568 (1966)
Blümcke, S., Rode, J., Niedorf, H. R.: Das Glomus caroticum nach Reizzuständen. Verh. dtsch. Ges. Path. 51, 376–381 (1967)
Chowdhary, D. S.: A comparative study of the carotid sinus of vertebrates. II. The carotid body and carotid sinus of the fowl (Gallus domesticus). Ph. D. Thesis, University of Edinburgh 1953
Fu, S.-K., Tcheng, K.-T.: Fine structure of the endothelial cells of the blood sinusoids in the carotid body. Sci. Sinica 15, 829–835 (1966)
Gould, R. P., Hodges, R. D.: Studies on the fine structure of the avian parathyroid glands and and ultimobranchial bodies. Mem. Soc. Endocr. 19, 567–604 (1971)
Hodges, R. D.: The histology of the fowl. London: Academic Press 1974
Höglund, R.: An ultrastructural study of the carotid body of horse and dog. Z. Zellforsch. 76, 568–576 (1967)
Ishii, K., Oosaki, T.: Fine structure of the chemoreceptor cell in the amphibian carotid labyrinth. J. Anat. (Lond.) 104, 263–280 (1969)
Karnovsky, M. J.: A formaldehyde/glutaraldehyde fixative of high osmolatity for use in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 27, 137A-138A (1965)
King, A. S., King, D. Zoe, Hodges, R. D., Henry, J.: Synaptic morphology of the carotid body of the domestic fowl. Cell Tiss. Res. 162, 459–473 (1975)
Kobayashi, S.: Fine structure of the carotid body of the dog. Arch, histol. jap. 30, 95–120 (1968)
Kobayashi, S.: Catecholamines in the avian carotid body. Experientia (Basel) 25, 1075–1076 (1969a)
Kobayashi, S.: On the fine structure of the carotid body of the bird Uroloncha domestica. Arch. histol. jap. 31, 9–19 (1969b)
Kobayashi, S.: Comparative cytological studies of the carotid body. I. Demonstration of monoamine-storing cells by correlated chromaffin reaction and fluorescence histochemistry Arch. histol. jap. 33, 319–339 (1971a)
Kobayashi, S.: Comparative cytological studies of the carotid body. 2. Ultrastructure of the synapses on the chief cell. Arch. histol. jap. 33, 397–420 (1971b)
Kobayashi, S., Uehara, M.: Occurrence of afferent synaptic complexes in the carotid body of the mouse. Arch. histol. jap. 32, 193–201 (1970)
Kock, L. L. de: On the carotid body of certain birds. Acta anat. (Basel) 35, 161–178 (1958)
Kondo, H.: An electron microscopic study on innervation of the carotid body of Guinea Pig. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 37, 544–562 (1971)
Kondo, H.: On the granule-containing cells in the aortic wall of the young chick. Anat. Rec. 178, 253–266 (1974)
Kose, W.: Über die Carotisdrüse und das chromaffine Gewebe der Vögel. Anat. Anz. 25, 609–617 (1904)
Kose, W.: Die Paraganglien bei den Vögeln. Zweiter Teil. Arch. mikr. Anat. 69, 665–790 (1907)
Morita, E., Chiocchio, S. R., Tramezzani, J. H.: Four types of main cells in the carotid body of the cat. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 28, 399–410 (1969)
Muratori, G.: Ricerche istologische e sperimentali sull' innovazione del tessuto paragangliare annesso al sistema del vago. (Paraganglio carotico; paraganglia iustavagali e intravagali). Boll. Soc. ital. Biol. sper. 7, 1–6 (1932)
Muratori, G.: Contributo istologico all' innervazione della zona arteriosa glomo-carotidea. Arch. ital. Anat. Embriol. 33, 421–442 (1934)
Nonidez, J. P.: The presence of depressor nerves in the aorta and carotid of birds. Anat. Ree. 62, 47–73 (1935)
Pearse, A. G. E.: The cytochemistry and ultrastructure of polypeptide hormone-producing cells of the APUD series and the embryologic, physiologic and pathologic implications of the concept. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 17, 303–313 (1969)
Pearse, A. G. E., Polak, J. M., Rost, F. W. D., Fontaine, J., Le Lièvre, C., Le Douarin, N.: Demonstration of the neural crest origin of Type I (APUD) cells in the avian carotid body, using a cytochemical marker system. Histochemie, 34, 191–203 (1973)
Verna, A.: Terminaisons nerveuses afférentes et efférentes dans le glomus carotidien du lapin. J. Microscopie, 16, 299–308 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors are grateful to Mr. R. P. Gould of the Department of Anatomy, Middlesex Hospital Medical School for permission to use some of his and Dr. Hodges' original material in the illustrations. Dr. Hodges also wishes to thank the A.R.C. and the University of London Central Research Fund for financial assistance. We are also most appreciative of the photographic assistance of J. Geary.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hodges, R.D., King, A.S., King, D.Z. et al. The general ultrastructure of the carotid body of the domestic fowl. Cell Tissue Res. 162, 483–497 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00209348
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00209348