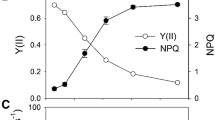
Abstract
Action spectra in the red region of the spectrum for light-dependent cytosolic alkalization in leaves of C3 plants which also received a low background of blue light differed from the action spectra for light-dependent vacuolar acidification. Light above 680 nm was less effective in supporting the cytosolic alkalization reaction than light below 680 nm. In contrast, in leaves illuminated in CO2-free air the light-dependent vacuolar acidification exhibited a maximum at or even above 700 nm. When photorespiratory carbohydrate oxidation was suppressed in low oxygen, a substantially changed action spectrum of the acidification reaction resembled in shape that of the cytosolic alkalization with the exception that it was extended towards the far-red. From the presented data and from previously published data (Yin et al., 1990b, Planta 182, 253–261; Yin et al., 1990c, Planta 182, 262–269) it is concluded that in the presence of a weak background of blue light, and in the absence of CO2 which drains electrons from the electron transport chain, cyclic photophosphorylation induced by far-red light permits increased export of dihydroxyacetone phosphate from the chloroplasts into the cytosol where its oxidation increases the cytosolic energy state giving rise to increased proton transport across the tonoplast. The data do not lend support to the view that export of malate from the chloroplasts and its oxidation in the mitochondria contribute significantly to cytosolic energization in the light.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CDCF:
-
5-(and-6)-carboxy-2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein
- DHAP:
-
dihydroxyacetone phosphate
- OAA:
-
oxaloacetate
- PGA:
-
phosphoglycerate
References
Delieu, T., Walker, D.A. (1972) An improved cathode for the measurement of photosynthetic oxygen evolution by isolated chloroplasts. New Phytol. 71, 201–225
Hampp, R. (1985) ADP, AMP: Luminometric method. In: Methods of enzymatic analysis, vol. 7, pp. 371–379, Bergmeyer, H.U., Bergmeyer, J., Graßl, M., eds. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, FRG
Heldt, H.W., Flügge, U.I. (1987) Subcellular transport of metabolites in plant cells. In: Biochemistry of plants, vol. 12, pp.49–85, Davies, D.D., ed. Academic Press, New York
Jensen, R.G., Bassham J.A. (1966) Photosynthesis by isolated chloroplasts. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. USA 56, 1095–1101
Li, Y.-S., Gibbs, M. (1985) Pyridoxal phosphate and 3-phosphoglycerate overcome the d-glyceraldehyde inhibition of CO2 fixation by intact spinach chloroplasts. (Abstr.) Plant Physiol. 77, Suppl., 227
Lüttge, U. (1973) Stofftransport der Pflanzen. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
MacRobbie, E.A.C. (1971) Fluxes and compartmentation in plant cells. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 22, 75–96
Michal, G. (1984): d-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, dihydroxyacetone phosphate and d-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. In: Methods of enzymatic analysis, vol. 4, pp. 342–350, Bergmeyer, H.U., Bergmeyer, J., Graßl, M., eds. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, FRG
Racker, E. (1984) l-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. In: Methods of enzymatic analysis, vol. 4, pp. 561–565, Bergmeyer, H. U., Bergmeyer, J., Graßl, M., eds. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, FRG
Raven, J.A. (1976) Transport in algal cells. In: Encyclopedia of plant physiology, N.S., vol. IIA: Transport in plants II, pp.129–188, Lüttge, U., Pitman, M.G., eds. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Stokes, D.M., Walker, D.A. (1972) Photosynthesis by isolated chloroplasts. Inhibition by dl-glyceraldehyde of carbon dioxide assimilation. Biochem. J. 128, 1147–1157
Sze, H. (1985) H+-translocating ATPases: Advances using membrane vesicles. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 36, 175–208
Wulff, K., Döppen, W. (1985) ATP: Luminometric method. In: Methods of enzymatic analysis, vol. 7, pp. 357–364, Bergmeyer, H.U., Bergmeyer, J., Graßl, M., eds. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, FRG
Yin, Z.-H., Neimanis, S., Wagner, U., Heber, U. (1990a) Light-dependent pH changes in leaves of C3 plants. I. Recording pH changes in various cellular compartments by fluorescent probes. Planta 182, 244–252
Yin, Z.-H., Neimanis, S., Heber, U. (1990b) Light-dependent pH changes in leaves of C3 plants. II. CO2- and O2-dependence of pH changes in the cytosol and vacuoles. Planta 182, 253–261
Yin, Z.-H., Dietz, K.-J., Heber, U. (1990c) Light-dependent pH changes in leaves of C3 plants. III. Effect of inhibitors of photosynthesis and of the development state of the photosyn-thetic apparatus on cytosolic and vacuolar pH changes. Planta 182, 262–269
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was performed within the Sonderforschungsbereiche 176 and 251 of the University of Würzburg. Z.-H. Y. acknowledges support by the Leibniz program of the Deutsche Forschungs-gemeinschaft.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, ZH., Siebke, K. & Heber, U. Light-dependent pH changes in leaves of C3 plants. Planta 184, 30–34 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00208232
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00208232