Abstract
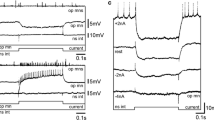
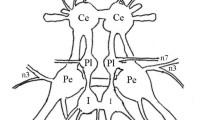
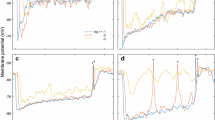
Fifteen local spiking interneurons (LSIs) and twentyone local non-spiking interneurons (LNIs) were identified in the terminal abdominal ganglion (TAG) of the cricket Gryllus bimaculatus on the basis of intracellular recording and staining (Figs. 1, 5, 6). Although the majority of LNIs showed sharp directionalities (Fig. 7) the LSIs did not (Fig. 3). The directionality of LNIs varied with the recording sites within a single cell (Fig. 8). Electrical stimulations of the cereal sensory nerve suggested that the LNIs are connected monosynaptically with the sensory afferents of both the cerci, and that LSIs may possess a variety of bilateral combinations of polysynaptic connections with the sensory afferents. We found that the spiking and the non-spiking local interneurons in the cereal sensory system differ not only in their membrane properties, but also in their afferent connections, and concluded that their differing connectivity to the sensory afferents will associate them with different roles in signal processing.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TAG :
-
terminal abdominal ganglion
- LSI :
-
local spiking interneuron
- LNI :
-
local non-spiking interneurons
- CNS :
-
central nervous system
- PSP :
-
post synaptic potential
- GI :
-
giant interneuron
References
Baba Y, Hirota K, Yamaguchi T (1991) Morphology and response properties of windsensitive nongiant interneurons in the terminal abdominal ganglion of crickets. Zool Sci 8:437–445
Bodner DA, Miller JP, Jacobs GA (1991) Anatomy and physiology of identified wind-sensitive local interneurons in the cricket cereal sensory system. J Comp Physiol A 168:553–564
Boyan GS (1988) Presynaptic inhibition of identified wind-sensitive afferents in the cereal system of the locust. J Neurosci 8:2748–2757
Boyan GS, Ball EE (1986) Wind-sensitive interneurons in the terminal abdominal ganglion of praying mantis. J Comp Physiol A 159:773–789
Boyan GS, Ball EE (1989) Parallel inputs shape the response of a giant interneuron in the cereal system of the locust. J Insect Physiol 35:305–312
Boyan GS, Williams JDL, Ball EE (1989) The wind-sensitive cereal receptor/giant interneurone system of the locust, Locusta migratoria. IV. The non-giant interneurons. J Comp Physiol A 165:539–552
Burrows M (1990) Processing of mechanosensory signals in local reflex pathways of the locust. J Exp Biol 146:209–227
Camhi JM (1980) The escape system of the cockroach. Sci Amer 243:158–172
Edwards JS, Palka J (1974) The cerci and abdominal giant fibers of the house cricket Acheta domesticus. I. Anatomy and physiology of normal adults. Proc R Soc Lond B 185:83–103
Hirota K, Sonoda Y, Baba Y, Yamaguchi T (1993) Distinction in morphology and behavioral role between dorsal and ventral groups of cricket giant interneurons. Zool Sci 10: 705–709
Jacobs GA, Miller JP, Murphey RK (1986) Integrative mechanisms controlling directional sensitivity of identified sensory interneuron. J Neurosci 6:2298–2311
Jacobs GS, Murphey RK (1987) Segmental origins of the cricket giant interneuron system. J Comp Neurol 265:145–157
Kanou M, Shimozawa T (1984) A threshold analysis of cricket cereal interneurons by an alternating air-current stimulus. J Comp Physiol A 154:357–365
Kobashi M, Yamaguchi T (1981) Local non-spiking interneurons in the cercus-to-giant interneurons system of the crickets. Naturwissenschaften 71:154–155
Kondoh Y, Hisada M (1986) Regional specialization in synaptic input and output in an identified local non-spiking interneuron of crayfish revealed by light and electron microscopy. J Comp Neurol 251:334–348
Kondoh Y, Morishita H, Arima T, Okuma J, Hasegawa Y (1991) White noise analysis of graded response in a wind-sensitive non-spiking interneuron of the cockroach. J Comp Physiol A 168:429–443
Levine RB, Murphey RK (1980) Pre- and post synaptic inhibition of identified giant interneurons in the cricket (Acheta domesticus). J Comp Physiol 135:269–282
Matsumoto SG, Murphey RK (1977) The cercus-to-giant interneuron system of crickets. IV. Patterns of connectivity between receptors and the medial giant interneuron. J Comp Physiol 119:319–330
Reichert H, Wine JJ (1983) Coordination of lateral giant and nongiant systems in crayfish escape behavior. J Comp Physiol 153:3–15
Sbrenna G (1971) Postembryonic growth of ventral nerve cord in Schistocerca gregaria Forsk. (Orthoptera: Acrididae). Boll Zool 38:49–74
Shepherd D (1988) The synaptic origins of receptive field properties in the cricket cereal sensory system. J Comp Physiol A 162:1–11
Siegler MVS, Burrows M (1979) The morphology of local non-spiking interneurons in metathoracic ganglion of the locust. J Comp Neurol 183:121–148
Takahashi TT (1989) The neural coding of auditory space. J Exp Biol 146: 307–322
Takahata M, Hisada M (1991) Local non-spiking interneurons as a separate integrator of motoneurons in crayfish. Comp Biochem Physiol A 98:73–78
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baba, Y., Hirota, K., Yamaguchi, T. et al. Differing afferent connections of spiking and nonspiking wind-sensitive local interneurons in the terminal abdominal ganglion of the cricket Gryllus bimaculatus . J Comp Physiol A 176, 17–30 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00197749
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00197749