Summary
Auditory response properties were studied in the superior colliculus (SC) of the echolocating horseshoe bat Rhinolophus rouxi, a long CF-FM bat, by the use of stationary, dichotic stimuli.
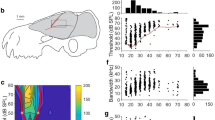
The most striking finding in the horseshoe bat was an enormous overrepresentation of neurons with best frequencies in the range of the constant frequency component of the species specific echolocation call (72% of the auditory neurons). These neurons had response thresholds as low as 0 dB SPL and were narrowly tuned with Q10 dB — values up to 400, just as in the nuclei of the primary auditory pathway in this species. This overrepresentation may suggest the importance of the superior colliculus in the context of echolocation behavior.
While noise stimuli were not particularly effective, other auditory response properties were similar to those described in other mammals. 65% of the SC neurons in the horseshoe bat responded only to monaural stimulation of one ear, primarily the contralateral one. 32% of the neurons received monaural input from both ears. The proportion of neurons responsive to ipsilateral stimulation (41%) was rather high. Mean response latency was 8.9 ms for contralateral stimulation.
A tonotopic organization is lacking, but high-frequency neurons are less frequent in rostral SC.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CF :
-
constant frequency component of echolocation call;
- >CF :
-
frequencies above range of CF-component
- FM :
-
frequency modulated component of echolocation call
- <FM :
-
frequencies below range of FM-component
- RF :
-
resting frequency of an individual bat
- Rh.r. :
-
Rhinolophus rouxi
- SC :
-
superior colliculus
References
Allom N, Wollberg Z (1978) Responses of cells in the superior colliculus of the squirrel monkey to auditory stimuli. Brain Res 159:321–330
Carlile S, Pettigrew AG (1987) Distribution of frequency sensitivity in the superior colliculus of the guinea pig. Hearing Res 31:123–136
Casagrande VA, Harting JK, Hall WC, Diamond IT, Martin GF (1972) Superior colliculus of the tree shrew: a structural and functional subdivision into superficial and deep layers. Science 177:444–447
Casseday JH, Kobler JB, Isbey SF, Covey E (1989) Central acoustic tract in an echolocating bat: An extralemniscal auditory pathway to the thalamus. J Comp Neurol 287:247–259
Chalupa LM, Rhoades RW (1977) Responses of visual, somatosensory, and auditory neurons in the golden hamster's superior colliculus. J Physiol 270:595–626
Cotter JR (1985) Retinofugal projections of the big brown bat, Eptesicus fuscus, and the neotropical fruit bat, Artibeus jamaicensis. Am J Anat 172:105–124
Cotter JR, Pentney RJP (1979) Retinofugal projections of nonecholocating (Pteropus giganteus) and echolocating (Myotis lucifugus) bats. J Comp Neurol 184:381–400
Covey E, Hall WC, Kobler JB (1987) Subcortical connections of the superior colliculus in the mustache bat, Pteronotus parnellii. J Comp Neurol 263:179–197
Dean P, Redgrave P, Westby GWM (1989) Event or emergency? Two response systems in the mammalian superior colliculus. Trends Neurosci 12:137–147
Dräger UC, Hubel DH (1975) Responses to visual stimulation and relationship between visual, auditory and somatosensory inputs in mouse superior colliculus. J Neurophysiol 38:690–713
Edwards SB, Ginsburg CL, Stein BE (1979) Sources of subcortical projections to the superior colliculus in the cat. J Comp Neurol 184:309–330
Feng AS, Vater M (1985) Functional organization of the cochlear nucleus of rufous horseshoe bats: frequencies and internal connections are arranged in slabs. J Comp Neurol 225:529–553
Graham J, Pearson HE, Berman N, Murphy EH (1981) Laminar organization of superior colliculus in the rabbit: A study of receptive field properties of single units. J Neurophysiol 45:915–932
Hirsch JA, Chan JCK, Yin TCT (1985) Responses of neurons in the cat's superior colliculus to acoustic stimuli: I. Monaural and binaural response properties, J Neurophysiol 53:726–745
Huerta MF, Harting JK (1984) The mammalian superior colliculus: studies of its morphology and connections. In : Vanegas H (ed) Comparative neurology of the optic tectum. Plenum Press, New York, pp 687–773
Jen PHS, Sun X, Kamada T, Zhang S, Shimozawa T (1984) Auditory response properties and spatial response areas of superior collicular neurons in the FM bat, Eptesicus fuscus. J Comp Physiol A 154:407–413
King AJ, Hutchings ME (1987) Spatial response properties of acoustically responsive neurons in the superior colliculus of the ferret: A map of auditory space. J Neurophysiol 57:596–624
King AJ, Palmer AR (1983) Cells responsive to free field auditory stimuli in guinea pig superior colliculus: distribution and response properties. J Physiol 342:361–381
Kobler JB, Isbey SF, Casseday JH (1987) Auditory pathways to the frontal cortex of the mustache bat, Pteronotus parnellii. Science 236:824–826
Lund RD, Lund JS (1965) The visual system of the mole Talpa europaea. Exp Neurol 13:302–316
Mast TE, Chung DY (1973) Binaural interactions in the superior colliculus of the chinchilla. Brain Res 62:227–230
Metzner W (1988) Die funktioneile Bedeutung tegmentaler Neurone bei der Echoortung der Hufeisennase Rhinolophus rouxi. PhD thesis, Universität München
Metzner W, Radtke-Schuller S (1987) The nuclei of the lateral lemniscus in the rufous horseshoe bat, Rhinolophus rouxi. J Comp Physiol A 160:395–411
Middlebrooks JC (1987) Binaural mechanisms of spatial tuning in the cat's superior colliculus distinguished using monaural occlusion. J Neurophysiol 57:688–701
Middlebrooks JC, Knudsen EI (1984) A neural code for auditory space in the cat's superior colliculus. J Neurosci 4:2621–2634
Möller J, Neuweiler G, Zöller H (1978) Response characteristics of inferior colliculus neurons of the awake CF-FM bat Rhinolophus ferrumequinum I. Single tone stimulation. J Comp Physiol 125:217–225
Neuweiler G (1970) Neurophysiologische Untersuchungen zum Echoortungssystem der Großen Hufeisennase Rhinolophus ferrumequinum. Z vergl Physiol 67:273–306
Neuweiler G, Bruns V, Schuller G (1980) Ears adapted for the detection of motion, or how echolocating bats have exploited the capacities of the mammalian auditory system. J Acoust Soc Am 68:741–753
Neuweiler G, Metzner W, Heilmann U, Rübsamen R, Eckrich M, Costa HH (1987) Foraging behavior and echolocation in the rufous horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus rouxi) of Sri Lanka. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 20:53–67
Northmore DPM, Levine ES, Schneider GE (1988) Behavior evoked by electrical stimulation of the hamster superior colliculus. Exp Brain Res 73:595–605
O'Neill WE, Suga N (1982) Encoding of target range and its representation in the auditory cortex of the mustached bat. J Neurosci 2:17–31
Palmer AR, King AJ (1985) A monaural space map in the guinea pig superior colliculus. Hearing Res 17:267–280
Pentney RP, Cotter JR (1976) Retinofugal projections in an echolocating bat. Brain Res 115:479–484
Pollak GD, Casseday JD (1989) The neural basis of echolocation in bats. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, New York
Poussin C, Schlegel P (1984) Directional sensitivity of auditory neurons in the superior colliculus of the bat, Eptesicus fuscus, using free field sound stimulation. J Comp Physiol A 154:253–261
Rauschecker JP, Harris LR (1989) Auditory and visual neurons in the cat's superior colliculus selective for the direction of apparent motion stimuli. Brain Res 490:56–63
Reimer K (1987) Coding of sinusoidally amplitude modulated acoustic stimuli in the inferior colliculus of the rufous horseshoe bat, Rhinolophus rouxi. J Comp Physiol A 161:305–313
Reimer K (1989a) Retinofugal projections in the rufous horseshoe bat, Rhinolophus rouxi. Anat Embryol 180:89–98
Reimer K (1989b) Bedeutung des Colliculus superior bei der Echoortung der Fledermaus Rhinolophus rouxi. PhD thesis, Universität München
Schlegel P (1977) Calibrated earphones for the echolocating bat, Rhinolophus ferrumequinum. J Comp Physiol 118:353–356
Schuller G (1980) Hearing characteristics and Doppler-shift compensation in South Indian CF-FM bats. J Comp Physiol 139:349–356
Schuller G, Pollak GD (1979) Disproportionate frequency representation in the inferior colliculus of Doppler compensating greater horseshoe bats: Evidence for an acoustic fovea. J Comp Physiol 132:47–54
Schuller G, Beuter K, Schnitzler HU (1974) Response to frequency shifted artificial echoes in the bat, Rhinolophus ferrumequinum. J Comp Physiol 89:275–286
Schuller G, Radtke-Schuller S, Betz M (1986) A stereotaxic method for small animals using experimentally determined reference profiles. J Neurosci Meth 18:339–350
Schuller G, Covey E, Casseday JH (1991) Auditory pontine grey: connections and response properties in the horseshoe bat. Eur J Neurosci (submitted)
Simmons JA (1969) Acoustic radiation patterns for the echolocating bats Chilonycteris rubiginosa and Eptesicus fuscus J Acoust Soc Am 46:1054–1056
Shimozawa T, Sun X, Jen PHS (1984) Auditory space representation in the superior colliculus of the big brown bat Eptesicus fuscus. Brain Res 311:289–296
Sparks DL (1986) Translation of sensory signals into commands for control of saccadic eye movements: Role of primate superior colliculus. Physiol Rev 66:118–171
Sparks DL (1988) Neural cartography: Sensory and motor maps in the superior colliculus. Brain Behav Evol 31:49–56
Sparks DL, Nelson JS (1987) Sensory and motor maps in the mammalian superior colliculus. Trends Neurosci 10:312–317
Stein BE (1984) Multimodal representation in the superior colliculus and optic tectum. In: Vanegas H (ed) Comparative neurology of the optic tectum. Plenum Press, New York, pp 819–841
Sun X, Jen PHS, Kamada T (1983) Neurons in the superior colliculus of echolocating bats respond to ultrasonic signals. Brain Res 275:148–152
Suthers R A, Braford MR (1980) Visual systems and the evolutionary relationships of the Chiroptera. Proc 5th Intern Bat Res Conf, pp 331–346
Tiao YC, Blakemore C (1976) Functional organization in the superior colliculus of the golden hamster. J Comp Neurol 168:483–504
Wise LZ, Irvine DRF (1983) Auditory response properties of neurons in deep layers of cat superior colliculus. J Neurophysiol 3:674–685
Wise LZ, Irvine DRF (1985) Topographic organization of interaural intensity difference sensitivity in deep layers of cat superior colliculus: implications for auditory spatial representation. J Neurophysiol 54:185–211
Wong D (1984) Spatial tuning of auditory neurons in the superior colliculus of the echolocating bat, Myotis lucifugus. Hearing Res 16:261–270
Wurtz RH, Albano JE (1980) Visual-motor functions of the primate superior colliculus. Annu Rev Neurosci 3:189–226
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reimer, K. Auditory properties of the superior colliculus in the horseshoe bat, Rhinolophus rouxi . J Comp Physiol A 169, 719–728 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00194900
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00194900