Abstract
-
1.
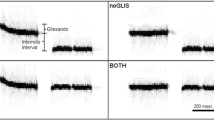
Male bullfrogs at two different natural calling sites were presented with playbacks of synthetic advertisement calls differing in phase spectra. Sounds were presented in a ABA design to analyze the ability of the animals to perceive changes in repeated series of stimuli.
-
2.
The number of individual croaks in an answering call significantly increased over repeated presentations of two of the three stimulus phase types in condition A1. There were significantly fewer croaks to the third stimulus. These data suggest that two stimuli were perceived in a similar manner.
-
3.
Latency of calling to stimuli presented in conditions A and B changed in response to shifts in phase spectrum at a low density calling site. These differences were significant when comparing latency to playbacks where shifts in the phase spectrum changed the temporal fine-structure and waveform periodicity of the stimulus.
-
4.
The increase in number of croaks and decrease in response latency across condition A1 and the increase in latency in condition B suggest that discrimination may take the form of stimulus-specific sensitization. In this context, sensitization might reflect an increase in arousal due to repeated presentation of a salient stimulus.
-
5.
The operation of a hypothetical ‘mating call detector,’ based on linear summation of temporal responses from the eighth nerve, provides output similar to the behavioral results.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FFT :
-
fast Fourier transform
- SPL :
-
sound pressure level
- ACF :
-
autocorrelation function
References
Allan SE, Simmons AM (1994) Temporal features mediating call recognition in the green treefrog, Hyla cinerea: Amplitude modulation. Anim Behav 47: 1073–1086
Bilsen FA (1973) On the influence of the number and phase of harmonics on the perceptibility of the pitch of complex signals. Acustica 28: 60–65
Bodnar DA (1996) The separate and combined effects of harmonic structure, phase, and FM on female preferences in the barking treefrog (Hyla gratiosa). J Comp Physiol A 178: 173–182
Bodnar DA, Capranica RR (1994) Encoding of phase spectra by the peripheral auditory system of the bullfrog. J Comp Physiol A 174: 157–171
Buunen TJF, Festen JM, Bilsen FA, van den Brink G (1974) Phase effects in a three-component signal. J Acoust Soc Am 55: 297–303
Capranica RR (1965) The evoked vocal response of the bullfrog: A study of communication by sound. MIT Press, Cambridge MA
Capranica RR (1968) The vocal repertoire of the bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana). Behaviour 31: 302–325
Capranica RR, Moffat AJM (1983) Neurobehavioral correlates of sound communication in anurans. In: Ewert JP, Capranica RR, Ingle DJ (eds) Advances in vertebrate neuroethology. Plenum Press, New York, pp 701–730
Fay RR (1988) Hearing in vertebrates: A psychophysical databook. Hill-Fay Associates, Winnetka, IL
Gerhardt HC (1978) Mating call recognition in the green treefrog (Hyla cinerea): the significance of some fine-temporal properties. J Exp Biol 74: 59–73
Gerhardt HC (1981) Discrimination of intermediate sounds in a synthetic call continuum by female green treefrogs. Science 199: 1089–1092
Gerhardt HC (1982) Sound pattern recognition in some North American treefrogs (Anura: Hylidae): Implications for mate choice. Am Zool 22: 581–595
Gerhardt HC (1988) Acoustic properties used in call recognition by frogs and toads. In: Fritzsch B, Ryan MJ, Wilczynski W, Hetherington TE, Walkowiak W (eds) The evolution of the amphibian auditory system. Wiley, New York, pp 455–483
Horst JW, Javel E, Farley GR (1990) Coding of spectral fine structure in the auditory nerve. II: Level-dependent nonlinear responses. J Acoust Soc Am 88: 2656–2681
Lundeen C, Small AM (1984) The influence of temporal cues on the strength of periodicity pitches. J Acoust Soc Am 75: 1578–1587
Megela AL, Capranica RR (1983) A neural and behavioral study of auditory habituation in the bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana. J Comp Physiol 151: 423–434
Megela-Simmons A (1984) Behavioral vocal response thresholds to mating calls in the bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana. J Acoust Soc Am 76: 676–681
Moore BCJ (1977) Effects of relative phase of the components on the pitch of three-component complex tones. In: Evans EF, Wilson JP (eds) Psychophysics and physiology of hearing. Academic Press, New York, pp 349–358
Mudry KM, Constantine-Paton M, Capranica RR (1977) Auditory sensitivity of the diencephalon of the leopard frog (Rana p. pipiens). J Comp Physiol 114: 1–13
Pumplin J (1985) Low-noise noise. J Acoust Soc Am 88: 100–104
Rose GJ, Capranica RR (1984) Processing amplitude-modulated sounds by the auditory midbrain of two species of toads: matched temporal filters. J Comp Physiol A 154: 211–219
Schwartz JJ, Simmons AM (1990) Encoding of a spectrally complex communication sound in the bullfrog's auditory nerve. J Comp Physiol A 166: 489–499
Sidman M (1960) Tactics of scientific research. Basic Books, New York
Simmons AM, Schwartz JJ, Ferragamo M (1992) Auditory nerve representation of a complex communication sound in background noise. J Acoust Soc Am 91: 2831–2844
Simmons AM, Reese G, Ferragamo M (1993a) Periodicity extraction in the anuran auditory nerve. II. Phase and temporal fine-structure. J Acoust Soc Am 93: 3374–3389
Simmons AM, Buxbaum RC, Mirin MP (1993b) Perception of complex sounds by the green treefrog, Hyla cinerea: envelope and fine-structure cues. J Comp Physiol A 173: 321–327
Thompson RF, Spencer WA (1966) Habituation: A model phenomenon for the study of neuronal substrates of behavior. Psychol Rev 173: 16–43
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hainfeld, C.A., Boatright-Horowitz, S.L., Boatright-Horowitz, S.S. et al. Discrimination of phase spectra in complex sounds by the bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana). J Comp Physiol A 179, 75–87 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193436
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193436