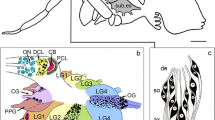
Summary
The presence of c-fos, a marker for cell activation, was investigated in cerebral neurons actively expressing ecdysteroid receptors during larval-pupal development in the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. Colocalization was accomplished by ecdysteroid autoradiography using the tritiated high affinity 20-hydroxyecdysone agonist ponasterone A and immunocytochemistry with an antibody to a peptide sequence which is highly conserved in both human and murine c-fos. Immunoreactivity to a c-fos-like protein(s) was present in nuclei of many neurons of all the developmental stages examined. However, with the exception of the optic lobe, cells expressing nuclear ecdysteroid receptors were more immunoreactive than non-ecdysteroid-binding neurons. These data suggest that ecdysteroid-induced gene activation and translation may involve c-fos expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrosio L, Mahowald A, Perimon N (1989) Requirement of the Drosophila raf homologue for torso function. Nature 342:288–291
Ashburner M, Chihara C, Meltzer P, Richards G (1974) Temporal control of puffing activity in polytene chromosomes. Symp Quant Biol 38:655–662
Bidmon H-J, Koolman J (1989) Ecdysteroid receptors located in the central nervous system of an insect. Experientia 45:106–109
Bidmon H-J, Sliter TJ (1990) The ecdysteroid receptor. Int J Invertebr Repr Dev 18:13–27
Bidmon H-J, Stumpf WE, Granger NA (1990a) Uptake and binding of ponasterone A in the brain of fifth stadium Manduca sexta larvae. In: Borkovec AB, Kelly TJ (eds) Insect neurochemistry and neurophysiology. Humana Press, Clifton New Jersey, pp 405–408
Bidmon H-J, Stumpf WE, Bollenbacher WE, Granger NA (1990b) Co-localization of ecdysteroid receptors (ER) and 29 K-prothoracicotropic hormone (PTTH) in the neuroendocrine complex of Manduca sexta. Soc Neurosci [Abstr] 16:325
Bidmon H-J, Stumpf WE, Seifert G, Granger NA (1990c) Organund Zell-speciflsche Induktion von Ecdysteroid-Rezeptoren wahrend der postembryonalen Entwicklung von Manduca sexta (Lepidoptera). Verb Dtsch Zool Ges 83:443–444
Bidmon H-J, Stumpf WE, Granger NA (1991) Ecdysteroid binding sites localized by autoradiography in the central nervous system of precommitment fifth stadium Manduca sexta larvae. Cell Tissue Res 263:183–194
Bohmann D. Bos TJ, Admon A, Nishimura T, Vogt PK, Tjian R (1987) Human proto-oncogene c jun encodes a DNA binding protein with structural and functional properties of transcription factor AP-1. Science 238:1386–1392
Bollenbacher WE (1988) The interendocrine regulation of larval-pupal development in the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta: A model. J Insect Physiol 34:941–948
Buttyan R, Zakeri Z, Lockshin R, Wolgemuth D (1988) Cascade induction of c-fos, c-myc, and heat shock 70K transcripts during regression of the rat ventral prostate. Mol Endocrinol 2:650–657
Clever U, Karlson P (1960) Induktion von Puff-Veränderungen in den Speicheldrüsenchromosomen von Chironomus tentans durch Ecdyson. Exptl Cell Res 20:623–626
Curran T, Morgan JI (1985) Superinduction of c-fos by nerve growth factor in the presence of peripherally active benzodiazepine. Science 229:1265–1268
Fahrbach SE, Truman JW (1989) Autoradiographic identification of ecdysteroid-binding cells in the nervous system of the moth Manduca sexta. J Neurobiol 20:681–702
Greenberg ME, Ziff EB, Greene LE (1986) Stimulation of neuronal acetylcholine receptors induces rapid gene transcription. Science 234:80–83
Halazonetis TD, Georgopoulos K, Greenberg ME, Leder P (1988) c-jun dimerizes with itself and with c-fos, forming complexes of different DNA binding affinities. Cell 55:917–924
Handler AM, Maroy P (1989) Ecdysteroid receptors in Drosophila melanogaster adult females. Mol Endocrinol 63:103–109
Hannink M, Donoghue DJ (1988) Autocrine stimulation by the v-sis gene product requires a ligand-receptor interaction at the cell surface. J Cell Biol 107:287–298
Hoffman GE, Lee WS, Attardi B, Yann V, Fitzsimmons MD (1990) Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone neurons express c-fos antigen after steroid activation. Endocrinology 126:1736–1741
Koistinaho J, Yang G (1990) Induction of c-fos-like immunoreactivity in the rat and hamster pineal gland after the onset of darkness. Histochemistry 95:73–76
Lee W, Mitchell P, Tjian R (1987) Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell 49:741–752
Lepesant J-A, Richards G (1989) Ecdysteroid-regulated genes. In: Koolman J (ed) Ecdysone. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart, pp 355–367
Levine RB, Weeks JC (1990) Hormonally mediated changes in simple reflex circuits during metamorphosis. J Neurobiol 21:1022–1036
Manetto V, Perry G, Tabaton M, Mulvihill P, Fried V, Smith HT, Gambetti P, Autilio-Gambetti L (1988) Ubiquitin is associated with abnormal cytoplasmic filaments characteristic of neurogenerative disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:4501–4505
Morgan JI, Curran T (1986) Role of ion flux in the control of c-fos expression. Nature 322:552–555
Mori H, Kondo J, Ihara I (1987) Ubiquitin is a component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease. Science 235:1641–1644
Morrison DK, Kaplan DR, Escobedo JA, Rapp UR, Roberts TM, Williams LT (1989) Direct activation of the serine/tyrosine phosphorylation by the PDGF β-receptor. Cell 58:649–657
Nakabeppu Y, Ryder K, Nathans D (1988) DNA binding activities of three murine Jun proteins: stimulation by fos. Cell 55:907–915
Perkins KK, Dailey GM, Tjian R(1988) Novel jun- and fos-related proteins in Drosophila are functionally homologues to enhancer factor AP-1. EMBO J 7:4265–4273
Presley RW, Menetrey D, Levine JD, Basbaum AI (1990) Systemic morphine suppressed noxious stimulus-evoked fos protein like immunoreactivity in rat spinal cord. J Neurosci 10:323–335
Richards G (1981) Insect hormones in development. Biol Rev 56:501–549
Riddiford LM (1987) Hormonal control of sequential gene expression in insect epidermis. In: Law JH (ed) Molecular entomology. AR Liss Publ, New York, pp 211–222
Ryder K, Nathans D (1988) Induction of protooncogene c-jun by serum growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:8464–8467
Schwartz LM, Myer A, Kosz L, Engelstein M, Meier C (1990) Activation of polyubiquitin gene expression during developmentally programmed cell death. Neuron 5:411–419
Segraves WA, Hogeness DS (1990) The 75E ecdysone-inducible gene responsible for the 75B early puff in Drosophila encodes two new members of the steroid receptor superfamily. Genes Dev 4:204–219
Sprenger F, Stevens LM, Nüsslein-Vollhard C (1989) The Drosophila gene torso encodes a putative receptor tyrosine kinase. Nature 338:478–483
Stachowiak MK, Sar M, Tuominen RK, Jiang H-K, An S, Iadarola MJ, Poisner AM, Hong JS (1990) Stimulation of adrenal medullary cells in vivo and in vitro induces expression of c-fos protooncogene. Oncogene 5:69–73
Stumpf WE, Duncan GE (1990) High-resolution autoradiographic mapping of drug and hormone receptors. In: Conn PM (ed) Methods in neuroscience, vol 3. Academic Press, New York, pp 35–50
Wasylyk C, Wasylyk B, Heideker G, Huleihel M, Rapp UR (1989) Expression of raf oncogenes activates the PEA-1 transcription factor motif. Mol Cell Biol 9:2247–2250
Zhang K, Chaillet JR, Perkins LA, Halazonetis TD, Perrimon N (1990) Drosophila homolog of the mammalian jun oncogene is expressed during embryonic development and activates transcription in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:6281–6285
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: H.-J. Bidmon
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bidmon, HJ., Granger, N.A. & Stumpf, W.E. Co-localization of ecdysteroid receptors and c-fos-like protein in the brain of Manduca sexta larvae. Roux's Arch Dev Biol 200, 149–155 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00190234
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00190234