Abstract
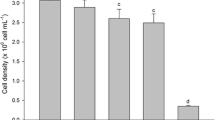
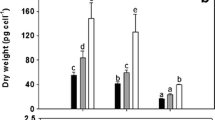
Discs of thallus cut from the macroalga Ulva lactuca were incubated in filtered seawater containing cadmium, zinc, copper or cobalt (30 μ m). The metal uptake rates differed for each metal in the order Cu > Zn > Cd > Co. Exposure of the macroalga to metals resulted in a disruption of intracellular monovalent cation composition. Intracellular potassium was irreversibly lost and sodium was accumulated by cadmium- or copper-treated U. lactuca, which was assumed to indicate irreversible disruption of the plasmalemma. Exposure to zinc caused an increase in sodium concentrations, whereas potassium concentrations were not significantly different from the controls, suggesting that the integrity of the plasmalemma had been maintained at the zinc concentration used. Intracellular magnesium was also lost from copper-treated algae, which again indicated a loss of integrity of the cell membrane.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Axelsson B, Axelsson L. 1987 A rapid and reliable method to quantify environmental effects on Laminaria based on measurements of ion leakage. Botanica Marina 30, 55–61.
De Filippis LF, Hampp R, Ziegler H. 1981 The effects of sublethal concentrations of zinc, cadmium and mercury on Euglena. Adenylates and energy charge. Z Pflanzenphysiol 103, 1–7.
Dickson DM, Wyn Jones RG, Davenport J. 1980 Steady state osmotic adaptation in Ulva lactuca. Planta 150, 158–165.
Gadd GM, Griffiths AJ. 1978 Microorganisms and heavy metal toxicity. Microbiol Ecol 4, 303–317.
Garnham GW, Codd GA, Gadd GM. 1991 Effect of salinity and pH on cobalt biosorption by the estuarine microalge Chlorella salina. Biol Met 4, 151–157.
Garnham GW, Codd GA, Gadd GM. 1992 Uptake of technetium by freshwater green algae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 37, 679–684.
Higinbotham N, Lüttge U. 1979 Transport in Plants. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Hughes MN. 1981 The Inorganic Chemistry of Biological Processes. New York: John Wiley.
Karamushka VI, Gadd GM. 1994 Influence of copper on proton efflux from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the protective effect of calcium and magnesium. FEMS Microbiol Lett 122, 33–38.
Lobban CS, Harrison PJ, Duncan MJ. 1985 Physiological Ecology of Seaweeds. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Markham JW, Kremer BP, Sperling K-R et al. 1980 Cadmium effects on growth and physiology of Ulva lactuca. Hfelgoländer Meersuntersuchungen 33, 103–110.
Mehlhorn RJ. 1986 The interaction of inorganic species with biomembranes. In: Bernhard M, Brinckman FE, Sadler PJ, eds. The Importance of Chemical ‘Speciation’ in Environmental Processes. Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 85–97.
Rai LC, Gaur JP, Kumar HD. 1981 Phycology and heavy metal pollution. Biol Rev 56, 99–151.
Raven JA. 1976 Transport in algal cells. In: Lüttge U, Pitman MG, eds. Transport in Plants II, part A. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Raven JA. 1984 Energetics and Transport in Aquatic Plants. New York: Alan R. Liss.
Reed RH, Gadd GM. 1990 Metal tolerance in eukaryotic and prokaryotic algae. In: Shaw J, ed. Heavy Metal Tolerance in Plants — Evolutionary Aspects. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 106–118.
Reed RH, Moffat L. 1983 Copper toxicity and copper tolerance in Enteromorpha compressa (L.). Grev J Exp Bot 69, 85–102.
Ritchie RJ. 1988 The ionic relations of Ulva lactuca. J Plant Physiol 133, 183–192.
Scanlan CM, Wilkinson M. 1987 The use of seaweeds in biocide toxicity testing. Part 1. The sensitivity of different stages in the life-history of Fucus, and of other algae, to certain biocides. Mar Environ Res 21, 11–29.
Trevors JT, Stratton GW, Gadd GM. 1986 Cadmium transport. resistance and toxicity in bacteria, algae and fungi. Can J Microbiol 32, 447–464.
Van Assche F, Clijsters H. 1990 Effects of metals on enzyme activity in plants. Plant Cell Environ 13, 195–206.
Webster EA, Gadd GM. 1992 Cadmium as an uncoupler of respiration in Ulva lactuca. Environ Toxicol Water Quality 7, 189–200.
Webster EA, Gadd GM. 1995 Stimulation of respiration in Ulva lactuca by cadmium and zinc; evidence for an alternative respiratory pathway Environ Toxicol Water Quality, in press.
West KR, Pitman MG. 1967 Ionic relations and ultrastructure in Ulva lactuca. Aust J Biol Sci 20, 901–14.
White C, Gadd GM. 1987 Inhibition of H+ efflux and K+ uptake, and induction of K+ efflux in yeast by heavy metals. Toxicity Assessment 2, 437–447.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Webster, E.A., Gadd, G.M. Perturbation of monovalent cation composition in Ulva lactuca by cadmium, copper and zinc. Biometals 9, 51–56 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00188090
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00188090