Abstract
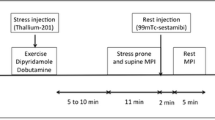
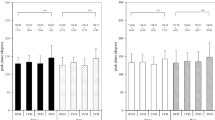
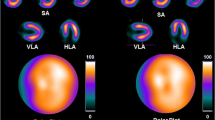
To determine the role of rest and stress gated technetium-99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile (sestamibi), in the detection of coronary artery disease, routine Fourier analysis of these images was performed with the best septal left anterior oblique (LAO) position of 20 patients (17 men, 3 women; aged 40–75 years) who also underwent rest or redistribution/stress single photon emission tomography (SPET) (99mTc-sestamibi and Thallium-201), gated blood pool imaging and coronary angiogram. There were 6 patients with single-vessel disease, 6 with two-vessel disease, 4 with three-vessel disease, 2 with coronary spasms, 1 with a patent graft and 1 with anginal episodes but a normal angiogram result. Three normal volunteers (2 women, 1 man; aged 24–26 years) also had rest and stress gated blood pool as well as rest and stress gated 99mTc-sestamibi imaging. Rest and stress 99mTc-ses-tamibi amplitude and phase images depicted regional myocardial wall shortening from the outer layer of the myocardium to the center of the left ventricle as follows a high amplitude halo of maximal negative count rate variaton; a circular thinner halo of negligible amplitude; a central region of maximal positive count rate variation, as the images evolved from end-diastole to end-systole. Similar patterns with regional differences represented abnormal myocardial wall shortening. (99mTc-sestamibi and 201T1 SPET) images were in agreement in 90% of the patients and 92% of myocardial regions. 201T1 SPET detected 83% of angiographically proven lesions, as compared with 80% for 99mTc-setamibi SPET and 80% for the amplitude images. The amplitude images demonstrated a larger number of other abnormalities not predicted on the angiogram, probably because they were able to detect regions with a potential for flow improvement and transient regional wall shortening abnormalities. Amplitude and phase analyses of gated rest and stress 99mTc-ses-tamibi images are easy to perform and may become an important adjunct to (99mTc-sestamibi SPET) images for a complete evaluation of both regional myocardial perfusion and regional contractile function using a single tracer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boucher CA (1990) Detection and location of myocardial infarction using technetium-99m sestamibi imaging at rest. Am J Cardiol 66:32E-35E
Camargo EE, Hironaka FH, Giorgi MCP, Soares J Jr, Meneguetti JC, Abe R, Robilotta CC, Munhoz ALL, Checchi H, Ramirez JAF, Pileggi F (1988) Amplitude analysis of stress 99mTc-MiBi (RP-30A) in the assessment of coronary artery disease. J Nucl Med 29:805
Clausen M, Henze E, Schmidt A, Weller R, Lietzenmayer R, Hellwig D, Bitter F, Hildebrand P, Hombach V, Adam W (1989) The contraction fraction (CF) in myocardial studies with technetium-99m isonitrile (MiBi). Correlations with radionuclide ventriculography and infarct size measured by SPECT. Eur J Nucl Med 15:661–664
Elliott AT, McKillop JH, Pringle SD, Gillen GJ, Wilson JT, Lorimer AR, Dargie HJ (1990) Simultaneous measurement of left ventricular function and perfusion. Eur J Nucl Med 17: 310–314
Garcia EV, Cooke CD, Train KF van, Folks R, Peifer J, DePuey EG, Maddahi J, Alazraki N, Galt J, Ezquerra N, Ziffer J, Berman DS (1990) Technical aspects of myocardial SPECT imaging with technetium-99m sestamibi. Am J Cardiol 66:23E-31E
Grucker D, Florentz P, Oswald T, Chambron J (1989) Myocardial gated tomo scintigraphy with 99Tcm-methoxy-isobutyl-isonitrile (MiBi): regional and temporal activity curve analysis. Nucl Med Commun 10: 539–549
Iskandrian AS, Heo J, Kong B, Lyons E, Marsch S (1989) Use of technetium-99m isonitrile (RP-30A) in assessing left ventricular perfusion and function at rest and during exercise in coronary artery disease, and comparison with coronary arteriography and exercise thallium-201 SPECT imaging. Am J Cardiol 64:270–275
Jones AG, Davison A, Abrahams MJ, Brodack JW, Toothaker AK, Adelstein SJ, Kassis AI (1984) Biological studies of a new class of technetium complexes: the hexakis (alkylisonitrile) technetium I cations. Int J Nucl Med Biol 11:225–234
Kahn JK, McGhie I, Akers MS, Sills MN, Faber TL, Kulkarni PV, Willerson JT, Corbett JR (1989) Quantitative rotational tomography with 201T1 and 99mTc 2-methoxy-isobutyl-isonitrile: a direct comparison in normal individuals and patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation 79:1282–1293
Larock MP, Cantineau R, Legrand V, Kulbertus V, Rigo P (1990) 99mTc-MiBi (RP-30) to define the extent of myocardial ischemia and evaluate ventricular function. Eur J Nucl Med 16:223–230
Maddahi J, Kiat H, Train KF Van, Prigent F, Friedman J, Garcia EV, Alazraki N, DePuey EG, Nichols K, Berman DS (1990) Myocardial perfusion imagining with technetium-99m sestamibi SPECT in the evaluation of coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol 66:55E-62E
Maisey MN, Mistry R, Sowton E (1990) Planar imaging techniques used with technetium-99m sestamibi to evaluate chronic myocardial ischemia. Am J Cardiol 66:47E-54E
Marcassa C, Marzullo P, Parodi O, Sambuceti G, L'Abbate A (1990) A new method for noninvasive quantitation of segmental myocardial wall thickening using technetium-99m 2-methoxyisobutyl-isonitrile scintigraphy — results in normal subjects. J Nucl Med 31:173–177
Najm YC, Timmis AD, Maisey MN, Ellam V, Mistry R, Curry PVL, Sowton E (1989) The evaluation of ventricular function using gated myocardial imaging with Tc-99m MiBi. Eur Heart J 10:142–148
Okada R, Glover D, Gaffney T, Williams S (1988) Myocardial kinetics of Tc-99m-hexakis-2-methoxy-2-methylpropyl isonitrite. Circulation 77:491–498
Smith WH, Watson DD (1990) Technical aspects of myocardial planar imaging with technetium-99m sestamibi. Am J Cardiol 66:16E-22E
Sochor H, Huber K, Probst P, Czernin J, Mayr H, Glogar DH, Kaindl F (1988) Assessment of myocardial perfusion and wall motion by the new perfusion agent Tc-99m MiBi and SPECT. Eur Heart J 9:1–364
Villanueva-Meyer J, Mena I, Narahara KA (1990) Simultaneous assessment of left ventricular wall motion and myocardial perfusion with technetium-99m-methoxy-isobutyl-isonitrile at stress and rest in patients with angina: comparison with thallium-201 SPECT. J Nucl Med 31:457–463
Wackers FJT (1990) Thrombolytic therapy for myocardial infarction: assessment of efficacy by myocardial perfusion imaging with technetium-99m sestamibi. Am J Cardiol 66:36E-41E
Wackers FJT, Berman DS, Maddahi J, Watson DD, Beller GA, Strauss HW, Boucher CA, Picard M, Holman LB, Fridrich R, Inglese E, Delaloye B, Bischof-Delaloye A, Camin L, McKusick K (1989) Technetium-99m hexakis-2-methoxy isobutyl isonitrite: human biodistribution, dosimetry, safety, and preliminary comparison to thallium-201 for myocardial perfusion imaging. J Nucl Med 30:301–311
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: E.E. Camargo
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Camargo, E.E., Hironaka, F.H., Giorgi, M.C.P. et al. Amplitude analysis of stress technetium-99m methoxy isobutylisonitrile images in coronary artery disease. Eur J Nucl Med 19, 484–491 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00185853
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00185853