Abstract
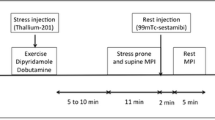
The aim of this study was to assess the reliability of the quantitative analysis of regional wall thickening with electrocardiographic-gated technetium-99m 2-methoxyisobutylisonitrile (SESTAMIBI) in predicting the reversibility of stress-induced perfusion defects. The assumption was that a preserved resting wall thickening in a segment with stress-induced perfusion defect would predict normal resting perfusion. Twenty-five patients with suspected coronary artery disease underwent planar stress-rest SESTAMIBI scintigraphy. The wall thickening was quantitatively evaluated as percentage increase in counts from diastole to systole; a ratio defined as the wall thickening index (WTI) between patient and normal profile (mean - 2 SD) below 1 was considered abnormal. Improvement of the perfusion pattern at rest was observed in 76% (54/71) of segments with a stress-induced perfusion defect; 90% of these segments had a (WTI) > 0.8. Five segments (9%) showed fixed perfusion defects despite a WTI value > 0.8. In conclusion, quantitative analysis of regional wall thickening by electrocardiographic-gated SESTAMIBI identifies segments with reversible perfusion defects; this may overcome the need for studies at rest and may direct the detection of hypoperfused but viable myocardium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker LC, Levine JH, DiPaula AF, Guarnieri T, Aversano T (1986) Reversal of dysfunction in postischemic stunned myocardium by epinephrine and postextrasystolic potentiation. J Am Coll Cardiol 7:580–589
Braunwald E, Rutheford JD (1986) Reversible ischemic left ventricular dysfunction: evidence for the “hibernating myocardium”. J Am Coll Cardiol 8:1467–1470
Kahn UK, Henderson EB, Akers MS, Jansen DE, Pippin JJ, Kulkarni P, Willerson JT, Corbett JR (1988) Prediction of reversibility of perfusion defects with a single post-exercise technetium-99m RP-30A gated tomographic image: the role of residual systolic thickening (abstract). J Am Coll Cardiol 11(2):31
Marcassa C, Marzullo P, Parodi O, Sambuceti G, L'Abbate A (1990) A new method for noninvasive quantitation of segmental myocardial wall thickening using technetium-99m 2-methoxyisobutyl-isonitrile. Results in normal subjects. J Nucl Med 31:173–177
Marzullo P, Marcassa C, Parodi O, Sambuceti G, Ferdeghini EM, L'Abbate A (1990) Noninvasive quantitative assessment of segmental myocardial wall motion using technetium-99m 2-methoxy-isobutyl-isonitrile. Am J Noninv Cardiol 4:22–28
Merz R, Maddahi J, Roy L, Berman DS (1987) Gated RP-30 perfusion study after stress predicts myocardial viability (abstract). J Am Coll Cardiol 9:27 A
Okada R, Glover D, Gaffney T, Williams S (1988) Myocardial kinetics of technetium-99m-hexakis-2-methoxy-2-methylpropyl-isonitrile. Circulation 77:491–498
Parodi O, Schelbert HR, Schwaiger M, Hansen H, Selin C, Hoffman EJ (1984) Cardiac emission tomography: underestimation of regional tracer concentration due to wall motion abnormalities. J Comp Assist Tomogr 8:1083–1092
Pierard LA, Landsheere CM de, Berthe C, Rigo P, Kulbertus HE (1990) Identification of viable myocardium by echocardiography during dobutamine infusion in patients with myocardial infarction after thrombolytic therapy: comparison with positron emission tomography. J Am Coll Cardiol 15:1021–1031
Yamashita K, Tamaki N, Yonekura Y, Ohtani H, Saij H, Mukai T, Kambara H, Kawai C, Ban T, Konishi J (1989) Quantitative analysis of regional wall motion by ECG-gated myocardial positron emission tomography: validation and comparison with left ventriculography. J Nucl Med 30:1775–1786
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: C. Marcassa
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marcassa, C., Marzullo, P., Sambuceti, G. et al. Prediction of reversible perfusion defects by quantitative analysis of post-exercise electrocardiogram-gated acquisition of technetium-99m 2-methoxyisobutylisonitrile myocardial perfusion scintigraphy. Eur J Nucl Med 19, 796–799 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00182822
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00182822