Abstract
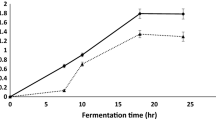
Maltooligosaccharides including maltotetraose (G4) have unique uses in biochemical, clinical, pharmaceutical, and food applications. G4 productivity utilizing a G4-producing amylase from Pseudomonas stutzeri in a membrane recycle bioreactor (MRB) was compared using four kinds of unmodified starches differing in the ration of amylose to amylopectin and the amylopectin chain lengths, and also one modified soluble starch. The specific activity of the enzyme used for the MRB system was 21.5 units/mg protein. The product purity using a native corn starch was 20.0% higher than that using a modified soluble starch in an MRB of bench-top scale. Four kinds of unmodified native corn starches were shown to be better substrates than the modified soluble starch considering all the criteria of product purity, production rate, and total product output.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernfeld P (1955) Amylases, α and β. Methods Enzymol 1:149–158
Fogarty WM, Kelly C (1980) Amylases, amyloglucosidases, and realted glucanases. In: Rose AH (ed) Microbial enzymes and bioconversions (Economic microbiology, vol. 5). Academic Press, New York, pp 115–136
Kainuma K (1984) Starch oligosaccharides: linear, branched, and cyclic. In: Whistler RY, Bemiller JN, Paschall EF (eds) Starch: chemistry and technology. Academic Press, New York, pp 125–152
Kimura T, Nakakuki T (1990) Maltotetraose, a new saccharide of tertiary property. Starch 42:151–157
Kimura T, Ogata M, Yoshida M, Nakakuki T (1988) Continuous production of maltotetraose using immobilized Pseudomonas stutzeri amylase. Biotechnol Bioeng 32:669–676
Kimura T, Ogata M, Kobayashi H, Yoshida M, Oishi K, Nakakuki T (1990) Continuous production of maltotetraose using a dual immobilized enzyme system of maltotetraose-forming amylase and pullulanase. Biotechnol Bioeng 36:790–796
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Nakakuki T, Azuma K, Kainuma K (1984) Action patterns of various exo-amylases and the anomeric configurations of their products. Carbohydr Res 128:297–310
Schmidt J, John M (1979) Starch metabolism in Pseudomonas stutzeri: I. Studies on maltotetraose forming amylase. Biochim Biophys Acta 566:88–99
Tsujisaka Y (1988) Manufacture of oligosaccharides: maltotetraose syrup. In: The Amylase Research Society of Japan (ed) Handbook of amylases and related enzymes. Pergamon Press, New York, pp 213–215
Woo GJ, McCord JD (1991) Maltotetraose production using Pseudomonas stutzeri exo-α-amylase in a membrane recycle bioreactor. J Food Sci 56:1019–1023, 1033
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: Gun-Jo Woo
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woo, GJ., McCord, J.D. Bioconversion of unmodified native starches by Pseudomonas stutzeri maltotetraohydrolase: effect of starch type. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 38, 586–591 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00182793
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00182793