Abstract
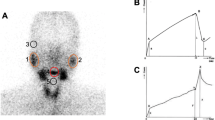
The study evaluated the possibility of using serum α-amylase and tissue polypeptide antigen (TPA) as biochemical markers of radiation injury in the salivary gland of patients with thyroid carcinoma treated with iodine-131. The results demonstrated that the two molecules increased 1 day after 1311 administration and returned to near control values on the 3rd day. The increase was greater and longer lasting in those patients treated with the higher 1311 administered activity. However, when the patients were divided into groups based on recovery time, which determined patients with different radionuclide elimination rates, the increase in the two molecules was greater and more lasting in those subjects with a longer period of hospitalization. A comparison with the values obtained from patients with tumours of the head and neck treated with external radiotherapy demonstrated that after the 1st day of treatment the salivary gland received an absorbed dose which, based on α-amylase levels, ranged between 0.24 and 1.89 Gy and, based on TPA levels, between 0.28 and 2.29 Gy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allweiss P, Braunstein GD, Katz A, Waxman A. Sialadenitis following I-131 therapy for thyroid carcinoma: concise communication. J Nucl Med 1984;25:755–758.
Becciolini A, Giannardi G, Cionini L, Porciani S, Fallai C, Pirtoli L. Plasma amylase activity as biochemical indicator of radiation injury on salivary glands. Acta Radiol Oncol 1984; 23:9–13.
Becciolini A, Porciani S, Lanini A, Chiavacci A, Cellai E. Effects of conventional and multiple fractionation treatments on the serum amylase activity. Acta Radiol Oncol 1987;26: 139–142.
Becciolini A, Tommasi MS, Porciani S, Fantappié B, Cellai E, Chiavacci A. Serum tissue polypeptide antigen (TPA): a marker of acute injury of salivary glands during radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1987;13:1339–1342.
Becciolini A, Porciani S, Lanini A, Tommasi M, Olmi P, Chiavacci A. Prognostic significance of tissue polypeptide antigen (TPA) in head and neck carcinomas. Acta Oncol 1993;32: 295–299.
Biörklund B, Biörklund V. Specificity and basis of the tissue polypeptide antigen. Cancer Detect Prev 1983;6:41–50.
Blahd WH. Treatment of malignant thyroid disease. Semin Nucl Med 1979;9:95–99.
Croll MN, Brady LW. Intracavitary uses of colloids. Semin Nucl Med 1979;9:108–113.
De Rossi G, Focacci C, Campioni P. Salivary gland physiology and radioisotope uptake. In: De Rossi G, ed. Radioisotope study of salivary glands. Boca Raton, Fl.: CCR Press; 1981: 1–28.
Dubray B, Girinski T, Thames HD, Becciolini A, Porciani S, Hennequin C, Socié G, Bonnay M, Cosset JM. Post-irradiation hyperamylasemia as a biological dosimeter. Radiother Oncol 1992;24:21–26.
Kashima HK, Kirkham WR, Andrews JR. Post-irradiation sialadenitis: a study of the clinical features, histopatological changes and serum enzyme variations following irradiation of human salivary glands. Am J Roentgenol 1965;94:271–291.
Spiegel W, Reiners C, Börner W. Sialadenitis following iodine-131 therapy for thyroid carcinoma. J Nucl Med 1985;26:816.
Street HW, Close JR. Determination of amylase activity in biological fluids. Clin Chim Acta 1956;1:256–259.
Van Der Brenk HAS, Hurley RA, Gomez C, Richeter W. Serum amylase as a measure of salivary gland radiation damage. Br J Radiol 1969;42:688–700.
Van Nostrand D, Neutze J, Atkins F. Side effects of “rational dose” iodine-131 therapy for metastatic well-differentiated thyroid carcinoma. J Nucl Med 1986;27:1519–1527.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Becciolini, A., Porciani, S., Laninil, A. et al. Serum amylase and tissue polypeptide antigen as biochemical indicators of salivary gland injury during iodine-131 therapy. Eur J Nucl Med 21, 1121–1125 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00181068
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00181068