Abstract
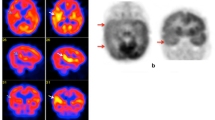
Single-photon emission tomography (SPET) using radioligands that are fixed on first pass through the cerebral circulation shows distinctive and rapidly changing blood flow patterns accompanying temporal lobe seizures. We sought to determine the optimal time to perform SPET studies for clinical seizure lateralization in temporal lobe epilepsy. Interictal, ictal and postictal SPET scans of 73 consecutively studied patients with unilateral temporal lobe epilepsy were read by three blinded observers to assess the accuracy of lateralization in each condition. The blinded observers correctly identified the side of focus in 97% of ictal studies, 72% of postictal studies and 50% of interictal studies. No incorrect scores were made in the ictal studies, whilst 5% of postictal and 12% of interictal studies were lateralized to the wrong side. Inter-observer agreement was best with the ictal studies. The dramatic perfusion changes of ictal SPET provide consistent, reliable and easily interpretable information that is superior to that provided by interictal and postictal studies. Injection of ligand during seizures is therefore the method of choice for SPET to aid the non-invasive lateralization of temporal seizure foci.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Uren RF, Magistretti PL. Royal HD, et al. Single photon emission computed tomography. A method of measuring cerebral blood flow in three dimensions (preliminary results of studies in patients with epilepsy and stroke). Med J Aust 1983; 1: 411–413.
Bonte FJ, Stokely EM, Devous MD, Homan RW. Single-photon tomographic study of regional cerebral blood flow in epilepsy: a preliminary report. Arch Neurol 1983; 40: 267–270.
Lee BI, Markand ON, Siddiqui AR, et al. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPELT) brain imaging using HIPDM: intractable complex partial seizures. Neurology 1986; 36: 1471–1477.
Rowe CC, Berkovic SF, Sia STB, et al. Localisation of epileptic foci with postictal single photon emission computed tomography. Ann Neurol 1989; 26: 660–668.
Duncan R, Patterson J, Hadley DM, et al. CT, MR and SPELT imaging in temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1990; 53: 11–15.
Stefan H, Bauer J, Feistel H, et al. Regional cerebral blood flow during focal seizures of temporal and frontocentral onset. Ann Neurol 1990; 27: 162–166.
Shen W, Lee BI, Park H-M, et al. HIPDM-SPELT brain imaging in the presurgical evaluation of patients with intractable seizures. J Nucl Med 1990; 31: 1280–1284.
Rowe CC, Berkovic SF, Austin MC, McKay WJ, Bladin PE Patterns of postictal cerebral blood flow in temporal lobe epilepsy: qualitative and quantitative analysis. Neurology 1991; 41: 1096–1103.
Rowe CC, Berkovic SF, Austin MC, et al. Visual and quantitative analysis of interictal SPELT with Tc-99m HMPAO in temporal lobe epilepsy. J Nucl Med 1991; 32: 1688–1694.
Newton MR, Berkovic SF, Austin MC, Rowe CC, Bladin PF, McKay WJ. A postictal switch in blood flow characterizes human temporal lobe seizures. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1992; 55: 891–894.
Newton MR, Berkovic SF, Austin MC, et al. Dystonia, clinical lateralization and regional cerebral blood flow in temporal lobe seizures. Neurology 1992; 42: 371–377.
Duncan R, Patterson J, Roberts R, Hadley DM, Bone I. Ictal/postictal SPECT in the presurgical localisation of complex partial seizures. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1993; 56: 141–148.
Engel JJr, Henry TR, Risinger MW et al. Pre-surgical evaluation for partial epilepsy: relative contributions of chronic depth-electrode recordings versus FDG-PET and scalp-sphenoidal ictal EEG. Neurology 1990; 40: 1670–1677.
Jackson GD, Berkovic SF, Tress BM, Kalnins RM, Fabinyi GCA, Bladin PF. Hippocampal sclerosis can be reliably detected by magnetic resonance imaging. Neurology 1990; 40: 1869–1875.
Newton MR, Austin MC, Chan JG, McKay WJ, Rowe CC, Berkovic SF. Ictal SPECT using 99-HMPAO: methods for rapid preparation and optimal deployment of tracer during spontaneous seizures. J Nucl Med 1993; 34: 666–670.
Breslow NE Day NE. Statistical methods in cancer research, vol. 1. The analysis of case control studies. Lyon: IARC Scientific Publication No. 32; 1980: 164–166.
Cohen J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ Psychol Meas 1960; 20: 37–46.
Cohen J. Weighted kappa: nominal scale agreement with provision for scaled disagreement or partial credit. Psychol Bull 1968; 70: 213–220.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Present address: Department of Nuclear Medicine, The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Woodville, South Australia, Australia
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Newton, M.R., Berkovic, S.F., Austin, M.C. et al. Ictal postictal and interictal single-photon emission tomography in the lateralization of temporal lobe epilepsy. Eur J Nucl Med 21, 1067–1071 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00181061
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00181061