Summary
Electrically-evoked release of [3H]acetylcholine from autonomic neurons (myenteric plexus), motoneurons (phrenic nerve) and the central nevous system (neocortex) was investigated in the presence and absence of the calcium channel antagonists ω-conotoxin GVIA, nifedipine and verapamil, whereby the same species (rat) was used in all experiments. Release of [3H]acetylcholine was measured after incubation of the tissue with [3H]choline.
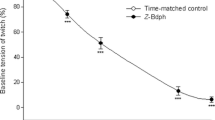
ω-Conotoxin GVIA markedly reduced (70%) the evoked release of [3H]acetylcholine from the myenteric plexus of the small intestine (IC50: 0.7 nmol/l) with a similar potency at 3 and 10 Hz stimulation. An increase in the extracellular calcium concentration attenuated the inhibitory effect of ω-conotoxin GVIA. Release of [3H]acetylcholine from the rat neocortex was also inhibited (90%) by ω-conotoxin GVIA, but the potency was 19-fold lower (IC50: 13 nmol/l). However, the release of [3H]acetylcholine from the phrenic nerve was not reduced by ω-conotoxin GVIA (100 nmol/l) at 1.8 mmol/l calcium (normal concentration), whereas ω-conotoxin GVIA inhibited evoked [3H]acetylcholine release by 47% at 0.9 mmol/l calcium. Neither nifedipine (0.1 and 1 μmol/l) nor verapamil (0.1, 1 and 10 μmol/l) modified the evoked release of [3H]acetylcholine from the myenteric plexus and the phrenic nerve.
Acetylcholine release from different neurons appears to be regulated by different types of calcium channels. N-type channels play the dominant role in regulating acetylcholine release from both the myenteric plexus and the neocortex, whereas acetylcholine release from motor nerves is regulated by calcium channel(s) not yet characterized.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson AJ, Harvey AL (1987) ω-Conotoxin does not block the verapamil-sensitive calcium channels at mouse motor nerve terminals. Neurosci Lett 82:177–180
Clasbrummel B, Osswalld H, Illes P (1989) Inhibition of noradrenaline release by ω-conotoxin GVIA in the rat tail artery. Br J Pharmacol 96:101–110
Dooley DJ, Lupp A, Hertting G (1987) Inhibition of central neurotransmitter release by ω-conotoxin GVIA, a peptide modulator of the N-type voltage-sensitive calcium channel. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 336:467–470
Dooley DJ, Lupp A, Hertting G, Osswald H (1988) ω-Conotoxin GVIA and pharmacological modulation of hippocampal noradrenaline release. Eur J Pharmacol 148:261–267
Fox AP, Nowycky MC, Tsien RW (1987) Kinetic and pharmacological properties distinguishing three types of calcium currents in chick sensory neurones. J Physiol (Lend) 394:149–172
Godfraind T, Miller R, Wibo M (1986) Calcium channel antagonism and calcium entry blockade. Pharmacol Rev 38:321–416
Kamp JT, Miller RJ (1987) Voltage-sensitive calcium channels and calcium antagonists. ICI Atlas of Science 1:133–138
Kilbinger H, Wessler I (1980) Inhibition by acetylcholine of the stimulation evoked release of [3H]acetylcholine from guinea-pig myenteric plexus. Neuroscience 5:1331–1340
Kilbinger H, Wessler I (1983) The variation of acetylcholine release from myenteric neurones with stimulation frequency and train length. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 324:130–133
Lundy PM, Frew R (1988) Evidence of ω-conotoxin GVIA-sensitive Ca2+ channels in mammalian peripheral nerve terminals. Eur J Pharmacol 156:325–330
Maggi CA, Patacchim R, Santicioli P, Lippe IT, Giuliani S, Geppetti P, Del Bianco E, Selleri S, Meli A (1988) The effect of omega conotoxin GVIA, a peptide modulator of the N-type voltage sensitive calcium channels, on motor responses produced by activation of efferent and sensory nerves in mammalian smooth muscle. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 338:107–113
McCleskey EW, Fox AP, Feldman DH, Cruz LJ, Olivera BM, Tsien RW (1987) ω-Conotoxin: direct and persistent blockade of specific types of calcium channels in neurons but not muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:4327–4331
Miller RJ (1988) Multiple calcium channels and neuronal function. Science 235:46–52
Mohy El-Din MM, Malik KU (1988) Differential effect of ω-conotoxin on release of the adrenergic transmitter and the vasoconstrictor response to noradrenaline in the rat isolated kidney. Br J Pharmacol 94:355–362
Nachshen DA, Blaustein MP (1980) Some properties of potassium-stimulated calcium influx in presynaptic nerve endings. J Gen Physiol 76:709–728
Olivera BM, Gray WR, Zeikus R, McIntosh JM, Varga J, Rivier J, deSantos V, Cruz LJ (1985) Peptide neurotoxins from fish-hunting cone snails. Science 230:1338–1343
Rivier J, Galyean R, Gray WR, Azimi-Zonooz A, McIntosh JM, Cruz LJ, Olivera BM (1987) Neuronal calcium channel inhibitors. Synthesis of ω-conotoxin GVIA and effects on 45Ca uptake by synaptosomes. J Biol Chem 262:1194–1198
Sano K, Enomoto K, Maeno T (1987) Effects of synthetic ω-onotoxin, a new type of Ca2+ antagonist, on frog and mouse neuromuscular transmission. Eur J Pharmacol 141:235–241
Sher E, Pandiella A, Clementi F (1988) ω-Conotoxin binding and effects on calcium channel function in human neuroblastoma and rat pheochromocytoma cell lines. FEBS Lett 235:178–182
Starke K, Späth L, Wichmann T (1984) Effects of verapamil, diltiazem and ryosidine on the release of dopamine and acetylcholine in rabbit caudate nucleus slices. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 325:124–130
Tsien RW, Lipscombe D, Madison DV, Bley KR, Fox AP (1988) Multiple types of neuronal calcium channels and their selective modulation. Trends Neurosci 11:431–438
Wachtel RE (1987) Effects of diltiazem and verapamil on responses to acetylcholine. Br J Pharmacol 92:561–566
Wagner JA, Snowman AM, Biswas A, Olivera BM, Snyder SH (1988) ω-Conotoxin GVIA binding to a high-affinity receptor in brain: characterization, calcium sensitivity, and solubilization. J Neurosci 8:3354–3359
Wallenstein S, Zucker CL, Fleiss JI (1980) Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Circ Res 47:1–9
Wessler I, Anschütz A (1988) Stimulation of β-adrenoceptors enhances electrically evoked [3H]ACh output from the rat phrenic nerve. Br J Pharmacol 94:669–674
Wessler I, Halank M, Rasbach J, Kilbinger H (1986) Presynaptic nicotine receptors mediating a positive feedback on transmitter release from the rat phrenic nerve. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 334:365–372
Wessler I, Schlemmer F, Werhand J, Dooley DJ (1989) Differential effects of ω-conotoxin (CT) on acetylcholine release from the central and peripheral nervous system. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 339: R84
Wessler I, Dooley D, Osswald H, Schlemmer F (1990) Differential blockade by nifedipine and ω-conotoxin GVIA of α1- and β2-drenoceptor-controlled calcium channels on motor nerve terminals of the rat. Neurosci Lett 108:173 -178
Wood JD (1979) Neurophysiology of the enteric nervous system. In: Brooks C, Koizumi K, Sato A (eds) Integrative functions of the autonomic nervous system. Univ Tokyo Press, Tokyo, pp 177–193
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to I. Wessler at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wessler, I., Dooley, D.J., Werhand, J. et al. Differential effects of calcium channel antagonists (ω-conotoxin GVIA, nifedipine, verapamil) on the electrically-evoked release of [3H]acetylcholine from the myenteric plexus, phrenic nerve and neocortex of rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 341, 288–294 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00180653
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00180653