Summary
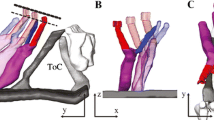
In the adult human cochlea, a cytokeratin (Ck) network exists along the entire surface of the organ of Corti, enclosing it like a shell. Only the surfaces of the outer and inner hair cells are not integrated in this network. In temporal bone specimens, Ck filaments in Hensen's cells were found to be arranged parallel with and closely apposed to the plasma membrane. In the stria vascularis, Cks were identified only in the marginal cells. Cells in Reissner's membrane and spiral prominence showed varying degrees of immunoreactivity to different monoclonal antibodies directed against Cks. A distinct positivity for Cks was found in most spiral ganglion cells, indicating their presence in all cells. The principal pattern of immunoreactivity was the same in the organ of Corti of the entire cochlea. However, a quantitative gradient in the expression of Cks was observed, with more Cks at the apex than at the base. This was correlated to a difference in the number of Hensen's cells between the two regions. The distinct shell configuration of the Ck network in Corti's organ gives it a tonotopically related difference in rigidity which must be of considerable importance for the perception of sound in the cochlea. The absence of Cks in inner and outer sulcus cells gives them cytoskeletal characteristics of mesenchymal cells with a possible regenerative potential.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anniko M, Arnold W (1990) Methods for cellular and subcellular visualization of intermediate filament proteins in the human inner ear. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) [Suppl] (in press)
Anniko M, Thornell L-E, Gustafsson H, Virtanen I (1986) Intermediate filaments in the newborn inner ear of the mouse. ORL 48:98–106
Anniko M, Thornell L-E, Virtanen I (1987) Cytoskeletal organization of the human inner ear. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) [Suppl] 437:1–76
Anniko M, Thornell L-E, Ramaekers FCS, Stigbrand T (1989) Cytokeratin diversity in epithelia of the human inner ear. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 108:385–396
Aniko M, Wenngren B-I, Thornell L-E, Virtanen I (1989) Expression of intermediate filament proteins in the inner ear of the dancer mouse mutant. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 108:45–54
Arnold WJ (1987) Possibilities of immunohistochemical investigation on human temporal bone. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) [Suppl] 436:62–68
Bagger-Sjöbäck D, Anniko M (1984) Development of intercellular junctions in the vestibular end organs. A freeze fracture study in the mouse. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 93:89–95
Borisi GG, Cleveland DW, Murphy DB (eds) (1984) Molecular biology of the cytoskeleton. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, pp 1–512
Flock A, Flock B, Ulfvendahl M (1986) Mechanisms of movement in outer hair cells and a possible structural basis. Arch Otorhinolryngol 243:83–90
Franke WW, Moll R, Schiller DL, Schmid E, Kartenbeck J, Müller H (1982) Desmoplakins of epithelial and myocardial desmosomes are immunologically and biochemically related. Differentiation 23:115–127
Gulley RL, Reese TS (1976) Intercellular junctions in the reticular lamina of the organ of Corti. J Neurocytol 5:479–507
Lazarides E (1982) Intermediate filaments. A chemically heterogenous, developmentally regulated class of proteins. Ann Rev Biochem 51:219–250
Ramaekers FCS, Huijsmans A, Schaart G, Moesker O, Vooijs P (1987) Tissue distribution of keratin 7 as monitored by a monoclonal antibody. Exp Cell Res 170:235–249
Raphael Y, Marshak G, Barash A, Geiger B (1987) Modulation of intermediate filament expression in developing cochlear epithelium. Differentiation 35:151–162
Regauer S, Franke WW, Virtanen I (1985) Intermediate filament cytoskeleton of amnion epithelium and cultured amnion epithelial cells: expression of epidermal cytokeratins in cells of a simple epithelium. J Cell Biol 100:997–1009
Sand PA (1988) Cochlear microanatomy and ultrastructure. In: Jahn AF, Santos-Sacchi J (eds) Physiology of the ear. Raven Press, New York, pp 173–199
Schliwa M (1986) The cytoskeleton. Springer, Vienna New York, pp 1–326
Steinert PM, Parry DAD (1985) Intermediate filaments: conformity and diversity of expression and structure. Ann Rev Cell Biol 1:41–65
Sundström B, Nathrath WBJ, Stigbrand T (1989) Diversity in immunoreactivity of tumour derived cytokeratin monoclonal antibodies. J Histochem Cytochem 37:1845–1854
Zenner H-P, Giller A, Zimmermann U, Schmitt U, Frbmter E (1985) Die isolierte, lebende Haarzelle ein neues Modell zur Untersuchung der Hörfunktion. Laryngol Rhinol Otol 64:642–648
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by grants from the Swedish Medical Research Council (M. A.: 12X-7305; L.-E. T.: 12X-3934), the Ragnar and Torsten Söderberg Foundation (M. A.), the Foundation Tysta Skolan (M. A.), the Swiss National Funds (W. A., C. R. P.: 3.997-1.86), the Finnish Cancer Research Fund (I. V.), the Sigrid Juselius Foundation (I. V.), the Dutch Cancer Foundation (K. W. F.) and the Medical Faculty University of Ume»
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anniko, M., Arnold, W., Thornell, L.E. et al. Regional variations in the expression of cytokeratin proteins in the adult human cochlea. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 247, 182–188 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00175974
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00175974