Abstract
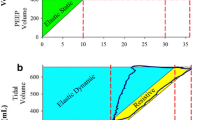
An animal model for congenital diaphragmatic hernia following interference with the development of the primary lung bud by 2,4-dinitro-p-diphenylether (nitrofen) is described. It has been used for pathogenetic studies to evaluate the presence of pulmonary hypoplasia and a closing defect of the diaphragm. Functional studies revealed abnormal surfactant levels and differences in pressure/volume curves following birth and during artificial ventilation for 6 h together with a disturbed antioxidant enzyme response. This animal model opens up new ways of studying the effects of prenatal hormonal modulation (corticosteroids, thyrotrophin-releasing hormone) on lung development as a novel therapeutic modality.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfonso LF, Vilanova J, Aldazabal P, Lopez de Torre B, Tovar JA (1993) Lung growth and maturation in the rat model of experimentally induced congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Eur J Pediatr Surg 3: 6–11
Askenazi SS, Perlman M (1979) Pulmonary hypoplasia: lung weight and radial alveolar count as criteria of diagnosis. Arch Dis Child 54: 614–618
Bos AP, Tibboel D, Hazebroek FWJ, Molenaar JC, Lachman B, Gommers D (1991) Surfactant replacement therapy in high-risk congenital diaphragmatic hernia (Letter to editor). Lancet 338: 1279
Brandsma AE, Tibboel D, Ten Have-Opbroek AAW (1994) Alveolar epithelial composition and architecture of the late fetal pulmonary acinus. Exp Lung Res 20: 491–515
Brandsma AE, Tibboel D, Vulto IM, Egberts J, Ten Have-Opbroek AAW (1993) Ultrastructural features of alveolar epithelial cells in the late fetal pulmonary acinus: A comparison between normal and hypoplastic lungs using a rat model of pulmonary hypoplasia and congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Microsc Res Tech 26: 389–399
Brandsma AE, Tibboel D, Vulto IM, Ten Have-Opbroek AAW, Wiersubga WM (1994) Inhibition of T3-receptor binding in nitrofen. BBH (in press)
Burri PH, Dbaly J, Weibel ER (1974) The postnatal growth of the rat lung. I. Morphometry. Anat Rec 178: 711–730
Cornish JD, Gerstmann DR, Clark RH, Carter JM, Null DM Jr, deLemos RA (1987) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and high frequency oscillatory ventilation: potential therapeutic relationships. Crit Care Med 15: 831–834
Costlow RD, Manson JM (1981) The heart and diaphragm: target organs in the neonatal death induced by nitrofen (2,4-dichlorophenyl-p-nitrophenyl ether). Toxicology 20: 209–227
Devaskar UP, deMello DE, Ackerman J (1991) Effect of maternal administration of thyrotropin-releasing hormone or DN1417 on functional and morphologic fetal rabbit lung maturation and duration of survival after premature delivery. Biol Neonate 59: 346–351
De Zegher F, Spitz B, De Vlieger H (1992) Prenatal treatment with thyrotrophin releasing hormone to prevent neonatal respiratory distress. Arch Dis Child 67: 231–237
Geggel RL, Murphy JD, Langleben D, Crone RK, Vacanti JP, Reid LM (1985) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: arterial structural changes and persistent pulmonary hypertension after surgical repair. J Pediatr 107: 457–464
Glick PL, Stannard VA, Leach CL, Rossman J, Hosada Y, Morin FC, Cooney DR, Allen JE, Holm B (1992) Pathophysiology of congenital diaphragmatic hernia II: the fetal lamb CDH model is surfactant deficient. J Pediatr Surg 27: 382–388
Gray LE, Kavlock RJ (1983) The effects of the herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenyl-p-nitrophenyl ether (Nit) on serum thyroid hormones in adult female mice. Toxicol Lett 15: 231–235
Harrison MR, Jester JA, Ross NA (1980) Correction of congenital diaphragmatic hernia in utero. I. The model: intrathoracic balloon produces fetal pulmonary hypoplasia. Surgery 88: 174–182
Harrison MR, Ross NA, deLorimier AA (1981) Correction of congenital diaphragmatic hernia in utero. III. Development of a successful surgical technique using abdominoplasty to avoid compromise of umbilical blood flow. J Pediatr Surg 16: 934–942
Hitchcock KR (1979) Hormones and the lung: I. Thyroid hormones and glucocorticoids in lung development. Anat Rec 194: 15–40
Ijsselstijn H, Zijlstra FJ, Bos AP, Molenaar JC, Tibboel D (1994) Eicosanoid content in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in newborn rats with pulmonary hypoplasia and congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Am Rev Respir Dis (Suppl) (in press)
Iritani I (1984) Experimental study on embryogenesis of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Anat Embryol 169: 133–139
Kimbrough RD, Gaines TB, Linder RE (1974) 2,4-Dichlorophenyl-p-nitrophenyl ether (TOK): effects on the lung maturation of rat fetus. Arch Environ Health 28: 316–320
Kitagawa M, Hislop A, Boyden EA, Reid L (1971) Lung hypoplasia in congenital diaphragmatic hernia: a quantitative study of airway, artery, and alveolar development. Br J Surg 58: 342–346
Kluth D, Kangah R, Reich P, Tenbrinck R, Tibboel D, Lambrecht W (1990) Nitrofen-induced diaphragmatic hernias in rats: an animal model. J Pediatr Surg 25: 850–854
Lachmann B, Grossmann G, Freyse J, Robertson B (1981) Lung-thorax compliance in the artificially ventilated premature rabbit neonate in relation to variations in inspiration: experation ratio. Pediatr Res 15: 833–838
Lau C, Cameron AM, Irsula O, Antolick LL, Langston C, Kavlock RJ (1988) Teratogenic effects of nitrofen on cellular and functional maturation of the rat lung. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 95: 412–422
Manson JM (1986) Mechanism of nitrofen teratogenesis. Environ Health Perspect 70: 137–147
Manson JM, Brown T, Baldwin DM (1984) Teratogenicity of nitrofen (2,4-dichlorophenyl-p-nitrophenyl ether) and its effects on thyroid function in the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 73: 323–335
Molenaar JC, Bos AP, Hazebroek FWJ, Tibboel D (1991) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia, what defect? J Pediatr Surg 26: 248–254
Nakamura Y, Yamamoto I, Fukuda S, Hashimoto T (1991) Pulmonary acinar development in diaphragmatic hernia. Arch Pathol Lab Med 115: 372–376
O'Rourke PP, Lillehei CW, Crone RK, Vacanti JP (1991) The effect of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation on the survival of neonates with high-risk congenital diaphragmatic hernia: 45 cases from a single institution. J Pediatr Surg 26: 147–152
Piersma AH, Hofstee-Hooftman MWA, Verhoef A, (1993) Early lung development in the rat and its perturbation by nitrofen treatment (abstract). Teratology 48: 31A
Scheffers EC, Ijsselstijn H, Tenbrinck R, Lachmann B, De Jongste JC, Molenaar JC, Tibboel D (1994) Evaluation of lung function changes before and after surfactant application during artificial ventilation in newborn rats with congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH). J Pediatr Surg (in press)
Shochat SJ (1987) Pulmonary vascular pathology in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Pediatr Surg Int 2: 331–335
Sluiter W, Bos AP, Silveri F, Tenbrinck R, Kraakslee R, Tibboel D, Koster JF, Molenaar JC (1992) Nitrofen-induced diaphragmatic hernias in rats: pulmonary antioxidant enzyme activities. Pediatr Res 32: 394–398
Springall DR, Polak JM (1993) Calcitonin gene-related peptide and pulmonary hypertension in experimental hypoxia. Anat Rec 236: 96–104
Stone LC, Manson JM (1981) Effects of the herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenyl-p-nitrophenyl ether (nitrofen) on fetal lung development in rats. Toxicology 20: 195–207
Suen HC, Catlin EA, Ryan DP, Wain JC, Donahoe PK (1993) Biochemical immaturity of lungs in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 28: 471–477
Tanswell AK, Freeman BA (1987) Liposome-entrapped antioxydant enzymes prevent lethal O2 toxicity in the newborn rat. J Appl Physiol 63: 347–352
Tenbrinck R, Gaillard JLJ, Tibboel D, Kluth D, Lachmann B, Molenaar JC (1992) Pulmonary vascular abnormalities in experimentally induced CDH in rats. J Pediatr Surg 27: 862–865
Tenbrinck R, Tibboel D, Gaillard JLJ, Kluth D, Bos AP, Lachmann B, Molenaar JC (1990) Experimentally induced congenital diaphragmatic hernia in rats. J Pediatr Surg 25: 426–429
Ten Have-Opbroek AAW (1981) The development of the lung in mammals: an analysis of concepts and findings. Am J Anat 162: 201–219
Ten Have-Opbroek AAW (1991) Lung development in the mouse embryo. Exp Lung Res 17: 111–130
Ten Have-Opbroek AAW, Dubbeldam JA, Otto-Verberne CJM (1988) Ultrastructural features of type II alveolar epithelial cells in early embryonic mouse lung. Anat Rec 221: 846–853
Ten Have-Opbroek AAW, Otto-Verberne CJM, Dubbeldam JA (1990) Ultrastructural characteristics of inclusion bodies of type II cells in late embryonic mouse lung. Anat Embryol 181: 317–323
Ueki R, Nakao Y, Nishida T, Nakao Y, Wakabayashi T (1990) Lung hypoplasia in developing mice and rats induced by maternal exposure to nitrofen. Cong Anom 30: 133–143
Warburton D, Lee M, Berberich MA, Bernfield M (1993) Molecular embryology and the study of lung development. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 9: 5–9
Wenstrom KD, Weiner CP, Hanson JW (1991) A five-year statewide experience with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Am J Obstet Gynecol 165: 838–842
Wilson JM, Lund DP, Lillehei GW, et al (1991) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: predictors of severity in the ECMO era. J Pediatr Surg 26: 1028–1034
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brandsma, A.E., Tenbrinck, R., Ijsselstijn, H. et al. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: new models, new ideas. Pediatr Surg Int 10, 10–15 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00174434
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00174434