Summary
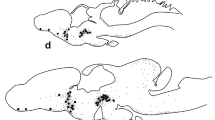
The presence of immunoreactive pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC)-derived peptides (adrenocorticotropin hormone, β-endorphin, α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone) and of cytokine-like molecules [interleukin (IL)-1α, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-6, tumour necrosis factor-α] was demonstrated in periodic acid-Schiff-positive epithelial cells in the thymus of the goldfish (Carassius c. auratus) using immunocytochemical procedures. POMC-derived peptide- and cytokine-like molecules were localized in the same cell type. Lymphocytes were negative for all the above mentioned molecules. Despite the smaller number of cells positive for neuropeptide- and cytokine-like molecules, our findings suggest that immune-neuroendocrine interactions are likely to occur in the thymus of goldfish.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
bancroft, j. d. & stevens, a. (1990) Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques, 3rd edn. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone.
batanero, e., deleeuw, f.-e., jansen, g. h., vanwichen, d. f., huber, j. & schuurman, h.-j. (1992) The neural and neuro-endocrine component of the human thymus. II. Hormone immunoreactivity. Brain Behav. Immun. 6, 249–64.
blalock, j. e. (1989) A molecular basis for bidirectional communication between the immune and neuroendocrine systems. Physiol. Rev. 69, 1–32.
dabrowski, m. p. & dabrowski-bernstein, b. k. (1990) Immunoregulatory Role of Thymus. Roca Raton, FL: CRC Press.
deschaux, p. & rouabhia, m. (1987) The thymus. Key organ between endocrinologic and immunologic systems. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 496, 49–55.
geenen, v., legros, j.-j., franchimont, p., baudrihaye, m., defresne, m.-p. & boniver, j. (1986) The neuroendocrine thymus: coexistence of oxytocin and neurophysin in the human thymus. Science 232, 508–11.
geenen, v., legros, j.-j., franchimont, p., defresne, m.-p., boniver, j., ivell, r. & richter, d. (1987) The thymus as a neuroendocrine organ. Synthesis of vasopressin and oxytocin in human thymic epithelium. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 496, 56–66.
genedani, s., bernardi, m., baldini, m. g. & bertolini, a. (1990) ACTH (1–24) stimulates the migration of human monocytes in vitro. Peptides 11, 1305–7.
genedani, s., bernardi, m., fontanili, p., ottaviani, e. & franceschi, c. (1994a) Influence of endorphins on the migration of molluscan hemocytes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 107C, 79–81.
genedani, s., bernardi, m., ottaviani, e., franceschi, c., leung, m. K. & stefano, g. b. (1994b) Differential modulation of invertebrate immunocyte motility by CRF, ACTH and its fragments. Peptides 15, 203–6.
gomariz, r. p., lorenzo, m. l., cacicedo, l., vicente, a. & zapata, a. G. (1990) Demonstration of immunoreactive vasoactive intestinal peptide (IR-VIP) and somatostatin (IR-SOM) in rat thymus. Brain Behav. Immun. 4, 151–61.
jessop, d. s., chowdrey, h. s. & lightman, s. l. (1993) Interleukin-1β measured by radioimmunoassay in the rat spleen and thymus is increased during chronic inflammatory stress. Neuropeptides 24, 367–71.
johnson, h. m., smith, e. m., torres, b. a. & blalock, j. e. (1982) Regulation of the in vitro antibody response by neuroendocrine hormones. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 79, 4171–4.
kendall, m. d. (1988) Anatomical and physiological factors influencing the thymic microenvironment. In Thymus Update 1. The Microenvironment of the Human Thymus (edited by kendall, m. d. & ritter, m. a.), pp. 27–65. Chur, Switzerland: Harwood Academic Publishers.
lazarides, e. (1980) Intermediate filaments as mechanical integrators of cellular space. Nature 283, 249–56.
manning, m. j. & turner, r. j. (1976) Comparative Immunobiology. Glasgow: Blackie.
miller, j. f. a. p. (1961) Immunological function of the thymus. Lancet ii, 748–9.
millington, g. & buckingham, j. c. (1992) Thymic peptides and neuroendocrine-immune communication. J. Endocrinol. 133, 163–8.
ottaviani, e., petraglia, f., montagnani, g., cossarizza, a., monti, d. & franceschi, c. (1990) Presence of ACTH and β-endorphin immunoreactive molecules in the freshwater snail Planorbarius corneus (L.) (Gastropoda, Pulmonata) and their possible role in phagocytosis. Regul. Pept. 27, 1–9.
ottaviani, e., cossarizza, a., ortolani, c., monti, d. & franceschi, c. (1991) ACTH-like molecules in gastropod molluscs: a possible role in ancestral immune response and stress. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 245, 215–8.
ottaviani, e., caselgrandi, e., petraglia, f. & franceschi, c. (1992a) Stress response in the fresh-water snail Planorbarius corneus (L.) (Gastropoda, Pulmonata): interaction between CRF, ACTH and biogenic amines. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 87, 354–60.
ottaviani, e., franchini, a., cossarizza, a. & franceschi, c. (1992b) ACTH-like molecules in lymphocytes. A study in different vertebrate classes. Neuropeptides 23, 215–9.
ottaviani, e., trevisan, p. & pederzoli, a. (1992c) Immunocytochemical evidence for ACTH- and β- endorphin-like molecules in phagocytic blood cells of urodelan amphibians. Peptides 13, 227–31.
ottaviani, e., franchini, a. & franceschi, c. (1993) Presence of several cytokine-like molecules in molluscan hemocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 195, 984–8.
ottaviani, e., franchini, a. & fontanili, p. (1994) The effect of corticotropin-releasing factor and pro-opiomelanocortin-derived peptides on the phagocytosis of molluscan hemocytes. Experientia 50, 857–9.
ottaviani, e., capriglione, t. & franceschi, c. (1995) Invertebrate and vertebrate immune cells express pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) mRNA. Brain Behav. Immun. 9, 1–8.
ritter, m. a. & crispe, i. n. (1992) The Thymus. New York: IRL Press at Oxford University Press.
robert, f., geenen, v., schoenen, j., burgeon, e., degroote, d., defresne, m. p., legros, j. j. & franchimont, p. (1991) Colocalization of immunoreactive oxytocin, vasopressin and interleukin-1 in the human thymic epithelial neuroendocrine cells. Brain Behav. Immun. 5, 102–15.
singer, k. h., le, p. t., denning, s. m., vollger, l. w., kurtzberg, j., lobach, d. f., tuck, d. t., scearce, r. m. & haynes, b. f. (1988) In vitro studies of thymic epithelium. In Thymus Update 1. The Microenvironment of the Human Thymus, (edited by kendall, m. d. & ritter, m. a.), pp. 155–69. Chur, Switzerland: Harwood Academic Publishers.
zapata, a. g. & cooper, e. l. (1990) The Immune System: Comparative Histophysiology. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ottaviani, E., Franchini, A. & Franceschi, C. Evidence for the presence of immunoreactive POMC-derived peptides and cytokines in the thymus of the goldfish (Carassius c. auratus). Histochem J 27, 597–601 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00173096
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00173096