Abstract
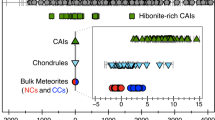
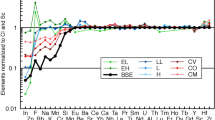
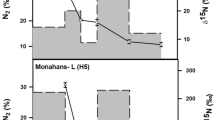
The composition, mineralogy and texture of chondritic meteorites suggest they are relatively unaltered relicts of the condensation and accretion processes which took place in the primitive solar nebula. Chondrites thus are thought to contain a unique record of the physico-chemical conditions which prevailed at the time and place (asteroid belt) of their origin. Elemental abundance patterns are an important clue to the events and processes. Most elements can be placed in one of four groups according to their observed fractionation behavior in chondritic material: refractory, siderophile, normally depleted and strongly depleted. This grouping can be explained in terms of four events which presumably took place during cooling, condensation and accretion in the nebula. In order of inferred occurrence these are: (1) partial loss of the initial condensates rich in refractory elements at T > 1300K, (2) partial loss of metallic Fe-Ni grains, perhaps because they were magnetic, at 1000 to 700K, (3) partial remelting and outgassing of the condensate (chondrule formation) at 600 to 350K, and (4) accretion, when the P-T conditions controlled the volatile content (500 to 350K). Total gas pressure at the time and place of accretion is estimated to fall between 10-−6 and 10−-4 atm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrens, L. H., von Michaelis, H., Erlank, A. J., and Willis, J. P.: 1969, in P. M. Millman (ed.), Meteorite Research, D. Reidel Publishing Company, pp. 166–173.
Anders, E. 1964, Space Sci. Rev. 3, 583–714.
Anders, E. 1971, Geochim Cosmochim. Acta 35, 516–522.
Anders, E. 1972, ‘Physico-Chemical Processes in the Solar Nebula, as Inferred from Meteorites’, Proc. of Colloq. on the Origin of the Solar System, Nice, France.
Anderson, E. L.: 1972, Moon 8, 33.
Cameron, A. G. W.: 1966, Earth Planetary Sci. Letters 1, 93–96.
Cameron, A. G, W.: 1968, in L. H. Ahrens (ed.), Origin and Distribution of the Elements, Pergamon, pp. 125–143.
Cameron, A. G. W.: 1973 ‘Accumulation Processes in the Primitive Solar Nebula’, Icarus, in press.
Christophe, Michel-Levy: 1968, Bull. Soc. Fr. Mineral. Cristallogr. 91, 212–214.
Dodd, R. T.: 1969, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 33, 161–203.
Gast, P. W.: 1973, Presented at this Symposium
Grossman, L.: 1972, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 36, 597–619.
Grossman, L.: 1973, ‘Refractory Trace Elements in Ca-Al Rich Inclusions in the Allende Meteorite’, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, in press.
Herbig, G. H.: 1970, Mem (8°) Soc. Roy. Sci. Liège 19, 13–26.
Keil, K., Huss, G. I., and Wiik, H. B.: 1969, in P. M. Millman (ed.), Meteorite Research, D.Reidel Publishing Company, p. 217.
Larimer, J. W.: 1967, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 31, 1215–1238.
Larimer, J. W.: 1973, ‘Chemical Fractionations in Meteorites-VII': Cosmothermometry and Cosmobarometry’, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 37, 1603–1624.
Larimer, J. W. and Anders, E.: 1967, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 31, 1239–1270.
Larimer, J. W. and Anders, E.: 1970, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 34, 367–388.
Laul, J. C., Ganapathy, R., Anders, E., and Morgan, J. W.: 1972, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 37, 329–358.
Lewis, J. S.: 1973, Presented at this symposium.
Lord, H. C., III: 1965, Icarus 4, 279–288.
Müller, O., Baedecker, P. A., and Wasson, J. T.: 1971, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 35, 1121–1137.
Onuma, N., Clayton, R. N., and Mayeda, T. K.: 1972, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 36, 169–188.
Van Schmus, W. R. and Wood, J. A.: 1967, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 31, 747–766.
Urey, H. C.: 1954, Astrophys. J.Supp. No. 6 1, 147–173.
Urey, H. C.: 1952a, The Planets, Yale University Press.
Urey, H. C.: 1952b, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2, 267–282.
Whipple, F. L.: 1966, Science 153, 54–56.
Whipple, F. L.: 1972, ‘On Certain Aerodynamic Processes for Asteroids and Comets’, in A. Elvius (ed.), From Plasma to Planet, Nobel Symp. 21, in press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Contribution No. 80, Center for Meteorite Studies.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larimer, J.W. Chemistry of the solar nebula. Space Sci Rev 15, 103–119 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00172439
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00172439