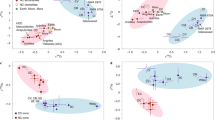
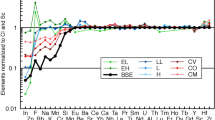
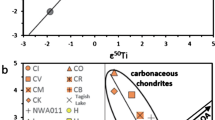
Abstract
Understanding the formation of our planetary system requires identification of the materials from which it originated and the accretion processes that produced the planets. The compositional evolution of the solar system can be constrained by synthesizing astronomical datasets and numerical models with elemental and isotopic compositions from objects that directly sampled the disk: meteorites and their constituents (chondrules, refractory inclusions, and matrix). This contribution reviews constraints on early solar system evolution provided by the so-called non-carbonaceous (NC) and carbonaceous chondrite (CC) groups and their relationship to the volatile element characteristics of chondritic meteorites. In previous work, the NC or CC character of a parent body was used to infer its accretion location in the protoplanetary disk. The NC groups purportedly originated in the inner disk, and the CC groups were derived from the outer disk, where the NC and CC regions of the disk may have been separated early on by proto-Jupiter, a pressure maximum, or a dust trap in the disk. The tenet that all CC parent bodies accreted in the outer disk is, in part, based on evidence that a handful of CC meteorites are enriched in volatile species compared to NC meteorites. Here, it is reviewed if and how the volatile element and nucleosynthetic isotope compositions of meteorites can be linked to accretion locations within the disk. The nucleosynthetic isotope compositions of whole rock meteorite samples contrast the trends found for their major volatile element compositions (i.e., C, N, and O). Although there may be an increase in volatile abundances when comparing some stony NC and CC meteorites and their inferred accretion locations within the disk, this is not necessarily a general rule. The difficulties with inferring parent body accretion locations are discussed. It is found that it cannot always be assumed that parent bodies which formed in the CC reservoir are “volatile-rich” relative to those that formed in the NC reservoir which are “volatile-poor”. Consequently, tracing the origin of terrestrial volatiles using the NC-CC isotope dichotomy remains challenging.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The IUPAC-IUGS convention for expressing dates following recommendation by Holden et al. (2011) is that annus (a) is used for one year as a unit of time, both for absolute time and time differences. Hence, considering the declensions, it is Ga = Giga annis (ablative for age; used as appellative) or Ga = Giga annos (pl. accusative, for how long ago).
The enrichments of C, N, and O (relative to solar) observed in outer planet atmospheres were caused by the accretion of ices bearing these highly volatile elements. Highly volatile elements have 50% condensation temperatures below 371 K, volatile elements below 665 K, moderately volatiles between 1335 and 665 K, and refractories above 1335 K (for a gas of solar composition at a total pressure of 10−4 bar; Lodders 2003). See last chapter in this edition by K. Lodders for elemental data for the Sun and meteorites.
Typically, isotope ratios are measured, and meteorite samples with an excess or depletion of a given isotope will have a higher or lower (respectively) isotope ratio than the terrestrial reference value. Positive or negative isotope anomalies arise from the definition of the isotope notation, which is the difference between the measured sample ratio from that of the terrestrial standard value in percent (%), permil (‰), on a scale of parts per 10,000 (\(\varepsilon \) units), or in parts per 1,000,000 (\(\mu \) units). The advantage of using the differences in the ratios is that these scales are easier to work with, especially for samples with small isotope anomalies (bulk meteorites, chondrules, CAIs). Terrestrial materials are generally defined as ‘normal’ (or equal to zero) in isotopic composition.
Additional sources of achondrites to Earth include Mars and the Moon. The meteorites referred to here do not include micrometeorites.
Measurable retention of any originally accreted water (ice) on the parent body requires post-accretion aqueous alteration; the water abundance then also depends on kinetics and the degree of aqueous processing and/or thermal metamorphism on the parent body. It should be noted that important intra- and inter-chondrite variations in water concentrations exist which can be explained, in part, by varying proportions of H-bearing components in a given (sub-)sample (e.g., Pearson et al. 2001). Analytically, not all extraction techniques may clearly distinguish between primordial and (terrestrial) adsorbed water (e.g., Robert and Epstein 1982; Vacher et al. 2020), and terrestrial exposure of “finds” can modify water concentrations (Stephant et al. 2018). Thus, the reported bulk water contents of chondrites cannot directly reflect the original accreted water in all cases.
Individual CI and CM chondrites record a wide range of hydrogen isotope (\(\delta \)D) values, possibly due, in part, to variable degrees of aqueous alteration and sampling biases (Alexander et al. 2012, 2018; Kerridge 1985; Robert 2003). Therefore, Alexander et al. (2018) used average values of 78 ± 7‰ and –53 ± 130‰ for the CI and CM chondrite groups, respectively.
The different chondrite groups (e.g., CI, CM, CR, CO, CV, CK) within a given class (e.g., carbonaceous chondrites) record a wide range of \(\delta ^{15}\)N values (e.g., Pearson et al. 2006). For a given group, the \(\delta ^{15}\)N value varies with petrologic type, i.e., the extent of thermal metamorphism; \(\delta ^{15}\)N generally decreases with increasing petrologic type from 1 to 4 (Pearson et al. 2006). In addition, the nitrogen extraction method (combustion \(\mathit{vs}\). pyrolysis) can yield distinct \(\delta ^{15}\)N values (e.g., Grady et al. 1986). Therefore, care should be taken when comparing data from different studies.
References
C.M.O’D. Alexander, The origin of inner solar system water. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A, Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 375, 20150384 (2017)
C.M.O’D. Alexander, Quantitative models for the elemental and isotopic fractionations in chondrites: the carbonaceous chondrites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 254, 277–309 (2019a)
C.M.O’D. Alexander, Quantitative models for the elemental and isotopic fractionations in the chondrites: the non-carbonaceous chondrites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 254, 246–276 (2019b)
C.M.O’D. Alexander, D.J. Barber, R. Hutchison, The microstructure of Semarkona and Bishunpur. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 53, 3045–3057 (1989)
C.M.O’D. Alexander, L.R. Nittler, The galactic evolution of Si, Ti, and O isotopic ratios. Astrophys. J. 519, 222–235 (1999)
C.M.O’D. Alexander, R. Bowden, M.L. Fogel, K.T. Howard, C.D. Herd, L.R. Nittler, The provenances of asteroids, and their contributions to the volatile inventories of the terrestrial planets. Science 337, 721–723 (2012)
C.M.O’D. Alexander, K.D. McKeegan, K. Altwegg, Water reservoirs in small planetary bodies: meteorites, asteroids, and comets. Space Sci. Rev. 214, 36 (2018)
S. Amari, L.R. Nittler, E. Zinner, K. Lodders, R.S. Lewis, Presolar SiC grains of Type A and B: Their isotopic compositions and stellar origins. Astrophys. J. 559, 463–483 (2001)
E.A. Bergin, L.I. Cleeves, Chemistry during the gas-rich stage of planet formation, in Handbook of Exoplanets, ed. by H. Deeg, J. Belmonte (Springer, Cham, 2018), pp. 2221–2250
K.R. Bermingham, K. Mezger, E.E. Scherer, M.F. Horan, R.W. Carlson, D. Upadhyay, T. Magna, A. Pack, Barium isotope abundances in meteorites and their implications for early Solar System evolution. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 175, 282–298 (2016)
K.R. Bermingham, R.J. Walker, The ruthenium isotopic composition of the oceanic mantle. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 474, 466–473 (2017)
K.R. Bermingham, N. Gussone, K. Mezger, J. Krause, Origins of mass-dependent and mass-independent Ca isotope variations in meteoritic components and meteorites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 226, 206–223 (2018a)
K.R. Bermingham, E.A. Worsham, R.J. Walker, New insights into Mo and Ru isotope variation in the nebula and terrestrial planet accretionary genetics. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 487, 221–229 (2018b)
K.R. Bermingham, Ancient rock bears isotopic fingerprints of Earth’s origins. Nature 579, 195–196 (2020)
T. Bernatowicz, G. Fraundorf, T. Ming, E. Anders, B. Wopenka, E. Zinner, P. Fraundorf, Evidence for interstellar SiC in the Murray carbonaceous chondrite. Nature 330, 728–730 (1987)
D.C. Black, R.O. Pepin, Trapped neon in meteorites - II. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 6, 395–405 (1969)
T. Blackburn, C.M.O’D. Alexander, R. Carlson, L.T. Elkins-Tanton, The accretion and impact history of the ordinary chondrite parent bodies. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 200, 201–217 (2017)
J. Bland-Hawthorn, K. Freeman, The Origin of the Galaxy and Local Group, Saas-Fee Advanced Course, vol. 37 (Springer, Berlin, 2014), p. 1
D. Bockelée-Morvan, U. Calmonte, S. Charnley, J. Duprat, C. Engrand, A. Gicquel, M. Hässig, E. Jehin, H. Kawakita, B. Marty, S. Milam, A. Morse, P. Rousellot, S. Sheridan, E.S. Wirström, Cometary isotopes measurements. Space Sci. Rev. 197, 47–83 (2015)
A.P. Boss, Collapse and fragmentation of molecular cloud cores. II. Collapse induced by stellar shock waves. Astrophys. J. 439, 224–236 (1995)
A.P. Boss, Evolution of the solar nebula. III. Protoplanetary disks undergoing mass accretion. Astrophys. J. 469, 906–920 (1996)
A.P. Boss, Mixing and transport of short-lived and stable isotopes and refractory grains in protoplanetary disks. Astrophys. J. 773, 5 (2013)
J. Boulliung, E. Füri, C. Dalou, L. Tissandier, L. Zimmermann, Y. Marrocchi, Oxygen fugacity and melt composition controls on nitrogen solubility in silicate melts. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 284, 120–133 (2020)
A.J. Brearley, The action of water, in Meteorites and the Early Solar System II, ed. by D. Lauretta, H.Y. McSween Jr. (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 2006), pp. 587–624
R. Brasser, S.J. Mojzsis, The partitioning of the inner and outer Solar System by a structured protoplanetary disk. Nat. Astron. 4, 492–499 (2020)
G. Budde, C. Burkhardt, G.A. Brennecka, M. Fischer-Gödde, T.S. Kruijer, T. Kleine, Molybdenum isotopic evidence for the origin of chondrules and a distinct genetic heritage of carbonaceous and non-carbonaceous meteorites. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 454, 293–303 (2016)
G. Budde, C. Burkhardt, T. Kleine, Molybdenum isotopic evidence for the late accretion of outer Solar System material to Earth. Nat. Astron. 3, 736–741 (2019)
C. Burkhardt, N. Dauphas, U. Hans, B. Bourdon, T. Kleine, Elemental and isotopic variability in solar system materials by mixing and processing of primordial disk reservoirs. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 261, 145–170 (2019)
A.G.W. Cameron, The first ten million years in the solar nebula. Meteoritics 30, 133–161 (1995)
A.G.W. Cameron, W. Truran, The supernova trigger for formation of the solar system. Icarus 30, 447–461 (1977)
P. Cartigny, B. Marty, Nitrogen isotopes and mantle geodynamics: the emergence of life and the atmosphere-crust-mantle connection. Elements 9, 359–366 (2013)
R.A. Chevalier, Young circumstellar disks near evolved massive stars and supernovae. Astrophys. J. 538, L151–L154 (2000)
C.-L. Chou, Fractionation of siderophile elements in the Earth’s upper mantle, in Proceedings of the 9th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (1978), pp. 219–230
L.A. Cieza, S. Casassus, J. Tobin, S.P. Bos, J.P. Williams, S. Perez, Z. Zhu, C. Caceres, H. Canovas, M.M. Dunham, A. Hales, J.L. Prieto, D.A. Principe, M.R. Schreiber, D. Ruiz-Rodriguez, A. Zurlo, Imaging the water snow-line during a protostellar outburst. Nature 535, 258–261 (2016)
R.N. Clayton, L. Grossman, T.K. Mayeda, A component of primitive nuclear composition in carbonaceous meteorites. Science 182, 485–488 (1973)
R.N. Clayton, T.K. Mayeda, A.E. Rubin, Oxygen isotopic compositions of enstatite chondrites and aubrites. J. Geophys. Res. 89, 245–249 (1984)
D.D. Clayton, Cosmic chemical memory: a new astronomy. Q. J. R. Astron. Soc. 23, 174–212 (1982)
R.N. Clayton, Solar system: self-shielding in the solar nebula. Nature 415, 860–861 (2002)
E.A. Cloutis, P. Hudon, T. Hiroi, M.J. Gaffey, P. Mann, J.F. Bell III., Spectral reflectance properties of carbonaceous chondrites: 6. CV chondrites. Icarus 221, 328–358 (2012a)
E.A. Cloutis, P. Hudon, T. Hiroi, M.J. Gaffey, Spectral reflectance properties of carbonaceous chondrites: 7. CK chondrites. Icarus 221, 911–924 (2012b)
J.N. Connelly, M. Bizzarro, Pb-Pb chronometry and the early Solar System. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 201, 345–363 (2017)
J.N. Connelly, M. Bizzarro, A.N. Krot, A. Nordlund, D. Wielandt, M.A. Ivanova, The absolute chronology and thermal processing of solids in the solar protoplanetary disk. Science 338, 651–655 (2012)
C. Dalou, E. Füri, C. Deligny, L. Piani, M.-C. Caumon, M. Laumonier, Redox control on nitrogen isotope fractionation during planetary core formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 116, 11485–14494 (2019)
N. Dauphas, The isotopic nature of the Earth’s accreting material through time. Nature 541, 521–524 (2017)
N. Dauphas, E.A. Schauble, Mass fractionation laws, mass-independent effects, and isotopic anomalies. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 44, 709–783 (2016)
A.M. Davis, The cosmochemical history of the pallasites. PhD dissertation, Yale University (1977)
A.M. Davis, J. Zhang, N.D. Greber, J. Hu, F.L.H. Tissot, N. Dauphas, Titanium isotopes and rare Earth patterns in CAIs: evidence for thermal processing and gas-dust decoupling in the protoplanetary disk. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 221, 275–295 (2018)
S.S. Davis, Condensation front migration in a protoplanetary nebula. Astrophys. J. 620, 994–1001 (2005)
E. Deloule, F. Albarède, S.M.F. Sheppard, Hydrogen isotope heterogeneities in the mantle from ion probe analysis of amphiboles from ultramafic rocks. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 105, 543–553 (1991)
E. Deloule, F. Robert, J.C. Doukhan, Interstellar hydroxyl in meteoritic chondrules: implications for the origin of water in the inner solar system. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 62, 3367–3378 (1998)
S.J. Desch, A. Kalyaan, A.C.M. O’D, The effect of Jupiter’s formation on the distribution of refractory elements and inclusions in meteorites. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 238, 11 (2018)
S.E. Dodson-Robinson, K. Willacy, P. Bodenheimer, N.J. Turner, C.A. Beichman, Ice lines, planetesimal composition and solid surface density in the solar nebula. Icarus 200, 672–693 (2009)
M.J. Drake, K. Righter, Determining the composition of the Earth. Nature 416, 39–44 (2002)
V.V. Dwarkadas, N. Dauphas, B. Meyer, P. Boyajian, M. Bojazi, Triggered star formation inside the shell of a Wolf–Rayet bubble as the origin of the solar system. Astrophys. J. 851, 147 (2017)
B. Fegley, Kinetics of gas-grain reactions in the solar nebula. Space Sci. Rev. 92, 177–200 (2000)
B. Fegley, H. Palme, Evidence for oxidizing conditions in the solar nebula from Mo and W depletions in refractory inclusions in carbonaceous chondrites. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 72, 311–326 (1985)
B. Fegley, K. Lodders, N.S. Jacobson, Volatile element chemistry during accretion of the Earth. Geochemistry 80, 125594 (2020)
B. Fegley Jr., R.G. Prinn, Solar nebula chemistry: implications for volatiles in the solar system, in The Formation and Evolution of Planetary Systems, ed. by H.A. Weaver, L. Danly (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1989), pp. 171–211
M. Fischer-Gödde, T. Kleine, Ruthenium isotopic evidence for an inner Solar System origin of the late veneer. Nature 541, 525–527 (2017)
M. Fischer-Gödde, B.-M. Magnus, C. Münker, K. Szilas, W.D. Maier, N. Messling, T. Morishita, M. Van Kranendonk, H. Smithies, Ruthenium isotope vestige of Earth’s pre-late-veneer mantle preserved in Archaean rocks. Nature 579, 240–244 (2020)
C. Floss, P. Haenecour, Presolar silicate grains: abundance, isotopic and elemental compositions, and the effects of secondary processing. Geochem. J. 50, 3–25 (2016)
P.N. Foster, A.P. Boss, Injection of radioactive nuclides from the stellar source that triggered the collapse of the presolar nebula. Astrophys. J. 489, 346–357 (1997)
E. Füri, B. Marty, Nitrogen isotope variations in the Solar System. Nat. Geosci. 8, 515–522 (2015)
E. Füri, P.H. Barry, L.A. Taylor, B. Marty, Indigenous nitrogen in the Moon: constraints from coupled nitrogen-noble gas analyses of mare basalts. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 431, 195–205 (2015)
E. Füri, E. Deloule, R. Trappitsch, The production rate of cosmogenic deuterium at the Moon’s surface. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 474, 76–82 (2017)
P. Garaud, D.N.C. Lin, The effect of internal dissipation and surface irradiation on the structure of disks and the location of the snow line around Sun-like stars. Astrophys. J. 654, 606–624 (2007)
S. Gerber, C. Burkhardt, G. Budde, K. Metzler, T. Kleine, Mixing and transport of dust in the early solar nebula as inferred from titanium isotope variations among chondrules. Astrophys. J. Lett. 841, L17 (2017)
M. Gounelle, A. Morbidelli, P.A. Bland, P. Spurný, E.D. Young, M. Sephton, Meteorites from the outer solar system? in The Solar System Beyond Neptune, ed. by M.A. Barucci, H. Boehnhardt, D.P. Cruikshank, A. Morbidelli (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 2008), pp. 525–541
M. Gounelle, P. Spurný, P.A. Bland, The orbit and atmospheric trajectory of the Orgueil meteorite from historical records. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 41, 135–150 (2006)
J. Gradie, E. Tedesco, Compositional structure of the asteroid belt. Science 216, 1405–1407 (1982)
M.M. Grady, I.P. Wright, Elemental and isotopic abundances of carbon and nitrogen in meteorite. Space Sci. Rev. 106, 231–248 (2003)
M.M. Grady, I.P. Wright, L.P. Carr, C.T. Pillinger, Compositional differences in enstatite chondrites based on carbon and nitrogen stable isotope measurements. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 50, 2799–2813 (1986)
L. Grossman, J.W. Larimer, Early chemical history of the solar system. Rev. Geophys. 12, 71–101 (1974)
F. Gyngard, S. Amari, E. Zinner, K.K. Marhas, Correlated silicon and titanium isotopic compositions of presolar SiC grains from Murchison CM2 chondrite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 221, 154–161 (2018)
L.J. Hallis, G.R. Huss, K. Nagashima, G.J. Taylor, S.A. Halldórsson, D.R. Hilton, M.J. Mottl, K.J. Meech, Evidence for primordial water in Earth’ s deep mantle. Science 350, 795–797 (2015)
K. Hashizume, N. Sugiura, Nitrogen isotopes in bulk ordinary chondrites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 59, 4057–4069 (1995)
C. Hayashi, Structure of the solar nebula, growth and degay of magnetic fields and effects of magnetic and turbulent viscosities on the nebula. Prog. Theor. Phys. Suppl. 70, 35–53 (1981)
P.R. Heck, J. Greer, L. Kööp, R. Trappitsch, F. Gyngard, H. Busemann, C. Maden, J.N. Ávila, A.M. Davis, R. Wieler, Lifetimes of interstellar dust from cosmic ray exposure ages of presolar silicon carbide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1107, 1884–1889 (2020)
S. Henke, H.-P. Gail, M. Trielof, W.H. Schwarz, T. Kleine, Thermal history modelling of the H chondrite parent body. Astron. Astrophys. 545, A135 (2012)
J.J. Hester, S.J. Desch, K.R. Healy, L.A. Leshin, The cradle of the solar system. Science 304, 1116 (2004)
P.J. Hevey, I.S. Sanders, A model for planetesimal meltdown by 26Al and its implications for meteorite parent bodies. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 41, 95–106 (2006)
D.C. Hezel, P.A. Bland, H. Palme, E. Jacquet, J. Bigolski, Compositions of chondrules and matrix and their complementary relationship in chondrites, in Chondrules: Records of Protoplanetary Disk Processes, ed. by S.S. Russell, H.C. Connolly Jr., A.N. Krot (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2019), pp. 91–121
C.D. Hilton, K.R. Bermingham, R.J. Walker, T.J. McCoy, Genetics, crystallization sequence, and age of the South Byron Trio iron meteorites: new insights to carbonaceous chondrite (CC) type parent bodies. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 251, 217–228 (2019)
M.M. Hirschmann, Comparative deep Earth volatile cycles: the case for C recycling from exosphere/ mantle fractionation of major (H2O, C, N) volatiles and from H2O/Ce, CO2/Ba, and CO2/Nb exosphere ratios. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 502, 262–273 (2018)
N.E. Holden, M.L. Bonardi, P. De Bièvre, P.R. Renne, I.M. andVilla, IUPAC-IUGS common definition and convention on the use of the year as a derived unit of time (IUPAC recommendations 2011). Pure Appl. Chem. 83, 1159–1162 (2011)
M. Honda, I. Mcdougall, D. Patterson, Solar noble gases in the Earth: the systematics of helium-neon isotopes in mantle derived samples. Lithos 30, 257–265 (1993)
T. Hopp, G. Budde, T. Kleine, Heterogeneous accretion of Earth inferred from Mo-Ru isotope systematics. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 534, 116065 (2020)
P. Hoppe, S. Amari, E. Zinner, T. Ireland, R.S. Lewis, Carbon, nitrogen, magnesium, silicon, and titanium isotopic compositions of single interstellar silicon carbide grains from the Murchison carbonaceous chondrite. Astrophys. J. 430, 870–890 (1994)
G.R. Huss, J.B. Smith, Titanium isotopic compositions of well-characterized silicon carbide grains from Orgueil (CI): implications for s-process nucleosynthesis. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 42, 1055–1075 (2007)
M. Hutson, A. Ruzicka, A multi-step model for the origin of E3 (enstatite) chondrites. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 35, 601–608 (2000)
T.R. Ireland, E.K. Zinner, S. Amari, Isotopically anomalous Ti in presolar SiC from the Murchison meteorite. Astrophys. J. 376, L53–L556 (1991)
M. Javoy, F. Pineau, H. Delorme, Carbon and nitrogen isotopes in the mantle. Chem. Geol. 57, 41–62 (1986)
J.F. Kerridge, Carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen in carbonaceous chondrites: abundances and isotopic compositions in bulk samples. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 49, 1707–1714 (1985)
R.S. Klessen, in Star Formation in the Local Universe. European Astronomical Society Publications Series, vol. 51 (2011), pp. 133–167
L. Kööp, A.M. Davis, D. Nakashima, C. Park, A.N. Krot, K. Nagashima, T.J. Tenner, P.R. Heck, N.T. Kita, A link between oxygen, calcium and titanium isotopes in 26Al-poor hibonite-rich CAIs from Murchison and implications for the heterogeneity of dust reservoirs in the solar nebula. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 189, 70–95 (2016)
S. Krijt, F.J. Ciesla, E.A. Bergin, Tracing water vapor and ice during dust growth. Astrophys. J. 883, 285 (2016)
A.N. Krot, K. Nagashima, G. Libourel, K.E. Miller, Multiple mechanisms of transient heating events in the protoplanetary disk: evidence from precursors of chondrules and igneous Ca, Al-rich inclusions, in Chondrules: Records of Protoplanetary Disk Processes, ed. by S.S. Russell, H.C. Connolly Jr., A.N. Krot (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2018), pp. 11–56
A.N. Krot, Refractory inclusions in carbonaceous chondrites: records of early solar system processes. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 54, 1647–1691 (2019)
T.S. Kruijer, M. Touboul, M. Fischer-Gödde, K.R. Bermingham, R.J. Walker, T. Kleine, Protracted core formation and rapid accretion of protoplanets. Science 344, 1150–1154 (2014)
T.S. Kruijer, C. Burkhardt, G. Budde, T. Kleine, Age of Jupiter inferred from the distinct genetics and formation times of meteorites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 114, 6712–6716 (2017)
T. Kudo, J. Hashimoto, T. Muto, H.B. Liu, R. Dong, Y. Hasegawa, T. Tsukagoshi, M. Konishi, A spatially resolved au-scale inner disk around DM Tau. Astrophys. J. Lett. 868, L5 (2018)
C.C. Kung, R.N. Clayton, Nitrogen abundances and isotopic compositions in stony meteorites. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 38, 421–435 (1978)
J. Labidi, P.H. Barry, D.V. Bekaert, M.W. Broadley, B. Marty, T. Giunta, O. Warr, B. Sherwood Lollar, T.P. Fischer, G. Avice, A. Caracausi, C.J. Ballentine, A. Halldórsson Stefánsson, M.D. Kurz, E.D. Young, Hydrothermal 15N15N abundances constrain the origins of mantle nitrogen. Nature 580, 367–371 (2020)
T. Lee, D.A. Papanastassiou, G.J. Wasserburg, Aluminum-26 in the early solar system: fossil or fuel? Astrophys. J. 211, L107–110 (1977)
T. Lee, F.H. Shu, S. Shang, A.E. Glassgold, K.E. Rehm, Protostellar cosmic rays and extinct radioactivities in meteorites. Astrophys. J. 506, 898–912 (1998)
J.S. Lewis, The temperature gradient in the solar nebula. Science 186, 440–443 (1974)
J.S. Lewis, R.G. Prinn, Kinetic inhibition of CO and N2 reduction in the solar nebula. Astrophys. J. 238, 357–364 (1980)
R.S. Lewis, T. Ming, J.F. Wacker, E. Anders, E. Steel, Interstellar diamonds in meteorites. Nature 326, 160–162 (1987)
Y. Li, B. Marty, S. Shcheka, L. Zimmermann, H. Keppler, Nitrogen isotope fractionation during terrestrial core-mantle separation. Geochem. Perspect. Lett. 2, 138–147 (2016)
G. Libourel, B. Marty, F. Humbert, Nitrogen solubility in basaltic melt. Part I. Effect of oxygen fugacity. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 67, 4123–4135 (2003)
K. Lodders, An oxygen isotope mixing model for the accretion and composition of rocky planets. Space Sci. Rev. 92, 341–354 (2000)
K. Lodders, Solar system abundances and condensation temperatures of the elements. Astrophys. J. 591, 1220–1247 (2003)
K. Lodders, Jupiter formed with more tar than ice. Astrophys. J. 611, 587–597 (2004)
K. Lodders, S. Amari, Presolar grains from meteorites: remnants from early times of the solar system. Chem. Erde 65, 93–166 (2005)
K. Lodders, B. Fegley, Chemistry of the Solar System (Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, 2011). 476 pp.
K. Lodders, R. Osborne, Perspectives on the comet-asteroid-meteorite link. Space Sci. Rev. 90, 289–297 (1999)
G.J. MacPherson, Calcium-aluminum-rich inclusions in chondritic meteorites, in Meteorites and Cosmochemical Processes, vol. 1, ed. by A.M. Davis (Elsevier, Oxford, 2014), pp. 139–179. Treatise on Geochemistry, 2nd edn., ed. by H.D. Holland, K.K. Turekian
B. Marty, The origins and concentrations of water, carbon, nitrogen and noble gases on Earth. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 313–314, 56–66 (2012)
B. Marty, M. Chaussidon, R.C. Wiens, A.J.G. Jurewicz, D.S. Burnett, A 15N-poor isotopic composition for the Solar System as shown by Genesis solar wind samples. Science 332, 1533–1536 (2011)
B. Marty, G. Avice, Y. Sano, K. Altwegg, H. Balsiger, M. Hässig, A. Morbidelli, O. Mousis, M. Rubin, Origins of volatile elements (H, C, N, noble gases) on Earth and Mars in light of recent results from the ROSETTA cometary mission. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 441, 91–102 (2016)
B. Mason, The enstatite chondrites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 30, 23–39 (1966)
K.J. Mathew, K. Marti, Early evolution of Martial volatiles: nitrogen and noble gas components in ALH84001 and Chassigny. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 1401–1422 (2001)
B. Mayer, N. Wittig, M. Humayun, I. Leya, Palladium isotopic evidence for nucleosynthetic and cosmogenic isotope anomalies in IVB iron meteorites. Astrophys. J. 809, 180–188 (2015)
W.F. McDonough, S.-S. Sun, The composition of the Earth. Chem. Geol. 120, 223–253 (1995)
R. Meijerink, K.M. Pontoppidan, G.A. Blake, D.R. Poelman, C.P. Dullemond, Radiative transfer models of mid-infrared H2O lines in the planet-forming region of circumstellar disks. Astrophys. J. 704, 1471–1481 (2009)
S. Mikhail, E. Füri, On the origin(s) and evolution of Earth’s carbon. Elements 15, 307–312 (2019)
A. Morbidelli, B. Bitsch, A. Crida, M. Gounelle, T. Guillot, S. Jacobson, A. Johansen, M. Lambrechts, E. Lega, Fossilized condensation lines in the Solar System protoplanetary disk. Icarus 267, 368–376 (2016)
A. Morbidelli, K.J. Walsh, D.P. O’Brien, D.A. Minton, W.F. Bottke, Dynamical evolution of the asteroid belt, in Asteroids IV, ed. by P. Michel, F. DeMeo, W.F. Bottke (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 2015), pp. 493–508
A. Morbidelli, J.I. Lunine, D.P.O. Brien, S.N. Raymond, K.J. Walsh, Building terrestrial planets. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 40, 251–278 (2012)
N. Moskovitz, E. Gaidos, Differentiation of planetesimals and the thermal consequences of melt migration. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 46, 903–918 (2011)
H. Nakano, A. Kouchi, S. Tachibana, A. Tsuchiyama, Evaporation of interstellar organic materials in the solar nebula. Astrophys. J. 592, 1252–1262 (2003)
H. Nakano, N. Hirakaw, Y. Matsubara, S. Yamashita, T. Okuchi, K. Asahina, R. Tanaka, N. Suzuki, H. Naraoka, Y. Takano, S. Tachibana, T. Hama, Y. Oba, Y. Kimura, N. Watanabe, A. Kouchi, Precometary organic matter: a hidden reservoir of water inside the snow line. Sci. Rep. 10, 7755 (2020)
J.A.M. Nanne, F. Nimmo, J.N. Cuzzi, T. Kleine, Origin of the non-carbonaceous–carbonaceous meteorite dichotomy. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 511, 44–54 (2019)
S. Niemeyer, Titanium isotope anomalies in chondrules from carbonaceous chondrites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 52, 309–318 (1988)
L.R. Nittler, F. Ciesla, Astrophysics with extraterrestrial materials. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 54, 53–93 (2016)
A. Oka, T. Nakamoto, S. Ida, Evolution of snow line in optically thick protoplanetary disks: effect of water ice opacity and dust grain size. Astrophys. J. 738, 141 (2011)
U. Ott, Planetary and pre-solar noble gases in meteorites. Chem. Erde 74, 519–544 (2014)
H. Palme, H. O’Neill, Cosmochemical estimates of mantle composition, in The Mantle and Core, vol. 3, ed. by R.W. Carlson (2003), pp. 1–39. Treatise on Geochemistry, vol. 3, 2nd edn., ed. by H.D. Holland, K.K. Turekian (Elsevier)
H. Palme, K. Lodders, A. Jones, Solar system abundances of the elements, in Treatise on Geochemistry, vol. 2, ed. by H.D. Holland, K.K. Turekian 2nd edn. (Elsevier, Oxford, 2014), pp. 15–36
M. Palot, P. Cartigny, J.W. Harris, F.V. Kaminsky, T. Stachel, Evidence for deep mantle convection and primordial heterogeneity from nitrogen and carbon stable isotopes in diamond. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 357–358, 179–193 (2012)
J. Pape, K. Mezger, A.-S. Bouvier, L.P. Baumgartner, Time and duration of chondrule formation: constraints from 26Al-26Mg ages of individual chondrules. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 244, 416–436 (2019)
A. Patzer, L. Schultz, Noble gases in enstatite chondrites II: the trapped component. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 37, 601–612 (2002)
V.K. Pearson, M.A. Sephton, I. Gilmour, I. Franchi, Hydrogen isotopic composition of the Tagish Lake meteorite: comparison with other carbonaceous chondrites, in 32nd Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Abstract 1861 (2001)
V.K. Pearson, M.A. Sephton, I.A. Franchi, J.M. Gibson, I. Gilmour, Carbon and nitrogen in carbonaceous chondrites: elemental abundances and stable isotopic compositions. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 41, 1899–1918 (2006)
L. Piani, F. Robert, L. Remusat, Micron-scale D/H heterogeneity in chondrite matrices: a signature of the pristine solar system water? Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 415, 154–164 (2015)
L. Piani, Y. Marrocchi, T. Rigaudier, L.G. Vacher, D. Thomassin, B. Marty, Earth’s water may have been inherited from material similar to enstatite chondrite meteorites. Science 369, 1110–1113 (2020).
G.M. Poole, M. Rehkämper, B.J. Coles, T. Goldberg, C.L. Smith, Nucleosynthetic molybdenum isotope anomalies in iron meteorites – new evidence for thermal processing of solar nebula material. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 473, 215–226 (2017)
L. Qin, R.W. Carlson, Nucleosynthetic isotope anomalies and their cosmochemical significance. Geochem. J. 50, 43–65 (2016)
S.N. Raymond, D.P. O’Brien, A. Morbidelli, N.A. Kaib, Building the terrestrial planets: constrained accretion in the inner solar system. Icarus 203, 644–662 (2009)
S.N. Raymond, A. Izidoro, Origin of water in the inner solar system: planetesimals scattered inward during Jupiter and Saturn’s rapid gas accretion. Icarus 297, 134–148 (2017)
S.N. Raymond, A. Izidoro, A. Morbidelli, Solar system formation in the context of extrasolar planets, in Planetary Astrobiology, ed. by V. Meadows, G.N. Arney, B.E. Schmidt D.J. Marais (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 2020), pp. 287–324
J. Render, S. Ebert, C. Burkhardt, T. Kleine, G.A. Brennecka, Titanium isotopic evidence for a shared genetic heritage of refractory inclusions from different carbonaceous chondrites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 254, 40–53 (2019)
J.H. Reynolds, G. Turner, Rare gases in chondrite Renazzo. J. Geophys. Res. 49, 3263–3281 (1964)
F. Robert, The D/H ratio in chondrites. Space Sci. Rev. 106, 87–101 (2003)
F. Robert, S. Epstein, The concentration and isotopic composition of hydrogen, carbon and nitrogen in carbonaceous meteorites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 46, 81–95 (1982)
D.C. Rubie, S.A. Jacobson, A. Morbidelli, D.P. O’Brien, E.D. Young, J. de Vries, F. Nimmo, H. Palme, D.J. Frost, Accretion and differentiation of the terrestrial planets with implications for the composition of early-formed Solar System bodies. Icarus 248, 89–108 (2015)
A.E. Rubin, B. Fegley, R. Brett, Oxidation state in chondrites, in Meteorites and the Early Solar System, ed. by J.F. Kerridge, M.S. Mathews (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 1988), pp. 488–511
A.E. Rubin, B.-G. Choi, Origin of halogens and nitrogen in enstatite chondrites. Earth Moon Planets 105, 41–53 (2009)
A.E. Rubin, J.T. Wasson, Variations of chondrite properties with heliocentric distance. Meteoritics 30, 569 (1995) (Abstr.)
A.E. Rubin, C. Ma, Meteoritic minerals and their origins. Geochemistry 77, 325–385 (2017)
S. Sahijpal, P. Soni, G. Gupta, Numerical simulations of the differentiation of accreting planetesimals with 26Al and 60Fe as the heat sources. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 42, 1529–1548 (2007)
D.D. Sasselov, M. Lecar, On the snow line in dusty protoplanetary disks. Astrophys. J. 528, 995–998 (2000)
T. Sato, S. Okuzumi, S. Ida, On the water delivery to terrestrial embryos by ice pebble accretion. Astron. Astrophys. 589, A15 (2016)
E.R.D. Scott, Formation of olivine-metal textures in pallasite meteorites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 41, 693–710 (1977)
E.R.D. Scott, A.N. Krot, Chondritic meteorites and the high-temperature nebular origins of their components, in Chondrites and the Protoplanetary Disk, ed. by A.N. Krot et al. ASP Conference Series, vol. 341 (Astronomical Society of the Pacific, San Francisco, 2005), pp. 15–52
E.R.D. Scott, A.N. Krot, I.S. Sanders, Isotopic dichotomy among meteorites and its bearing on the protoplanetary disk. Astrophys. J. 854, 164 (2018)
F.H. Shu, F.C. Adams, S. Lizano, Star formation in molecular clouds: observation and theory. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 25, 23–72 (1987)
F.H. Shu, X-rays and fluctuating X-winds from protostars. Science 277, 1475–1479 (1997)
F.H. Shu, H. Shang, M. Gounelle, A.E. Glassgold, T. Lee, The origin of chondrules and refractory inclusions in chondritic meteorites. Astrophys. J. 548, 1029–1050 (2001)
A. Shukolyukov, G.W. Lugmair, Live iron-60 in the early solar system. Science 259, 1138–1142 (1993a)
A. Shukolyukov, G.W. Lugmair, 60Fe in eucrites. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 119, 159–166 (1993b)
F. Spitzer, C. Burkhardt, G. Budde, T.S. Kruijer, A. Morbidelli, T. Kleine, Isotopic evolution of the inner Solar System inferred from molybdenum isotopes in meteorites. Astrophys. J. Lett. 898, L2 (2020)
T. Stephan, A.M. Davis, Molybdenum in presolar silicon carbide grains reveal details of s-, r-, and p-process nucleosynthesis, in 82nd Annual Meeting of the Meteoritical Society (2019). LPI Contrib. No. 2157, abstract #6107
A. Stephant, L.A.J. Garvie, P. Mane, R. Hervig, M. Wadhwa, Terrestrial exposure of a fresh Martian meteorite causes rapid changes in hydrogen isotopes and water concentrations. Sci. Rep. 8, 12385 (2018)
N. Sugiura, W. Fujiya, Correlated accretion ages and \(\varepsilon ^{54}\)Cr of meteorite parent bodies and the evolution of the solar nebula. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 49, 772–787 (2014)
S. Sutton, C.M.O’D. Alexander, A. Bryant, A. Lanzirotti, M. Newville, E.A. Cloutis, The bulk valence state of Fe and the origin of water in chondrites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 211, 115–132 (2017)
S.R. Taylor, Solar System Evolution, 2nd edn. (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2001). 484 pp.
A. Takigawa, R.M. Stroud, L.R. Nittler, C.M.O’D. Alexander, A. Miyake, High-temperature dust condensation around an AGB star: evidence from a highly pristine presolar corundum. Astrophys. J. 862, L13 (2018)
M.H. Thiemens, J.E. Heidenreich, The mass independent fractionation of oxygen: a novel isotope effect and its possible cosmochemical implications. Science 219, 1073–1075 (1983)
Z.A. Torrano, G.A. Brennecka, C.D. Williams, S.J. Romaniello, V.K. Rai, R.R. Hines, M. Wadhwa, Titanium isotope signatures of calcium-aluminum-rich inclusions from CV and CK chondrites: implications for early Solar System reservoirs and mixing. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 263, 13–30 (2019)
J.M. Trigo-Rodríguez, A. Rimola, S. Tanbakouei, V. Cabedo Soto, M. Lee, Accretion of water in carbonaceous chondrites: current evidence and implications for the delivery of water to early Earth. Space Sci. Rev. 215, 18 (2019)
A. Trinquier, J.L. Birck, C.J. Allègre, Widespread 54Cr heterogeneity in the inner solar system. Astrophys. J. 655, 1179–1185 (2007)
A. Trinquier, T. Elliott, D. Ulfbeck, C. Coath, A.N. Krot, M. Bizzarro, Origin of nucleosynthetic isotope heterogeneity in the Solar protoplanetary disk. Science 324, 374–376 (2009)
H.C. Urey, The Planets: Their Origin and Development (Yale University Press, New Haven, 1952), 245 pp.
L. Vacher, L. Piani, T. Rigaudier, D. Thomassin, G. Florin, M. Piralla, Y. Marrocchi, Hydrogen in chondrites: influence of parent body alteration and atmospheric contamination on primordial components. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 281, 53–66 (2020)
P. Vernazza, B. Zanda, R.P. Binzel, T. Hiroi, F.E. DeMeo, M. Birlan, R. Hewins, L. Ricci, P. Barge, M. Lockhart, Multiple and fast: the accretion of ordinary chondrite parent bodies. Astrophys. J. 791, 120–144 (2014)
P. Vernazza, M. Marsset, P. Beck, R.P. Binzel, M. Birlan, E.A. Cloutis, F.E. DeMeo, C. Dumas, T. Hiroi, Compositional homogeneity of CM parent bodies. Astrophys. J. 152, 54–64 (2016)
J. Villeneuve, M. Chaussidon, G. Libourel, Homogeneous distribution of 26Al in the Solar System from the Mg isotopic composition of chondrules. Science 325, 985–988 (2009)
R. Visser, E.F. van Dishoeck, S.D. Doty, C.P. Dullemond, The chemical history of molecules in circumstellar disks. Astron. Astrophys. 495, 881–897 (2009)
R.J. Walker, Highly siderophile elements in the Earth, Moon and Mars: update and implications for planetary accretion and differentiation. Geochemistry 69, 101–125 (2009)
R.J. Walker, K. Bermingham, J. Liu, I.S. Puchtel, M. Touboul, E.A. Worsham, In search of late-stage planetary building blocks. Chem. Geol. 411, 125–142 (2015)
N.P. Walte, G.F.D. Solferino, G.J. Golabek, D.S. Souza, A. Bouvier, Two-stage formation of pallasites and the evolution of their parent bodies revealed by deformation experiments. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 546, 116419 (2020)
K.J. Walsh, A. Morbidelli, S.N. Raymond, D.P. O’Brien, A.M. Mandell, A low mass for Mars from Jupiter’s early gas-driven migration. Nature 475, 206–209 (2011)
K.J. Walsh, H.F. Levison, Planetesimals to terrestrial planets: collisional evolution amidst a dissipating gas disk. Icarus 329, 88–100 (2019)
H. Wang, R.C. Bell, M.J. Iemeda, A.A. Tsekouras, J.P. Cowin, Sticky ice grains aid planet formation: unusual properties of cryogenic water ice. Astrophys. J. 620, 1028–1032 (2005)
P.H. Warren, Stable-isotopic anomalies and the accretionary assemblage of the Earth and Mars: a subordinate role for carbonaceous chondrites. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 311, 93–100 (2011)
J.T. Wasson, Meteorites: Their Record of Early Solar-System History (W.H. Freeman, New York, 1985)
J.T. Wasson, The building stones of the planets, in Mercury, ed. by F. Vilas, C.R. Chapman, M.S. Matthews (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 1988), pp. 622–650
J.T. Wasson, G.W. Kallemeyn, Compositions of chondrites. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A, Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 32, 391–403 (1988)
M.K. Weisberg, T.J. McCoy, A.N. Krot, Systematics and evaluation of meteorite classification, in Meteorites and the Early Solar System II, ed. by D.D. Lauretta, H.Y. McSween (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 2006), pp. 19–52
C.D. Williams, S. Muhkopadyay, Capture of nebular gases during Earth’s accretion is preserved in deep-mantle neon. Nature 565, 78–81 (2018)
J.P. Williams, L.A. Cieza, Protoplanetary disks and their evolution. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 49, 67–117 (2011)
J.A. Wood, The chondrite types and their origins, in Chondrites and the Protoplanetary Disk, ed. by A.N. Krot, E.R.D. Scott, B. Reipurth (Astronomical Society of the Pacific, Hawai’i, 2005), pp. 953–971
B.J. Wood, J. Li, A. Shahar, Carbon in the core: its influence on the properties of core and mantle. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 75, 231–250 (2013)
E.A. Worsham, K.R. Bermingham, R.J. Walker, Characterizing cosmochemical materials with genetic affinities to the Earth: genetic and chronological diversity within the IAB iron meteorite complex. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 467, 157–166 (2017)
J. Wu, S.J. Desch, L. Schaefer, L.T. Elkins-Tanton, K. Pahlevan, P.R. Buseck, Origin of Earth’s water: chondritic inheritance plus nebular ingassing and storage of hydrogen in the core. J. Geophys. Res., Planets 123, 2691–2712 (2018)
L. Yang, F.J. Ciesla, The effects of disk building on the distributions of refractory materials in the solar nebula. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 47, 99–119 (2012)
J. Yang, J.I. Goldstein, E.R.D. Scott, Iron meteorite evidence for early formation and catastrophic disruption of protoplanets. Nature 446, 888–891 (2007)
J. Yang, J.I. Goldstein, E.R.D. Scott, Main-group pallasites: thermal history, relationship to IIIAB iron, and origin. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 74, 4471–4492 (2010)
R. Yokochi, B. Marty, A determination of the neon isotopic composition of the deep mantle. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 225, 77–88 (2004)
T. Yokoyama, Y. Nagai, R. Fukai, T. Hirata, Origin and evolution of distinct molybdenum isotopic variabilities within carbonaceous and non-carbonaceous reservoirs. Astrophys. J. 883, 62 (2019)
J. Zhang, N. Dauphas, A.M. Davis, I. Leya, A. Fedkin, The proto-Earth as a significant source of lunar material. Nat. Geosci. 5, 251–255 (2012)
K. Zhang, G.A. Blake, E.A. Bergin, Evidence of fast pebble growth near condensation fronts in the HL Tau protoplanetary disk. Astrophys. J. Lett. 806, L7 (2015)
E. Zinner, Presolar grains, in Meteorites and Cosmochemical Processes, ed. by A.M. Davis (Elsevier, New York, 2014), pp. 181–213. Treatise on Geochemistry, vol. 1, 2nd edn., ed. by H.D. Holland, K.K. Turekian
E. Zinner, M. Tang, E. Anders, Nature 330, 730–732 (1987)
E. Zinner, S. Amari, R. Guinness, C. Jennings, A.F. Mertz, A.N. Nguyen, R. Gallino, P. Hoppe, M. Lugaro, L.R. Nittler, R.S. Lewis, NanoSIMS isotopic analysis of small presolar grains: search for Si3N4 grains from AGB stars and Al and Ti isotopic compositions of rare presolar SiC grains. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 71, 4786–4813 (2007)
Acknowledgements
We thank the International Space Science Institute (Bern, CH) for hosting and supporting the workshop “Reading Terrestrial Planet Evolution in Isotopes and Element Measurements” and the editors of this book. Our sincere thanks to editor in chief H. Lammer for his guidance and patience. We also thank thorough reviews by A.M. Davis and C.M.O’D. Alexander. KRB was supported by NASA Emerging Worlds grants 80NSSC18K0496 and NNX16AN07G, NASA SSERVI grant NNA14AB07A, and the Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Rutgers University. EF and BM were supported by the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program (grant agreements no. 715028 and no. 695618, respectively). Work by KL was supported in part by NSF grant AST 1517541 and the McDonnell Centre for the Space Sciences. This is CRPG-CNRS contribution 2374.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Reading Terrestrial Planet Evolution in Isotopes and Element Measurements
Edited by Helmut Lammer, Bernard Marty, Aubrey L. Zerkle, Michel Blanc, Hugh O’Neill and Thorsten Kleine
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bermingham, K.R., Füri, E., Lodders, K. et al. The NC-CC Isotope Dichotomy: Implications for the Chemical and Isotopic Evolution of the Early Solar System. Space Sci Rev 216, 133 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-020-00748-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-020-00748-w