Abstract
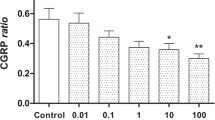
The possible inhibitory control by the novel analgesic S 12813-4 (3-(2-(4-phenylpiperazine-1-yl)-ethyl)2-oxo-2,3-dihydrooxazolo(b)pyridine) of spinal neurones containing substance P (SP) and/or calcitonin generelated peptide (CGRP) was assessed in vitro and in vivo in the rat. S 12813-4 (10 nM - 0.1 mM) did not affect the spinal release of CGRP-like material (CGRPLM) but inhibited in a concentration dependent manner the K+-evoked overflow of SP-like material (SPLM) from slices of the dorsal half of the rat lumbar enlargement. The inhibitory effect of 10 μM S 12813-4 on SPLM release was not additive with that of Na (0.1 mM), and could be prevented by the α2-adrenoceptor antagonist idazoxan (10 μM). Similarly, idazoxan (10 μM) suppressed the inhibition by intrathecally administered S 12813-4 (10 μM) of the spinal outflow of SPLM in halothane anaesthetized rats whose intrathecal space was perfused with an artificial cerebrospinal fluid. These data suggest that the analgesic effect of S 12813-4 might involve some α2-adrenoreceptor-mediated control of SPLM release within the spinal cord. Whether this control concerns SP-containing primary afferent fibres (presynaptic inhibition) or SP-containing interneurones and/or bulbo-spinal SP-ergic pathways (postsynaptic inhibition) deserves further investigations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bourgoin S, Pohl M, Benoliel JJ, Mauborgne A, Collin E, Hamon M, Cesselin F (1992) Gamma-aminobutyric acid, through GABAA receptors, inhibits the potassium-stimulated release of calcitonin gene-related peptide- but not that of substance P-like material from rat spinal cord slices. Brain Res 583:344–348
Bourgoin S, Pohl M, Mauborgne A, Benoliel JJ, Collin E, Hamon M, Cesselin F (1993) Monoaminergic control of the release of calcitonin gene-related peptide- and substance P-like materials from rat spinal cord slices. Neuropharmacology 32:633–640
Calvillo O, Ghignone M (1986) Presynaptic effect of clonidine on unmyelinated afferent fibers in the spinal cord of the cat. Neurosci Lett 64:335–339
Carstens E, Gilly H, Schreiber H, Zimmermann M (1987) Effects of midbrain stimulation and iontophoretic application of serotonin, noradrenaline, morphine and GABA on electrical thresholds of afferent C- and A-fibre terminals in cat spinal cord, Neuroscience 21:395–406
Cesselin F, Bourgoin S, Artaud F, Hamon M (1984) Basic and regulatory mechanisms of in vitro release of met-enkephalin from the dorsal zone of the rat spinal cord. J Neurochem 43:763–773
Collin E, Mauborgne A, Bourgoin S, Chantrel D, Hamon M, Cesselin F (1991) In vivo tonic inhibition of spinal substance P (like material) release by endogenous opioid(s) acting at δ receptors. Neuroscience 44:725–731
Collin E, Frechilla D, Pohl M, Bourgoin S, Le Bars D, Hamon M, Cesselin F (1993) Opioid control of the release of calcitonin generelated peptide-like material from the rat spinal cord in vivo. Brain Res 609:211–222
Davies J (1989) Effects of tizanidine, eperisone and afloqualone on feline dorsal horn neuronal responses to peripheral cutaneous noxious and innocuous stimuli. Neuropharmacology 28:1357–1362
Franco-Cereceda A, Henke H, Lundberg JM, Petermann JB, Hökfelt T, Fischer JA (1987) Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in capsaicin-sensitive substance P-immunoreactive sensory neurons in animals and man: distribution and release by capsaicin. Peptides 8:399–410
Go VLW, Yaksh TL (1987) Release of substance P from the cat spinal cord. J Physiol (Lond) 391:41–167
Hamon MD, Collin E, Chantrel D, Vergé D, Bourgoin S (1991) The contribution of monoamines and their receptors to pain control. In: Basbaum AI, Besson JM (eds) Towards a new pharmacotherapy of pain. Wiley, Chichester, pp 83–102
Headley PM, Duggan AW, Griersmith BJ (1978) Selective reduction by noradrenaline and 5-hydroxytryptamine of nociceptive responses of cat dorsal horn neurones. Brain Res 145:185–189
Hökfelt T, Ljungdahl A, Terenius L, Elde R, Nilsson G (1977) Immunohistochemical analyses of peptide pathways possibly related to pain and analgesia: enkephalin and substance P. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:3081–3085
Howe JR, Wang JY, Yaksh TL (1983) Selective antagonism of the antinociceptive effect of intrathecally applied α-adrenergic agonists by intrathecal prazosin and intrathecal yohimbine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 224:552–558
Howe JR, Yaksh TL, Go VL (1987) The effect of unilateral dorsal root ganglionectomies or ventral rhizotomies on α2-adrenoreceptor binding to, and the substance P, enkephalin, and neurotensin content of, the cat lumbar spinal cord. Neuroscience 21:385–394
Hughes HE, Barr GA (1988) Analgesic effects of intrathecally applied noradrenergic compounds in the developing rat: differences due to thermal vs mechanical nociception. Devl Brain Res 41:109–120
Hutchison WD, Morton CR (1989) Electrical stimulation of primary afferent A fibres does not reduce substance P release in the dorsal horn of the cat. Pain 37:357–363
Jeftinija S, Semba K, Randic M (1981) Norepinephrine reduces excitability of single cutaneous primary afferent C-fibres in the cat spinal cord. Brain Res 219:456–463
Kayser V, Desmeules J, Gullbaud G (1992) Effects of noradrenergic agonists on animal chronic pain models: arthritic and mononeuropathic rats. In: Besson JM, Guilbaud G (eds) Towards the use of noradrenergic agonists for the treatment of pain. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 151–167
Kuraishi Y, Hirota N, Sato Y, Hino Y, Satoh M, Takagi H (1985a) Evidence that substance P and somatostatin transmit separate information related to pain in the spinal dorsal horn. Brain Res 325: 294–298
Kuraishi Y, Hirota N, Sato Y, Kaneko S, Satoh M, Takagi H (1985b) Noradrenergic inhibition of the release of substance P from the primary afferents in the rabbit spinal cord dorsal horn. Brain Res 359:177–182
Mauborgne A, Lutz O, Legrand JC, Hamon M, Cesselin F (1987) Opposite effects of μ and δ opioid receptor agonists on the in vitro release of substance P-like material from the rat spinal cord. J Neurochem 48:529–537
Mauborgne A, Bourgoin S, Benoliel JJ, Hamon M, Cesselin F (1991) Is substance P released from slices of the rat spinal cord inactivated by peptidase(s) distinct from both “enkephalinase” and “angiotensin-converting enzyme”? Neurosci Lett 123:221–225
Ono H, Mishima A, Ono S, Fukuda H, Vasko MR (1991) Inhibitory effects of clonidine and tizanidine on release of substance P from slices of rat spinal cord and antagonism by α-adrenergic receptor antagonists. Neuropharmacology 30:585–589
Ossipov MH, Harris S, Lloyd P, Messineo E (1990) An isobolographic analysis of the antinociceptive effect of systemically and intrathecally administered combinations of clonidine and opiates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 255:1107–1116
Pang IH, Vasko MR (1986) Morphine and norepinephrine but not 5-hydroxytryptamine and γ-aminobtuyric acid inhibit the potassium-stimulated release of substance P from rat spinal cord slices. Brain Res 376:268–279
Pohl M, Lombard MC, Bourgoin S, Carayon A, Benoliel JJ, Mauborgne A, Besson JM, Hamon M, Cesselin F (1989a) Opioid control of the in vitro release of calcitonin gene-related peptide from primary afferent fibres projecting in the rat cervival cord. Neuropeptides 14:151–159
Pohl M, Mauborgne A, Bourgoin S, Benoliel JJ, Hamon M, Cesselin F (1989b) Neonatal capsaicin treatment abolishes the modulations by opioids of substance P release from rat spinal cord slices. Neurosci Lett 96:102–107
Pohl M, Collin E, Bourgoin S, Clot AM, Hamon M, Cesselin F, Le Bars D (1992) In vivo release of calcitonin gene-related peptide-like material from the cervico-trigeminal area in the rat. Effects of electrical and noxious stimulations of the muzzle. Neuroscience 50:697–706
Puke MJC, Xu XJ, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z (1991) Intrathecal administration of clonidine suppresses autotomy, a behavioral sign of chronic pain in rats after sciatic nerve section. Neurosci Lett 133:199–202
Ruffolo RRJ, Waddell JE, Yaden EL (1980) Receptor interactions of imidazolines. IV. Structural requirements for alpha adrenergic receptor occupation and receptor activity by clonidine and a series of structural analogs in rat aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 213:267–272
Ruffolo RR, Nichols AJ, Stadel JM, Hieble JP (1991) Structure and function of α-adrenoceptors. Pharmacol Rev 43:475–505
Skofitsch G, Jacobowitz DM (1985) Calcitonin gene-related peptide coexists with substance P in capsaicin sensitive neurons and sensory ganglia of the rat. Peptides 6:747–754
Sullivan AF, Dashwood MR, Dickenson AH (1987) α2-Adrenoceptor modulation of nociception in rat spinal cord: location, effects and interactions with morphine. Eur J Pharmacol 138:169–177
Takahashi T, Otsuka M (1975) Regional distribution of substance P in the spinal cord and nerve roots of the cat and the effect of dorsal root section. Brain Res 87:1–11
Takano Y, Yaksh TL (1992) Characterization of the pharmacology of intrathecally administered alpha-2 agonists and antagonists in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 261:764–772
Takano M, Takano Y, Yaksh TL (1993) Release of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), substance P (SP), and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) from rat spinal cord: modulation by α2 agonists. Peptides 14:371–378
Tiseo PJ, Adler MW, Liu-Chen L-Y (1990) Differential release of substance P and somatostatin in the rat spinal cord to noxious cold and heat; effect of dynorphin A (1–17). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 252:539–545
Villanueva L, Chitour D, Le Bars D (1988) Effects of tizanidine (DS 103–282) on dorsal horn convergent neurones in the rat. Pain 35:187–197
Weihe E (1992) Neurochemical anatomy of the mammalian spinal cord: functional implications. Ann Anat 174:89–118
Willcockson WS, Chung JM, Hori Y, Lee KH, Willis WD (1984) Effects of iontophoretically released amino acids and amines on primate spinothalamic tract cells. J Neurosci 4:732–740
Yaksh TL, Stevens CW (1988) Properties of the modulation of spinal nociceptive transmission by receptor-selective agents. In: Dubner R, Gebhart GF and Bond MR (eds) Proceedings of the Vth World Congress on Pain. Elsevier Amsterdam, pp 417–435
Yaksh TL, Tyce GM (1980) Resting and K+-evoked release of serotonin and norepinephrine in vivo from rat and cat spinal cord. Brain Res 192:133–146
Zemlan FP, Corrigan SA, Pfaff DW (1980) Noradrenergic and serotonergic mediation of spinal analgesia mechanisms. Eur J Pharmacol 61:111–114
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: E. Collin at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Collin, E., Frechilla, D., Pohl, M. et al. Differential effects of the novel analgesic, S 12813-4, on the spinal release of substance P- and calcitonin gene-related peptide-like materials in the rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 349, 387–393 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170885
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170885