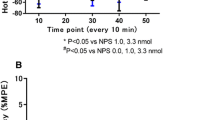
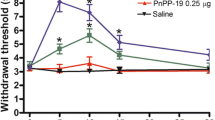
The effects of peptide ACTH4-7-PGP (Semax) were studied in 12 min after its intraperitoneal (in doses of 5, 15, 50, 150, and 450 μg/kg) or intracerebroventricular (in doses of 16, 40, and 400 pg) administration to rats with different types of pain and pain-induced behavior. It was found that the peptide increased pain sensitivity and induced avoidance behavior during thermal stimulation (“hot plate” test), but had an analgesic effect (more pronounced after central administration) and weakened emotional-affective behavior in electrocutaneous stimulation of the paws (foot-shock model) and tail in rats. It was shown that changes in activity of supraspinal brain structures were of primary importance in the mechanism of action on the nociceptive process and the formation of behavior.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashmarin IP, Koroleva SV. The patterns of interactions and functional continuum of neuropeptides (on the way to a common concept). Vestn. Ross. Akad. Med. Nauk. 2002;(6):40-48. Russian.
V’unova TV, Andreeva LA, Shevchenko KV, Shevchenko VP, Bobrov MY, Bezuglov VV, Myasoedov NF. Binding of tripeptide Pro-Gly-Pro labeled at the C-terminal proline residue to plasma membranes of the rat forebrain. Dokl Biol Sci. 2008;419:95-6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1134/s0012496608020075
V’unova TV, Shevchenko KV, Shevchenko VP, Bobrov MYu, Bezuglov VV, Myasoedov NF. Binding of regulatory neuropeptide [3h] Semax, labeled in terminal pro, to plasma membranes of the rat forebrain. Neirokhimiya. 2006;23(1):57-62. Russian.
Glazova NY, Atanov MS, Pyzgareva AV, Andreeva LA, Manchenko DM, Markov DD, Inozemtseva LS, Dolotov OV, Levitskaya NG, Kamensky AA, Grivennikov IA, Myasoedov NF. Neurotropic activity of ACTH(7-10)PGP, an analog of an ACTH fragment. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2011;440:270-4. doi: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0012496611050140
Dolotov OV, Zolotarev YuA, Dorokhova EM, Andreeva LA, Alfeeva LYu, Grivennikov IA, Myasoedov NF. The binding of Semax, ACTH 4-10 heptapeptide, to plasma membranes of the rat forebrain basal nuclei and its biodegradation. Russ. J. Bioorgan. Chem. 2004;30(3):213-217.
Eremin KO, Kudrin VS, Grivennikov IA, Miasoedov NF, Rayevsky KS. Effects of Semax on dopaminergic and serotoninergic systems of the brain. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2004;394:1-3. doi: https://doi.org/10.1023/b:dobs.0000017114.24474.40
Ivanova DM, Levitskaya NG, Andreeva LA, Alfeeva LY, Kamenskii AA, Myasoedov NF. The effect of semax on animal pain sensitivity in various experimental models. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2003;388:5-8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1022475321901.
Koroleva SV, Myasoedov NF. Semax as a universal drug for therapy and research. Biol. Bull. 2018;45(6):589-600.
Levitskaya NG, Sebentsova EA, Andreeva LA, Myasoedov NF, Vilenskii DA, Kamensky AA. Influence of Semax on the emotional state of white rats in the norm and against the background of cholecystokinin-tetrapeptide action. Biol. Bull. 2010;37(2):186-192.
Levitskaya NG, Glazova NYu, Sebentsova EA, Manchenko DM, Vilenskii DA, Andreeva LA, Kamenskii AA, Myasoedov NF. Study of the spectrum of physiological activity of ACTH4-10 heptapeptide analog Semax. Neirokhimiya. 2008;25(1-2):111-118. Russian.
Yasenyavskaya AL, Samotrueva MA, Myasoedov NF, Andreeva LA. Stress-protective and immunomodulatory effects of Semax under experimental informational stress. Chelovek Ego Zdorov’e. 2019;(2):57-65. Russian.
Schmidt R, Schmelz M, Forster C, Ringkamp M, Torebjörk E, Handwerker H. Novel classes of responsive and unresponsive C nociceptors in human skin. J. Neurosci. 1995;15(1, Pt 1):333-41.
Treede RD, Margel W. Modern concepts of pain and hyperalgesia beyond the polymodal C-nociceptor. Physiology. 1995;10(5):216-228. doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/physiologyonline.1995.10.5.216
Weidner C, Schmelz M, Schmidt R, Hansson B, Handwerker HO, Torebjörk HE. Functional attributes discriminating mechano-insensitive and mechano-responsive C nociceptors in human skin. J. Neurosci. 1999;19(22):10 184-10 190.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 170, No. 8, pp. 148-154, August, 2020
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Severyanova, L.A., Kryukov, A.A., Plotnikov, D.V. et al. Peptide ACTH4-7-PGP: Effects on Various Types of Pain and Pain-Induced Behavior in Rats after Systemic and Central Administration. Bull Exp Biol Med 170, 185–190 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-05029-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-05029-8