Summary
Stimulation of α1-adrenoceptors evokes a different pattern of inotropic responses in atrial and ventricular heart muscle preparations from rats. The inotropic effects are accompanied by different changes in membrane potential. In an attempt to clarify the question whether or to which extent these events are causally related, the effects of phenylephrine on force of contraction, transmembrane potential, Ca2+ current (ICa) and K+ currents were comparatively studied in either tissue.
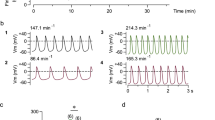
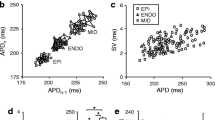
In atrial preparations, phenylephrine 10 μmol/l caused an increase in force of contraction, a marked prolongation of the action potential duration and a depolarization of the membrane at rest. In the ventricle, however, the addition of phenylephrine 10 μmol/l produced first a decline in force of contraction associated with a hyperpolarization of the membrane and a reduction in the action potential duration. These changes were followed by an increase in force,of contraction and a slight prolongation of the action potential, whereas the resting membrane potential remained increased. The hyperpolarization was eliminated in the presence of ouabain 100 μmol/l.
In enzymatically isolated atrial and ventricular myocytes, the whole-cell voltage clamp technique was used to study membrane currents on exposure to phenylephrine. Phenylephrine 30 μmol/l did not affect the magnitude of ICa in either cell type. Transient and steady state K+ outward currents, however, were significantly diminished to a similar extent in atrial and in ventricular myocytes.
It is concluded that the positive inotropic effect of α1-adrenoceptor stimulation in the rat atrium is related to an increase in action potential duration and a decrease in resting membrane potential due to a decrease in K+ currents. In the ventricle, phenylephrine additionally activates the Na+/K+ pump thereby hyperpolarizing the membrane. The rapid onset of pump stimulation seems to overwhelm, in the beginning, the phenylephrine-induced decrease in K+ conductance and therefore to evoke a transient negative inotropic effect.
It is assumed that phenylephrine can alter the intracellular Ca2+ concentration due to changes in the action potential duration. The way how Ca 2+ enters the cell remains speculative, since direct changes of Ica were not detected. The more complicated changes in membrane potential in the ventricle suggest that also other mechanisms for the positive inotropic response to phenylephrine must be considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apkon M, Nerbonne JM (1988) α1-Adrenergic agonists selectively suppress voltage-dependent K+ currents in rat ventricular myocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:8756–8760
Arnold A (1980) Sympathomimetic amine-induced responses of effector organs subserved by alpha-, beta1,-, and beta2-adrenoceptors. In: Szekeres L (ed) Handbook of experimental pharmacology, vol 54/1. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 63–88
Berridge MJ, Irvine RF (1989) Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature 341:197–205
Braun AP, Fedida D, Clark RB, Giles WR (1990) Intracellular mechanisms for α1-adrenergic regulation of the transient outward current in rabbit atria] myocytes. J Physiol (Lond) 431:689–712
Brückner R, Mügge A, Scholz H (1985) Existence and functional role of alpha1-adrenoceptors in the mammalian heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol 17:639–645
Castagna M, Takai Y, Kaibuchi K, Sano K, Kikkawa U, Nishizuka Y (1982) Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem 257:7847–7851
Clark RB, Giles WR, Imaizumi Y (1988) Properties of the transient outward current in rabbit atrial cells. J Physiol (Lond) 405:147–168
Ehrlich BE, Watras J (1988) Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate activates a channel from smooth muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature 336:583–586
Endoh M (1982) Adrenoceptors and the myocardial inotropic response: Do alpha and beta receptor sites functionally coexist? In: Kalsner S (ed) Trends in autonomic pharmacology. Urban and Schwarzenberg, Baltimore, pp 303–322
Endoh M, Blinks JR (1988) Actions of sympathomimetic amines on the Ca2+ transients and contractions of rabbit myocardium: reciprocal changes in myofibrillar responsiveness to Cat+ mediated through α- and α-adrenoceptors. Circ Res 62:247–265
Erdmann E, Philipp G, Scholz H (1980) Cardiac glycoside receptor, (Na+ K+) ATPase activity and force of contraction in rat heart. Biochem Pharmacol 29:3219–3229
Fedida D, Shimoni Y, Giles WR (1989) A novel effect of norepinephrine on cardiac cells is mediated by α1-adrenoceptors. Am J Physiol 256:H1500-H1504
Fedida D, Shimoni Y, Giles WR (1990) α-Adrenergic modulation of the transient outward current in rabbit atrial myocytes. J Physiol (Lond) 423:257–277
Hamill OP, MartyA, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391:85–100
Hille B (1984) Ionic channels of excitable membranes. Sinauer, Sunderland
Iwakura K, Hori M, Watanabe Y, Kitabatake A, Cragoe EJ, Yoshida H, Kamada T (1990) α1-Adrenoceptor stimulation increases intracellular pH and Ca+ in cardiomyocytes through Na+/H+ and Na+/Ca2+ exchange. Eur J Pharmacol 186:29–40
Jahnel U, Nawrath H, Carmeliet E, Vereecke J (1991) Depolarization-induced influx of sodium in response to phenylephrine in rat atrial heart muscle. J Physiol (Lond) 432:621–637
Mitra R, Morad M (1985) A uniform enzymatic method for dissociation of myocytes from hearts and stomachs of vertebrates. Am J Physiol 249:H1056-H1060
Movsesian MA, Thomas AP, Selak M, Williamson JR (1985) Inositol triphosphate does not release Ca2+ from permeabilized cardiac myocytes and sarcoplasmic reticulum. FEBS Lett 185:328–332
Nawrath H (1989) Adrenoceptor-mediated changes of excitation and contraction in isolated heart muscle preparations. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 14 [Suppl III]:S1-S10
Nishizuka Y (1988) The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature 334:661–665
Nosek TM, Clein PD, Godt RE (1990) Inositol trisphosphate has no direct effect on the contractile apparatus of skinned cardiac muscle. Pflügers Arch 417:370–374
Osnes J-B, Refsum H, Skomedal T, Oye I (1978) Qualitative differences between β-adrenergic and α-adrenergic inotropic effects in rat heart muscle. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 42:235–247
Otani H, Otani H, Das DK (1988) α1-Adrenoceptor-mediated phosphoinositide breakdown and inotropic response in rat left ventricular papillary muscle. Circ Res 62:8–17
Otani H, Otani H, Uriu T, Hara M, Inoue M, Omori K, Cragoe EJ, Inagaki C (1990) Effects of inhibitors of protein kinase C and Na+/H+ exchange on α1-adrenoceptor-mediated inotropic responses in the rat left ventricular papillary muscle. Br J Pharmacol 100:207–210
Puceat M, Clement O, Lechene P, Pelosin JM, Ventura-Clapier R, Vassort G (1990) Neurohormonal control of calcium sensitivity of myofilaments in rat single heart cells. Circ Res 67:517–524
Rana RS, Hokin LE (1990) Role of phosphoinositides on transmembrane signaling. Physiol Rev 70:115–164
Ravens U, Wang X-L, Wettwer E (1989) Alpha adrenoceptor stimulation reduces outward currents in rat ventricular myocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 250:364–370
Sakmann B, Trube G (1984) Conductance properties of single inwardly rectifying potassium channels in ventricular cells from guinea-pig heart. J Physiol (Lond) 347:641–657
Shah A, Cohen IS, Rosen MR (1988) Stimulation of cardiac alpha receptors increases Na/K pump current and decreases GK via a pertussis toxin-sensitive pathway. Biophys J 54:219–225
Terzic A, Vogel SM (1990) Amiloride-sensitive actions of an α-adrenoceptor agonist and ouabain in rat atria. J Mol Cell Cardiol 22:391–402
Tohse N, Hattori Y, Nakaya H, Kanno M (1987) Effects of α-adrenoceptor stimulation on electrophysiological properties and mechanics in rat papillary muscle. Gen Pharmacol 18:539–546
Tohse N, Nakaya H, Hattori Y, Endou M, Kanno M (1990) Inhibitory effect mediated by α1-adrenoceptors in transient outward current in isolated rat ventricular cells. Pflügers Arch 415:575–581
Wagner J, Brodde O-E (1978) On the presence and distribution of α-adrenoceptors in the heart of various mammalian species. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 302:239–254
Wallenstein S, Zucker CL, Fleiss JL (1980) Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Circ Res 47:1–19
Wenzel DG, Su JL (1966) Interactions between sympathomimetic amines and blocking agents on rat ventricle strips. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Therap 160:379–389
Yue S, Marban E (1988) A novel cardiac potassium channel that is active and conductive at depolarized potentials. Pflügers Arch 413:127–133
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to H. Nawrath at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ertl, R., Jahnel, U., Nawrath, H. et al. Differential electrophysiologic and inotropic effects of phenylephrine in atrial and ventricular heart muscle preparations from rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 344, 574–581 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170655
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170655