Summary
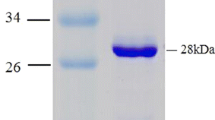
An enzyme catalyzing the interconversion of 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol (DCP) to epichlorohydrin (ECH) was purified from Escherichia coli JM109/ pST001, which carried the gene from Corynebacterium sp. N-1074. The enzyme was crystallized by the addition of ammonium sulphate. The enzyme had a relative molecular mass (Mr) of about 105 000 and consisted of four subunits identical in Mr (approx. 28 000). The enzyme catalysed both the transformation of various halohydrins into the corresponding epoxides with liberation of halide and its reverse reaction. These facts indicated that the enzyme was halohydrin hydrogen-halidelyase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartnicki EW, Castro CE (1969) Biodehalogenation: the pathway for transhalogenation and the stereochemistry of epoxide formation from halohydrins. Biochemistry 8:4677–4680
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein, utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Castro CE, Bartnicki EW (1968) Biodehalogenation: epoxidation of halohydrins, epoxide opening, and transhalogenation by a Flavobacterium sp. Biochemistry 7:3213–3218
Iwasaki I, Utsumi S, Ozawa T (1952) New colorimetric determination of chloride using mercuric thiocyanate and ferric ion. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 25:226
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Nakamura T, Yu F, Mizunashi W, Watanabe I (1991a) Microbial transformation of prochiral 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol into optically active 3-chloro-1,2-propanediol. Agric Biol Chem 55:1931–1933
Nakamura T, Nagasawa T, Yu F, Watanabe I, Yamada H (1991b) A new catalytic function of halohydrin hydrogen-halide-lyase, synthesis of β-hydroxynitriles from epoxides and cyanide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun (in press)
Wijingaard AJ van den, Janssen DB, Witholt B (1989) Degradation of epichlorohydrin and halohydrins by bacterial cultures isolated from freshwater sediment. J Gen Microbiol 135:2199–2208
Wijingaard AJ van den, Reuvekamp PTW, Janssen DB (1991) Purification and characterization of haloalcohol dehalogenase from Anthrobacter sp. strain AD2. J Bacteriol 173:124–129
Winter A, Karlson C (1976) LKB Application Note, no 219, LKB-Producter AB, Bromma, Sweden
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: T. Nagasawa
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagasawa, T., Nakamura, T., Yu, F. et al. Purification and characterization of halohydrin hydrogen-halide lyase from a recombinant Escherichia coli containing the gene from a Corynebacterium sp.. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 36, 478–482 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170187
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170187