Abstract
In the guinea-pig proximal colon, 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) relaxes the longitudinal muscle by stimulating neuronal 5-HT receptors, which induces the release of nitric oxide (NO). It was investigated whether the inhibitory neurotransmitters adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP) and/or vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) could be involved as well.
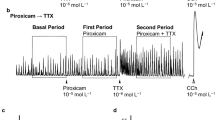
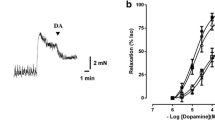
Antagonists to block the contractile response to 5-HT via 5-HT2, 5-HT3 or 5-HT4 receptors were present throughout the experiments and methacholine was administered to precontract the strips. ATP, VIP and 5-HT induced concentration-dependent relaxations, in the case of 5-HT yielding a non-monophasic concentration-response curve. Tetrodotoxin (TTX; 300 nM), NG-nitro-l-arginine (l-NNA, 100 μM) and their combination did not inhibit the relaxations induced by VIP (up to 0.3 μM) or 0.3–3 μM ATP but reduced those by 10 μM ATP. Suramin (300 μM) strongly inhibited the relaxations to ATP and VIP. l-NNA and suramin also inhibited the relaxations to 5-HT. In the presence of l-NNA (100 μM), suramin did not significantly inhibit the relaxations to 5-HT. Suramin did not affect the relaxations to isoprenaline, nitroglycerin or exogenous NO (1 μM), demonstrating its specificity. Apamin (30 nM) inhibited both the relaxations to ATP (by 70–100%) and to 5-HT; relaxations to isoprenaline were partially inhibited, indicating a non-specific component in the inhibitory action of apamin. However, relaxations to exogenous VIP (up to 0.3 μM), NO (1 μ,M) and to nitroglycerin were not inhibit ed. In the presence of l-NNA (100 μM), apamin inhibited the relaxations to 5-HT only at 30 μM. α,\-methylene-ATP (α,β-Me-ATP; 100 μM) did not desensitize the responses to ATP. Reactive blue 2 affected the relaxations to isoprenaline at concentrations necessary to significantly inhibit the relaxations to ATP (i.e. from 10 μM onwards). Thus, it was not possible to test either α,β-Me-ATP or reactive blue 2 against the relaxations to 5-HT. α-Chymotrypsin (0.015 mg·ml−1) and trypsin (0.005 mg·ml−1) almost abolished the relaxations to VIP, but did not affect those to isoprenaline and 5-HT. The VIP receptor antagonists [p-Cl-d-Phe6, Leu17]VIP (1 μM) and VIP10–28 (1 and 3 μM) did not affect the concentration-response curve to VIP and were hence not tested against 5-HT. Phosphoramidon (1 μM) had no effect on the relaxations to VIP or 5-HT.
It can be concluded that in the guinea-pig colon longitudinal muscle, VIP and ATP induce relaxation via a direct effect on the smooth muscle, not involving NO. 5-HT-induced relaxations are mediated by NO as well as by a substance which is sensitive to inhibition by suramin but not apamin. It is suggested that this substance is ATP and not a peptide.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banks BEC, Brown C, Burgess GM, Burnstock G, Claret M, Cocks TM, Jenkinson DH (1979) Apamin blocks certain neurotransmitter-induced increases in potassium permeability. Nature 282:415–417
Belvisi MG, Miura M, Stretton D, Barnes PJ (1993) Endogenous vasoactive intestinal peptide and nitric oxide modulate cholinergic neurotransmission in guinea-pig trachea. Eur J Pharmacol 231:97–102
Boeckxstaens GE, Pelckmans PA, Bult H, De Man JG, Herman AG, Van Maercke YM (1991) Evidence for nitric oxide as mediator of non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic relaxations induced by ATP and GABA in the canine gut. Br J Pharmacol 102:434–438
Briejer MR, Akkermans LMA, Meulemans AL, Lefebvre RA, Schuurkes JAJ (1992) Nitric oxide is involved in 5-HT-induced relaxations of the guinea-pig colon ascendens in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 107:756–761
Briejer MR, Akkermans LMA, Meulemans AL, Lefebvre RA, Schuurkes JAJ (1993) Pharmacological characterization of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor types in the guinea-pig proximal colon. J Gastrointestin Motil 5:239–246
Briejer MR, Veen GJ, Akkermans LMA, Schuurkes JAJ (1994a) Cisapride facilitates inhibitory purinergic transmission in the guinea pig colon. Gastroenterology 106:A471
Briejer MR, Akkermans LMA, Schuurkes JAJ (1994b) Novel 5-HT receptor type mediating neurogenic relaxation of guinea pig colon. In: Huston JP (ed) Proceedings of the Third IUPHAR Satellite Meeting of Serotonin. Elsevier, Amsterdam (in press)
Broadly KJ, Grassby PF (1985) Alpha- and beta-adrenoceptor-mediated responses of the guinea-pig ileum and the effects of neuronal uptake inhibition. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 333:316–323
Burnstock G (1972) Purinergic nerves. Pharmacol Rev 24:509–581
Burnstock G, Warland JJI (1987) P2-purinoceptors of two subtypes in the rabbit mesenteric artery: reactive blue 2 selectively inhibits responses mediated via the P2y- but not the P2x-purinoceptor. Br J Pharmacol 90:383–391
Costa M, Furness JB (1983) The origins, pathways and terminations of neurons with VIP-like immunoreactivity in the guinea-pig small intestine. Neuroscience 8:665–676
Costa M, Furness JB, Humphreys CMS (1986) Apamin distinguishes two types of relaxation mediated by enteric nerves in the guinea-pig gastrointestinal tract. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 332:79–88
Crist JR, He XD, Goyal RK (1992) Both ATP and the peptide VIP are inhibitory neurotransmitters in guinea-pig ileum circular muscle. J Physiol 447:119–131
D'Amato M, De Beurme FA, Lefebvre RA (1988) Comparison of the effect of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and non-adrenergic non-cholinergic neurone stimulation in the cat gastric fundus. Eur J Pharmacol 152:71–82
De Beurme FA, Lefebvre RA (1987) Influence of α-chymotrypsin and trypsin in the non-adrenergic non-cholinergic relaxation in the rat gastric fundus. Br J Pharmacol 91:171–177
De Beurme FA, Lefebvre RA (1988) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide as possible mediator of relaxation in the rat gastric fundus. J Pharm Pharmacol 40:711–715
Den Hertog A, Nelemans A, Van den Akker J (1989) The inhibitory action of suramin on the P2-purinoceptor response in smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig taenia caeci. Eur J Pharmacol 166:531–534
Ellis JL, Farmer SG (1989a) The effects of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) antagonists, and VIP and peptide histidine isoleucine antisera on non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic relaxations of tracheal smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol 96:513–520
Ellis JL, Farmer SG (1989b) Effects of peptidases on non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic inhibitory responses of tracheal smooth muscle: a comparison with effects on VIP- and PHI-induced relaxation. Br J Pharmacol 96:521–526
Feelish M (1991) The biochemical pathways of nitric oxide formation from nitrovasodilators: appropriate choice of exogenous NO donors and aspects of preparation and handling of aqueous NO solutions. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 17 [Suppl 3]:S25-S33
Goyal RK, Rattan S, Said S (1980) VIP as a possible neurotransmitter of non-cholinergic non-adrenergic inhibitory neurones. Nature 288:378–380
Grider JR, Cable MB, Bitar KN, Said SI, Makhlouf GM (1985) Vasoactive intestinal peptide: relaxant neurotransmitter in the tenia coli of the guinea pig. Gastroenterology 89:36–42
Gu ZF, Menozzi D, Okamoto A, Maton PN, Bunnett NW (1993) Neutral endopeptidase (EC 3.4.24.11) modulates the contractile effects of neuropeptides on muscle cells from the guinea-pig stomach. Exp Physiol 78:35–48
Hoyle CHV, Knight GE, Burnstock G (1990) Suramin antagonizes responses to P2-purinoceptor agonists and purinergic nerve stimulation in the guinea-pig urinary bladder and taenia coli. Br J Pharmacol 99:617–621
Jury J, Jager LP, Daniel EE (1985) Unusual potassium channels mediate nonadrenergic noncholinergic nerve-mediated inhibition in oposum esophagus. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 63:107–112
Katsoulis S, Clemens A, Schwörer H, Creutzfeldt W, Schmidt WE (1993) PACAP is a stimulator of neurogenic contraction in guinea pig ileum. Am J Physiol 265:G295-G302
Kennedy C (1990) P1- and P2-purinoceptor subtypes — an update. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 303:30–50
Lefebvre RA, Burnstock G (1990) Effect of adenosine triphosphate and related purines in the rat gastric fundus. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 303:199–215
Maas AJJ, Den Hertog A, Van den Akker J (1980) The action of apamin on the guinea-pig taenia caeci. Eur J Pharmacol 67:265–274
Nau R, Schafer G, Deacon CF, Cole T, Agoston DV, Conlon JM (1986) Proteolytic inactivation of substance P and neurokinin A in the longitudinal muscle layer of guinea-pig small intestine. J Neurochem 47:856–864
Pandol SJ, Dharmsathaphorn K, Schoeffield MS, Vale W, Rivier J (1986) Vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor antagonist [4-Cl-d-Phe6,Leu17]VIP. Am J Physiol 250:G553-G577
Presti ME, Gardner JD (1993) Receptor antagonists for gastrointestinal peptides. Am J Physiol 264:G399-G406
Probert L, De Mey J, Polak JM (1983) Ultrastructural localization of four different neuropeptides within separate populations of p-type nerves in the guinea-pig colon. Gastroenterology 85:1094–1104
Rhoden KJ, Barnes PJ (1989) Epithelial modulation of NANC and VIP-induced responses: role of neutral endopeptidase. Eur J Pharmacol 171:247–250
Shuba MF, Vladimirova IA (1980) Effect of apamin on the electrical responses of smooth muscle to adenosine 5′-triphosphate and to non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic nerve stimulation. Neuroscience 5:853–859
Stark ME, Szurszewski JH (1992) Role of nitric oxide in gastrointestinal and hepatic function and disease. Gastroenterology 103:1928–1949
Turner JT, Jones SB, Byland DB (1986) A fragment of VIP (10–28), is an antagonist of VIP in the colon carcinoma cell line, HT29. Peptides 7:849–854
Venugopalan CS, Holmes EP, Malley NA (1990) Evidence for vasoactive intestinal peptide as a mediator of non-adrenergic non-cholinergic neurotransmission in the trachea. J Auton Pharmacol 10:297–304
Wallenstein S, Zucker CL, Fleiss JL (1980) Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Ore Res 47:1–9
Ward SM, McKeen EM, Sanders KM (1992) Role of nitric oxide in non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic inhibitory junction potentials in canine ileocolonic sphincter. Br J Pharmacol 105:776–782
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Briejer, M.R., Akkermans, L.M.A., Meulemans, A.L. et al. 5-HT-induced neurogenic relaxations of the guinea-pig proximal colon: investigation into the role of ATP and VIP in addition to nitric oxide. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 351, 126–135 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00169326
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00169326